C語言中常用的內存分配函數有malloc、calloc和realloc等三個,其中,最常用的肯定是malloc,這裡簡單說一下這三者的區別和聯系。
1、聲明
這三個函數都在stdlib.h庫文件中,聲明如下:
void* realloc(void* ptr, unsigned newsize);
void* malloc(unsigned size);
void* calloc(size_t numElements, size_t sizeOfElement);
它們的功能大致類似,就是向操作系統請求內存分配,如果分配成功就返回分配到的內存空間的地址,如果沒有分配成功就返回NULL。
2、功能
malloc(size):在內存的動態存儲區中分配一塊長度為“size”字節的連續區域,返回該區域的首地址。
calloc(n,size):在內存的動態存儲區中分配n塊長度為“size”字節的連續區域,返回首地址。
realloc(*ptr,size):將ptr內存大小增大或縮小到size。
需要注意的是realloc將ptr內存增大或縮小到size,這時新的空間不一定是在原來ptr的空間基礎上,增加或減小長度來得到,而有可能(特別是在用realloc來增大ptr的內存空間的時候)會是在一個新的內存區域分配一個大空間,然後將原來ptr空間的內容拷貝到新內存空間的起始部分,然後將原來的空間釋放掉。因此,一般要將realloc的返回值用一個指針來接收,下面是一個說明realloc函數的例子。
#include運行結果如下:#include int main() { //allocate space for 4 integers int *ptr=(int *)malloc(4*sizeof(int)); if (!ptr) { printf("Allocation Falure!\n"); exit(0); } //print the allocated address printf("The address get by malloc is : %p\n",ptr); //store 10、9、8、7 in the allocated space int i; for (i=0;i<4;i++) { ptr[i]=10-i; } //enlarge the space for 100 integers int *new_ptr=(int*)realloc(ptr,100*sizeof(int)); if (!new_ptr) { printf("Second Allocation For Large Space Falure!\n"); exit(0); } //print the allocated address printf("The address get by realloc is : %p\n",new_ptr); //print the 4 integers at the beginning printf("4 integers at the beginning is:\n"); for (i=0;i<4;i++) { printf("%d\n",new_ptr[i]); } return 0; }
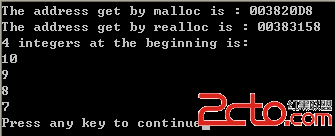
從上面可以看出,在這個例子中新的空間並不是以原來的空間為基址分配的,而是重新分配了一個大的空間,然後將原來空間的內容拷貝到了新空間的開始部分。
3、三者的聯系
calloc(n,size)就相當於malloc(n*size),而realloc(*ptr,size)中,如果ptr為NULL,那麼realloc(*ptr,size)就相當於malloc(size)。