前言
一直沒有系統去看過c++,因為懂得一些c的基本語法,在實際編程中用到c++,只能用到哪些看哪些,發現這樣雖然能夠完成大部分工作,但是有時候效率實在太低,比如說這節要講的Std::sort()函數的使用,調了半天才調通。開通c/c++序列博客是記錄在使用c++中一些難題,避免以後重犯錯,當然以後會盡量擠出時間來較系統學習下c++。
開發環境:QtCreator2.5.1+OpenCV2.4.3
實驗基礎
首先來看看std中的快速排序算法sort的使用方法:
template <class RandomAccessIterator, class Compare> void sort ( RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp );
這是一個帶模板的函數,參數1和2表示需要排序的元素在隨機迭代器的起始位置和結束位置,其迭代器指向的數據類型可以自己定義,常見的數據類型包括結構體,vector,類等都可以被使用。參數comp是用來決定所采用的排序是升序還是逆序的,默認情況下是升序排列。但是這種默認情況的優勢是處理迭代器指向的元素為普通的數據類型,比如說整型,字符型等。如果指向的數據類型為類或者結構體,然後使用該類或者結構體中的某個元素進行排序,這時候需要自己定義排序的重載符號”<”。比如說在本次實驗中該重載符號的定義為:
代碼如下:
/*按照降序排列*/
bool compare(const PAIR &x, const PAIR &y)
{
return x.point_value > y.point_value;
}
如果將comp定義為一個函數(網上好像很多都是用這種類似的函數),比如說該函數如下:
代碼如下:
/*按照降序排列*/
bool operator<(const PAIR &x, const PAIR &y)
{
return x.point_value > y.point_value;
}
則會報錯如下錯誤:

std::sort因為函數參數不明確,所以無法推導出模板參數等.
實驗結果
本次實驗是基於這樣一個問題的:有一些坐標點集合(2d的坐標點,坐標點之間沒有重復),每個坐標點對應一個數,現在需要對這些數排序從而達到對這些坐標點排序。有嘗試過把點的坐標和它對應的值放在map中,然後對map中的元素用std::sort()進行排序,但是由於開始沒有發現那個重載符號的使用,所以沒有調試成功。現在直接不用map了,而是用vector,vector裡面放的是帶有坐標點和其對應值的struct。
本次實驗是在vector中存入3個結構體對象,每個結構體中放入一個二維點和它對應的值,然後采用sort()對齊排序,排序結果如下:
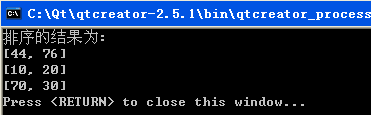
實驗代碼及注釋
main.cpp:
代碼如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
typedef struct
{
cv::Point point;
long point_value;
} PAIR;
/*按照降序排列*/
bool operator<(const PAIR &x, const PAIR &y)
{
return x.point_value > y.point_value;
}
///*按照降序排列*/
//bool compare(const PAIR &x, const PAIR &y)
//{
// return x.point_value > y.point_value;
//}
void main()
{
PAIR pair1, pair2, pair3;
std::vector<PAIR> vec;
pair1.point = Point(10, 20);
pair1.point_value = 100;
pair2.point = Point(70, 30);
pair2.point_value = 99;
pair3.point = Point(44, 76);
pair3.point_value = 101;
vec.push_back(pair1);
vec.push_back(pair2);
vec.push_back(pair3);
// std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), compare);
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
cout << "排序的結果為:" << endl;
for(vector<PAIR>::iterator it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->point << endl;
}
return ;
}
實驗總結
std::sort()函數的功能很強大,且可以對類,結構體等元素進行排序。