CheatSheet文檔中包含了GMock所有常用的東西,看了這個基本上就可以用它了,本文接上篇博文:Google C++單元測試框架GoogleTest---Google Mock簡介--概念及基礎語法 ,建議先看上一篇,再看本篇內容。
本文翻譯自:https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googlemock/docs/CheatSheet.md
給:
class Foo {
...
virtual ~Foo();
virtual int GetSize() const = 0;
virtual string Describe(const char* name) = 0;
virtual string Describe(int type) = 0;
virtual bool Process(Bar elem, int count) = 0;
};
(note that ~Foo() must be virtual) we can define its mock as,定義模擬類。
#include "gmock/gmock.h"
class MockFoo : public Foo {
MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(GetSize, int());
MOCK_METHOD1(Describe, string(const char* name));
MOCK_METHOD1(Describe, string(int type));
MOCK_METHOD2(Process, bool(Bar elem, int count));
};
創建一個“nice”模擬對象忽略所有無趣的調用,或一個“strict”模擬對象,將它們視為失敗:
NiceMock<MockFoo> nice_foo; // The type is a subclass of MockFoo. StrictMock<MockFoo> strict_foo; // The type is a subclass of MockFoo.
To mock:
template <typename Elem>
class StackInterface {
public:
...
virtual ~StackInterface();
virtual int GetSize() const = 0;
virtual void Push(const Elem& x) = 0;
};
(note that ~StackInterface() must be virtual) just append _T to the MOCK_* macros:
template <typename Elem>
class MockStack : public StackInterface<Elem> {
public:
...
MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_T(GetSize, int());
MOCK_METHOD1_T(Push, void(const Elem& x));
};
如果您的mock函數不使用默認調用約定,您可以通過將_WITH_CALLTYPE附加到前兩個部分中描述的任何宏並指定調用約定作為宏的第一個參數來指定它。例如,
MOCK_METHOD_1_WITH_CALLTYPE(STDMETHODCALLTYPE,Foo,bool(int n)); MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(STDMETHODCALLTYPE,Bar,int(double x,double y));
其中STDMETHODCALLTYPE由Windows上的<objbase.h>定義。
典型的流程是:
這裡是一個例子:
using ::testing::Return; // #1
TEST(BarTest, DoesThis) {
MockFoo foo; // #2
ON_CALL(foo, GetSize()) // #3
.WillByDefault(Return(1));
// ... other default actions ...
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Describe(5)) // #4
.Times(3)
.WillRepeatedly(Return("Category 5"));
// ... other expectations ...
EXPECT_EQ("good", MyProductionFunction(&foo)); // #5
} // #6
Google Mock對任何返回void,bool,數值或指針的函數都有一個內置的默認動作。
要為全局返回類型T的函數自定義默認操作:
using ::testing::DefaultValue; // Sets the default value to be returned. T must be CopyConstructible. DefaultValue<T>::Set(value); // Sets a factory. Will be invoked on demand. T must be MoveConstructible. // T MakeT(); DefaultValue<T>::SetFactory(&MakeT); // ... use the mocks ... // Resets the default value. DefaultValue<T>::Clear();
要自定義特定方法的默認操作,請使用ON_CALL():
ON_CALL(mock_object, method(matchers))
.With(multi_argument_matcher) ?
.WillByDefault(action);
EXPECT_CALL()在模擬方法上設置期望(如何調用它?它會做什麼?):
EXPECT_CALL(mock_object, method(matchers))
.With(multi_argument_matcher) ?
.Times(cardinality) ?
.InSequence(sequences) *
.After(expectations) *
.WillOnce(action) *
.WillRepeatedly(action) ?
.RetiresOnSaturation(); ?
如果省略Times(),則基數假定為:
沒有EXPECT_CALL()的方法可以被任意調用多次,並且每次都將采取默認操作。
匹配器匹配單個參數。 您可以在ON_CALL()或EXPECT_CALL()中使用它,或使用它直接驗證值:
EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher)value matches matcher.ASSERT_THAT(value, matcher)
The same as EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher), except that it generates a fatal failure.
內置的匹配(其中參數是函數參數)分為幾類:
_argument can be any value of the correct type可以代表任意類型.A<type>() or An<type>()
argument can be any value of type可以是type類型的任意值.
