首先來看一個簡單的例子(官方文件ev.pod中可以找到)
#include <ev.h>
#include <stdio.h>
ev_io stdin_watcher;
ev_timer timeout_watcher;
static void
stdin_cb(EV_P_ ev_io *w, int revents)
{
puts("stdin ready");
ev_io_stop(EV_A_ w);
ev_break(EV_A_ EVBREAK_ALL);
}
static void
timeout_cb(EV_P_ ev_timer *w, int revents)
{
puts("timeout");
ev_break(EV_A_ EVBREAK_ONE);
}
int main()
{
struct ev_loop *loop = EV_DEFAULT;
ev_io_init(&stdin_watcher, stdin_cb, 0, EV_READ);
ev_io_start(loop, &stdin_watcher);
ev_timer_init(&timeout_watcher, timeout_cb, 5.5, 0. );
ev_timer_start(loop, &timeout_watcher);
ev_run(loop,0);
return 0;
}
我們只關心如下幾句:
struct ev_loop *loop = EV_DEFAULT;
ev_io_init(&stdin_watcher, stdin_cb, 0, EV_READ);
ev_io_start(loop, &stdin_watcher);
ev_run(loop, 0);
首先來看ev_io_init中做了些什麼操作:
ev.h文件中
#define ev_io_init(ev,cb,fd,events)
do { ev_init ((ev), (cb)); ev_io_set ((ev),(fd),(events)); } while (0)
#define ev_init(ev,cb_) do { \
((ev_watcher *)(void *)(ev))->active = \
((ev_watcher *)(void *)(ev))->pending = 0; \
ev_set_priority ((ev), 0); \
ev_set_cb ((ev), cb_); \
} while (0)
#define ev_io_set(ev,fd_,events_)
do { (ev)->fd = (fd_); (ev)->events = (events_) | EV__IOFDSET; } while (0)
#define ev_set_cb(ev,cb_)
ev_cb (ev) = (cb_)
#define ev_cb(ev)
(ev)->cb /* rw */
通過定義可以看出ev_io_init主要操作時:
&stdin_watcher->active=stdin_watcher->pending=0;
&stdin_watcher->priority=0;
&stdin_watcher->cb=stdin_cb(函數);
&stdin_watcher->fd;
&stdin_watcher->events=EV_READ|EV__IOFDSET
同樣,ev_io_start做了一些賦值操作,這裡不過多講解;
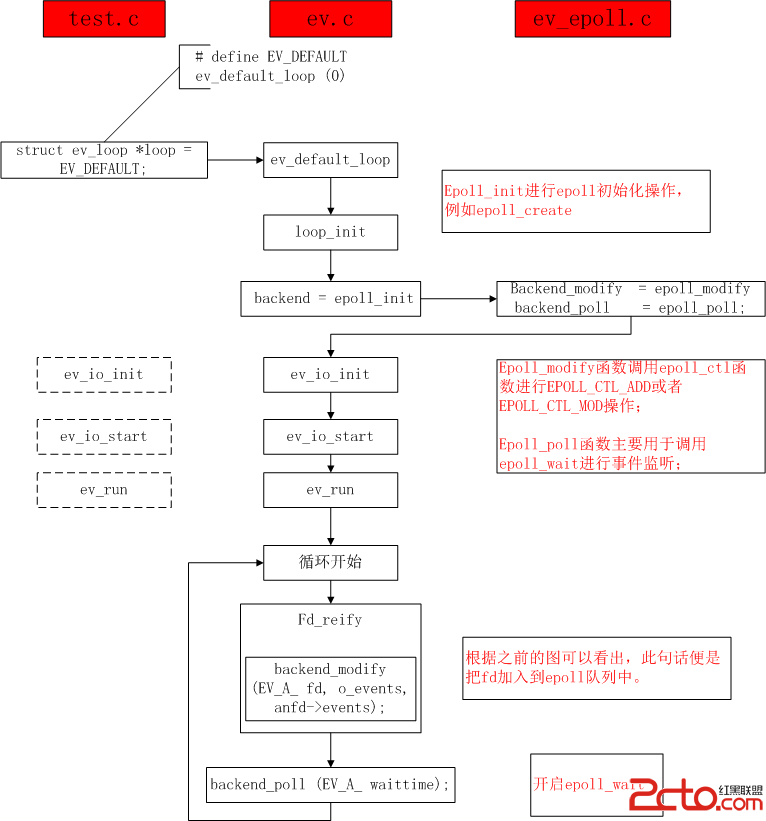
下面通過一張函數調用圖來展libev的函數調用: