注:個人習慣原因,帶了點c++語句
一、 用牛頓法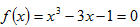 求在
求在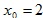 附近的實根,取四位有效數字。
附近的實根,取四位有效數字。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-4;
const double x0=2;
double FunOfSet(double x)
{
return pow(x,3.0)-3*x-1;
}
void ProGetRes()
{
double Begin=x0-1,End=x0+1;
double Mid;
while(fabs(FunOfSet(Begin)-FunOfSet(End))>eps)
{
Mid=(Begin+End)/2;
if(FunOfSet(Begin)*FunOfSet(Mid)<0)
End=Mid;
else Begin=Mid;
}
printf("The root of fuction beside 2 is: %.4f\n",Mid) ;
}
int main()
{
ProGetRes();
return 0;
}
二、 用高斯消去法求解下列方程組
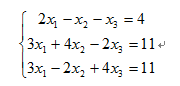
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const int LenOfMatrix=3;
double a[LenOfMatrix+1][LenOfMatrix+2]={{0,0,0,0,0},{0,2,-1,-1,4},{0,3,4,-2,11},{0,3,-2,4,11}};
double Res[LenOfMatrix+1];
void GussPro()
{
int i,j,k,MaxPos,n=3;
double mmax;
for(k=1;k<n-1;k++)
{
mmax=-1;
for(i=k;i<=n;i++)
if(fabs(a[i][k])>mmax)
{
mmax=a[i][k];
MaxPos=i;
}
double temp;
for(j=1;j<=n+1;j++)
{
temp=a[k][j];
a[k][j]=a[MaxPos][j];
a[MaxPos][j]=temp;
}
for(i=k+1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=k+1;j<=n+1;j++)
a[i][j]=a[i][j]-(a[i][k])*(a[k][j])/(a[k][k]);
}
Res[n]=(a[n][n+1])/(a[n][n]);
double sum;
for(k=n-1;k>=1;k--)
{
sum=0;
for(j=k+1;j<=n;j++)
sum+=(a[k][j])*(Res[j]);
Res[k]=(a[k][n+1]-sum)/(a[k][k]);
}
cout<<"For the follow matrix :"<<endl;
cout<<"2x1-1x2-1x3=4"<<endl;
cout<<"3x1+4x2-2x3=11"<<endl;
cout<<"3x1-2x2+4x3=11"<<endl;
cout<<"The answer is: ";
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("x[%d]=%.4f ",i,Res[i]);
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
GussPro();
return 0;
}
三、已知函數表
x 1.1275
1.1503
1.1735
1.1972
f(x) 0.1191
0.13954
0.15932
0.17903
應用拉格朗日插值公式計算f(1.1300)的近似值。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int LenOfNum=4;
double x[]={1.1275,1.1503,1.1735,1.1972};
double y[]={0.1191,0.13954,0.15932,0.17903};
double Li[LenOfNum];
int i,j;
void GetLi(double x0)
{
for(i=0;i<LenOfNum;i++)
{
Li[i]=1;
for(j=0;j<LenOfNum;j++)
if(i!=j)Li[i]*=((x0-x[j])/(x[i]-x[j]));
}
}
void ProLag()
{
double x0=1.1300;
double res=0;
GetLi(x0);
for(i=0;i<LenOfNum;i++)
res+=(y[i]*Li[i]);
printf("f(1.1300)= %f\n",res);
}
int main()
{
ProLag();
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int LenOfNum=4;
double x[]={1.1275,1.1503,1.1735,1.1972};
double y[]={0.1191,0.13954,0.15932,0.17903};
double Li[LenOfNum];
int i,j;
void GetLi(double x0)
{
for(i=0;i<LenOfNum;i++)
{
Li[i]=1;
for(j=0;j<LenOfNum;j++)
if(i!=j)Li[i]*=((x0-x[j])/(x[i]-x[j]));
}
}
void ProLag()
{
double x0=1.1300;
double res=0;
GetLi(x0);
for(i=0;i<LenOfNum;i++)
res+=(y[i]*Li[i]);
printf("f(1.1300)= %f\n",res);
}
int main()
{
ProLag();
}
摘自 int64Ago的專欄