注意** 除了Ref()之外,這些匹配器會創建一個值的副本,以備日後修改或銷毀。 如果編譯器抱怨該值沒有公共副本構造函數,請嘗試將其包裝在ByRef()中,例如。 Eq(ByRef(non_copyable_value))。 如果你這樣做,請確保non_copyable_value之後不改變,否則你的匹配器的含義將被改變。
上述匹配器使用基於ULP的比較(與Google Test中使用的比較相同)。 它們根據期望值的絕對值自動選擇合理的誤差界限。 DoubleEq()和FloatEq()符合IEEE標准,這需要比較兩個NaNs的相等性返回false。 NanSensitive *版本將兩個NaNs相等,這通常是用戶想要的。
DoubleNear(a_double, max_abs_error)argument is a double value close to a_double (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as unequal.FloatNear(a_float, max_abs_error)
argument is a float value close to a_float (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as unequal.
NanSensitiveDoubleNear(a_double, max_abs_error)
argument is a double value close to a_double (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as equal.
NanSensitiveFloatNear(a_float, max_abs_error)
argument is a float value close to a_float (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as equal.
這裡的字符串即可以是C風格的字符串,也可以是C++風格的。
ContainsRegex(string) 形參匹配給定的正則表達式 EndsWith(suffix) 形參以suffix截尾 HasSubstr(string) 形參有string這個子串 MatchesRegex(string) 從第一個字符到最後一個字符都完全匹配給定的正則表達式. StartsWith(prefix) 形參以prefix開始 StrCaseEq(string) 參數等於string,並且忽略大小寫 StrCaseNe(string) 參數不是string,並且忽略大小寫 StrEq(string) 參數等於string StrNe(string) 參數不等於string很多STL的容器的比較都支持==這樣的操作,對於這樣的容器可以使用上述的Eq(expected_container)來比較或者只是expect_container來完全匹配容器。但如果你想寫得更為靈活,可以使用下面的這些容器匹配方法:
ContainerEq(container)Eq(container) except that the failure message also includes which elements are in one container but not the other.Contains(e)
argument contains an element that matches e, which can be either a value or a matcher.
Each(e)
argument is a container where every element matches e, which can be either a value or a matcher.
ElementsAre(e0, e1, ..., en)
argument has n + 1 elements, where the i-th element matches ei, which can be a value or a matcher. 0 to 10 arguments are allowed.
ElementsAreArray({ e0, e1, ..., en }), ElementsAreArray(array), or ElementsAreArray(array, count)
The same as ElementsAre() except that the expected element values/matchers come from an initializer list, STL-style container, or C-style array.
IsEmpty()
argument is an empty container (container.empty()).
Pointwise(m, container)
argument contains the same number of elements as in container, and for all i, (the i-th element in argument, the i-th element in container) match m, which is a matcher on 2-tuples. E.g. Pointwise(Le(), upper_bounds) verifies that each element in argument doesn't exceed the corresponding element in upper_bounds. See more detail below.
SizeIs(m)
argument is a container whose size matches m. E.g. SizeIs(2) or SizeIs(Lt(2)).
UnorderedElementsAre(e0, e1, ..., en)
argument has n + 1 elements, and under some permutation each element matches an ei (for a different i), which can be a value or a matcher. 0 to 10 arguments are allowed.
UnorderedElementsAreArray({ e0, e1, ..., en }), UnorderedElementsAreArray(array), or UnorderedElementsAreArray(array, count)
The same as UnorderedElementsAre() except that the expected element values/matchers come from an initializer list, STL-style container, or C-style array.
WhenSorted(m)
When argument is sorted using the < operator, it matches container matcher m. E.g. WhenSorted(UnorderedElementsAre(1, 2, 3)) verifies that argument contains elements 1, 2, and 3, ignoring order.
WhenSortedBy(comparator, m)
The same as WhenSorted(m), except that the given comparator instead of < is used to sort argument. E.g. WhenSortedBy(std::greater<int>(), ElementsAre(3, 2, 1)).
注意:
這些匹配器也可以匹配:
i. 通過引用傳遞的本地數組(例如在Foo(const int(&a)[5])中)和
ii. 作為指針和計數傳遞的數組(例如,在Bar(const T * buffer,int len) - 參見 Multi-argument Matchers)。
匹配的數組可以是多維的(即其元素可以是數組)。
在Pointwise(m,...)中的m應該是:: testing :: tuple <T,U>的匹配器,其中T和U分別是實際容器和預期容器的元素類型。 例如,要比較兩個Foo容器,其中Foo不支持operator ==但是有一個Equals()方法,可以寫:
using ::testing::get;
MATCHER(FooEq, "") {
return get<0>(arg).Equals(get<1>(arg));
}
...
EXPECT_THAT(actual_foos, Pointwise(FooEq(), expected_foos));
Field(&class::field, m)argument.field (or argument->field when argument is a plain pointer) matches matcher m, where argument is an object of type class.Key(e)
argument.first matches e, which can be either a value or a matcher. E.g. Contains(Key(Le(5))) can verify that a map contains a key <= 5.
Pair(m1, m2)
argument is an std::pair whose first field matches m1 and second field matches m2.
Property(&class::property, m)
argument.property() (or argument->property() when argument is a plain pointer) matches matcher m, where argument is an object of type class.
ResultOf(f, m)f(argument) matches matcher m, where f is a function or functor.Pointee(m)
argument (either a smart pointer or a raw pointer) points to a value that matches matcher m.
WhenDynamicCastTo<T>(m)
when argument is passed through dynamic_cast<T>(), it matches matcher m.
從技術上講,完全匹配器匹配單個值。 “多參數”匹配器只是匹配元組的匹配器。 以下匹配器可用於匹配元組(x,y):
Eq()x == yGe()
x >= y
Gt()
x > y
Le()
x <= y
Lt()
x < y
Ne()
x != y
您可以使用以下選擇器來選擇參數的子集(或對其重新排序)以參與匹配:
AllArgs(m)m. Useful as syntactic sugar in .With(AllArgs(m)).Args<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(m)
The tuple of the k selected (using 0-based indices) arguments matches m, e.g. Args<1, 2>(Eq()).
你可以從一個或多個其他匹配器做一個匹配器:
AllOf(m1, m2, ..., mn)argument matches all of the matchers m1 to mn.AnyOf(m1, m2, ..., mn)
argument matches at least one of the matchers m1 to mn.
Not(m)
argument doesn't match matcher m.
MatcherCast<T>(m)m to type Matcher<T>.SafeMatcherCast<T>(m)
safely casts matcher m to type Matcher<T>.
Truly(predicate)
predicate(argument) returns something considered by C++ to be true, where predicate is a function or functor.
Matches(m)(value)true if value matches m. You can use Matches(m) alone as a unary functor.ExplainMatchResult(m, value, result_listener)
evaluates to true if value matches m, explaining the result to result_listener.
Value(value, m)
evaluates to true if value matches m.
MATCHER(IsEven, "") { return (arg % 2) == 0; }IsEven() to match an even number.MATCHER_P(IsDivisibleBy, n, "") { *result_listener << "where the remainder is " << (arg % n); return (arg % n) == 0; }
Defines a macher IsDivisibleBy(n) to match a number divisible by n.
MATCHER_P2(IsBetween, a, b, std::string(negation ? "isn't" : "is") + " between " + PrintToString(a) + " and " + PrintToString(b)) { return a <= arg && arg <= b; }
Defines a matcher IsBetween(a, b) to match a value in the range [a, b].
筆記:
ASSERT_THAT(expression, m)expression doesn't match matcher m.EXPECT_THAT(expression, m)
Generates a non-fatal failure if the value of expression doesn't match matcher m.
操作指定了mock函數在調用時應該執行的操作。
Return()void mock function.Return(value)
Return value. If the type of value is different to the mock function's return type, value is converted to the latter type at the time the expectation is set, not when the action is executed.
ReturnArg<N>()
Return the N-th (0-based) argument.
ReturnNew<T>(a1, ..., ak)
Return new T(a1, ..., ak); a different object is created each time.
ReturnNull()
Return a null pointer.
ReturnPointee(ptr)
Return the value pointed to by ptr.
ReturnRef(variable)
Return a reference to variable.
ReturnRefOfCopy(value)
Return a reference to a copy of value; the copy lives as long as the action.
Assign(&variable, value)value to variable.DeleteArg<N>()
Delete the N-th (0-based) argument, which must be a pointer.
SaveArg<N>(pointer)
Save the N-th (0-based) argument to *pointer.
SaveArgPointee<N>(pointer)
Save the value pointed to by the N-th (0-based) argument to *pointer.
SetArgReferee<N>(value)
Assign value to the variable referenced by the N-th (0-based) argument.
SetArgPointee<N>(value)
Assign value to the variable pointed by the N-th (0-based) argument.
SetArgumentPointee<N>(value)
Same as SetArgPointee<N>(value). Deprecated. Will be removed in v1.7.0.
SetArrayArgument<N>(first, last)
Copies the elements in source range [first, last) to the array pointed to by the N-th (0-based) argument, which can be either a pointer or an iterator. The action does not take ownership of the elements in the source range.
SetErrnoAndReturn(error, value)
Set errno to error and return value.
Throw(exception)
Throws the given exception, which can be any copyable value. Available since v1.1.0.
Invoke(f)f with the arguments passed to the mock function, where f can be a global/static function or a functor.Invoke(object_pointer, &class::method)
Invoke the {method on the object with the arguments passed to the mock function.
InvokeWithoutArgs(f)
Invoke f, which can be a global/static function or a functor. f must take no arguments.
InvokeWithoutArgs(object_pointer, &class::method)
Invoke the method on the object, which takes no arguments.
InvokeArgument<N>(arg1, arg2, ..., argk)
Invoke the mock function's N-th (0-based) argument, which must be a function or a functor, with the k arguments.
被調用函數的返回值被用作動作的返回值。
定義要與Invoke *()一起使用的函數或函數時,可以將任何未使用的參數聲明為未使用:
double Distance(Unused, double x, double y) { return sqrt(x*x + y*y); }
...
EXPECT_CALL(mock, Foo("Hi", _, _)).WillOnce(Invoke(Distance));
在Invoke Argument <N>(...)中,如果一個參數需要通過引用傳遞,則將其包裝在ByRef()中。 例如,
InvokeArgument<2>(5, string("Hi"), ByRef(foo))
調用模擬函數#2參數,通過值傳遞給它5和字符串(“Hi”),並通過引用傳遞foo。
DoDefault()ON_CALL() or the built-in one).Note: due to technical reasons, DoDefault() cannot be used inside a composite action - trying to do so will result in a run-time error.
DoAll(a1, a2, ..., an)a1 to an and return the result of an in each invocation. The first n - 1sub-actions must return void.IgnoreResult(a)
Perform action a and ignore its result. a must not return void.
WithArg<N>(a)
Pass the N-th (0-based) argument of the mock function to action a and perform it.
WithArgs<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(a)
Pass the selected (0-based) arguments of the mock function to action a and perform it.
WithoutArgs(a)
Perform action a without any arguments.
ACTION(Sum) { return arg0 + arg1; }Sum() to return the sum of the mock function's argument #0 and #1.ACTION_P(Plus, n) { return arg0 + n; }
Defines an action Plus(n) to return the sum of the mock function's argument #0 and n.
ACTION_Pk(Foo, p1, ..., pk) { statements; }
Defines a parameterized action Foo(p1, ..., pk) to execute the given statements.
The ACTION* macros cannot be used inside a function or class.
這些在Times()中用於指定將調用模擬函數的次數:
AnyNumber()AtLeast(n)
The call is expected at least n times.
AtMost(n)
The call is expected at most n times.
Between(m, n)
The call is expected between m and n (inclusive) times.
Exactly(n) or n
The call is expected exactly n times. In particular, the call should never happen when n is 0.
默認情況下,期望可以按任何順序匹配。如果一些或所有期望必須在給定的順序中匹配,則有兩種方式來指定它們。 它們可以單獨使用或一起使用。
using ::testing::Expectation;
...
Expectation init_x = EXPECT_CALL(foo, InitX());
Expectation init_y = EXPECT_CALL(foo, InitY());
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar())
.After(init_x, init_y);
上邊說,只有在InitX()和InitY()被調用之後才能調用Bar()。
如果你不知道你寫的期望有多少個前提條件,你可以使用ExpectationSet來收集它們:
using ::testing::ExpectationSet;
...
ExpectationSet all_inits;
for (int i = 0; i < element_count; i++) {
all_inits += EXPECT_CALL(foo, InitElement(i));
}
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar())
.After(all_inits);
上面說,只有在所有元素都被初始化之後才能調用Bar()。(但我們不關心哪些元素在其他元素之前被初始化)。
在 .After(all_inits)中使用ExpectationSet之後再修改ExpectationSet不會影響.After()的含義。
當你有一個長鏈的順序期望,使用序列指定順序更容易,這不需要給鏈中的每個期望一個不同的名稱。同一序列中的所有預期調用必須按其指定的順序發生。
using ::testing::Sequence;
Sequence s1, s2;
...
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Reset())
.InSequence(s1, s2)
.WillOnce(Return(true));
EXPECT_CALL(foo, GetSize())
.InSequence(s1)
.WillOnce(Return(1));
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Describe(A<const char*>()))
.InSequence(s2)
.WillOnce(Return("dummy"));
上邊說,Reset()必須在GetSize()和Describe()之前調用,後兩個可以以任何順序發生。
在一個序列中方便地提出許多期望:
using ::testing::InSequence;
{
InSequence dummy;
EXPECT_CALL(...)...;
EXPECT_CALL(...)...;
...
EXPECT_CALL(...)...;
}
上邊說,在dummy范圍內的所有預期調用必須以嚴格的順序發生。 名稱dummy是不相關的。)
Google Mock會在模擬對象被破壞時驗證對模擬對象的期望,或者您可以更早地執行:
using ::testing::Mock; ... // Verifies and removes the expectations on mock_obj; // returns true iff successful. Mock::VerifyAndClearExpectations(&mock_obj); ... // Verifies and removes the expectations on mock_obj; // also removes the default actions set by ON_CALL(); // returns true iff successful. Mock::VerifyAndClear(&mock_obj);
您還可以告訴Google Mock模擬對象可以洩漏,無需進行驗證:
Mock::AllowLeak(&mock_obj);
Google Mock定義了一個方便的模擬類模板
class MockFunction<R(A1, ..., An)> {
public:
MOCK_METHODn(Call, R(A1, ..., An));
};
---恢復內容結束---
CheatSheet文檔中包含了GMock所有常用的東西,看了這個基本上就可以用它了,本文翻譯自:https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googlemock/docs/CheatSheet.md
給:
class Foo {
...
virtual ~Foo();
virtual int GetSize() const = 0;
virtual string Describe(const char* name) = 0;
virtual string Describe(int type) = 0;
virtual bool Process(Bar elem, int count) = 0;
};
(note that ~Foo() must be virtual) we can define its mock as,定義模擬類。
#include "gmock/gmock.h"
class MockFoo : public Foo {
MOCK_CONST_METHOD0(GetSize, int());
MOCK_METHOD1(Describe, string(const char* name));
MOCK_METHOD1(Describe, string(int type));
MOCK_METHOD2(Process, bool(Bar elem, int count));
};
創建一個“nice”模擬對象忽略所有無趣的調用,或一個“strict”模擬對象,將它們視為失敗:
NiceMock<MockFoo> nice_foo; // The type is a subclass of MockFoo. StrictMock<MockFoo> strict_foo; // The type is a subclass of MockFoo.
To mock:
template <typename Elem>
class StackInterface {
public:
...
virtual ~StackInterface();
virtual int GetSize() const = 0;
virtual void Push(const Elem& x) = 0;
};
(note that ~StackInterface() must be virtual) just append _T to the MOCK_* macros:
template <typename Elem>
class MockStack : public StackInterface<Elem> {
public:
...
MOCK_CONST_METHOD0_T(GetSize, int());
MOCK_METHOD1_T(Push, void(const Elem& x));
};
如果您的mock函數不使用默認調用約定,您可以通過將_WITH_CALLTYPE附加到前兩個部分中描述的任何宏並指定調用約定作為宏的第一個參數來指定它。例如,
MOCK_METHOD_1_WITH_CALLTYPE(STDMETHODCALLTYPE,Foo,bool(int n)); MOCK_CONST_METHOD2_WITH_CALLTYPE(STDMETHODCALLTYPE,Bar,int(double x,double y));
其中STDMETHODCALLTYPE由Windows上的<objbase.h>定義。
典型的流程是:
這裡是一個例子:
using ::testing::Return; // #1
TEST(BarTest, DoesThis) {
MockFoo foo; // #2
ON_CALL(foo, GetSize()) // #3
.WillByDefault(Return(1));
// ... other default actions ...
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Describe(5)) // #4
.Times(3)
.WillRepeatedly(Return("Category 5"));
// ... other expectations ...
EXPECT_EQ("good", MyProductionFunction(&foo)); // #5
} // #6
Google Mock對任何返回void,bool,數值或指針的函數都有一個內置的默認動作。
要為全局返回類型T的函數自定義默認操作:
using ::testing::DefaultValue; // Sets the default value to be returned. T must be CopyConstructible. DefaultValue<T>::Set(value); // Sets a factory. Will be invoked on demand. T must be MoveConstructible. // T MakeT(); DefaultValue<T>::SetFactory(&MakeT); // ... use the mocks ... // Resets the default value. DefaultValue<T>::Clear();
要自定義特定方法的默認操作,請使用ON_CALL():
ON_CALL(mock_object, method(matchers))
.With(multi_argument_matcher) ?
.WillByDefault(action);
EXPECT_CALL()在模擬方法上設置期望(如何調用它?它會做什麼?):
EXPECT_CALL(mock_object, method(matchers))
.With(multi_argument_matcher) ?
.Times(cardinality) ?
.InSequence(sequences) *
.After(expectations) *
.WillOnce(action) *
.WillRepeatedly(action) ?
.RetiresOnSaturation(); ?
如果省略Times(),則基數假定為:
沒有EXPECT_CALL()的方法可以被任意調用多次,並且每次都將采取默認操作。
匹配器匹配單個參數。 您可以在ON_CALL()或EXPECT_CALL()中使用它,或使用它直接驗證值:
EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher)value matches matcher.ASSERT_THAT(value, matcher)
The same as EXPECT_THAT(value, matcher), except that it generates a fatal failure.
內置的匹配(其中參數是函數參數)分為幾類:
_argument can be any value of the correct type可以代表任意類型.A<type>() or An<type>()
argument can be any value of type可以是type類型的任意值.
注意** 除了Ref()之外,這些匹配器會創建一個值的副本,以備日後修改或銷毀。 如果編譯器抱怨該值沒有公共副本構造函數,請嘗試將其包裝在ByRef()中,例如。 Eq(ByRef(non_copyable_value))。 如果你這樣做,請確保non_copyable_value之後不改變,否則你的匹配器的含義將被改變。
上述匹配器使用基於ULP的比較(與Google Test中使用的比較相同)。 它們根據期望值的絕對值自動選擇合理的誤差界限。 DoubleEq()和FloatEq()符合IEEE標准,這需要比較兩個NaNs的相等性返回false。 NanSensitive *版本將兩個NaNs相等,這通常是用戶想要的。
DoubleNear(a_double, max_abs_error)argument is a double value close to a_double (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as unequal.FloatNear(a_float, max_abs_error)
argument is a float value close to a_float (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as unequal.
NanSensitiveDoubleNear(a_double, max_abs_error)
argument is a double value close to a_double (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as equal.
NanSensitiveFloatNear(a_float, max_abs_error)
argument is a float value close to a_float (absolute error <= max_abs_error), treating two NaNs as equal.
這裡的字符串即可以是C風格的字符串,也可以是C++風格的。
ContainsRegex(string) 形參匹配給定的正則表達式 EndsWith(suffix) 形參以suffix截尾 HasSubstr(string) 形參有string這個子串 MatchesRegex(string) 從第一個字符到最後一個字符都完全匹配給定的正則表達式. StartsWith(prefix) 形參以prefix開始 StrCaseEq(string) 參數等於string,並且忽略大小寫 StrCaseNe(string) 參數不是string,並且忽略大小寫 StrEq(string) 參數等於string StrNe(string) 參數不等於string很多STL的容器的比較都支持==這樣的操作,對於這樣的容器可以使用上述的Eq(expected_container)來比較或者只是expect_container來完全匹配容器。但如果你想寫得更為靈活,可以使用下面的這些容器匹配方法:
ContainerEq(container)Eq(container) except that the failure message also includes which elements are in one container but not the other.Contains(e)
argument contains an element that matches e, which can be either a value or a matcher.
Each(e)
argument is a container where every element matches e, which can be either a value or a matcher.
ElementsAre(e0, e1, ..., en)
argument has n + 1 elements, where the i-th element matches ei, which can be a value or a matcher. 0 to 10 arguments are allowed.
ElementsAreArray({ e0, e1, ..., en }), ElementsAreArray(array), or ElementsAreArray(array, count)
The same as ElementsAre() except that the expected element values/matchers come from an initializer list, STL-style container, or C-style array.
IsEmpty()
argument is an empty container (container.empty()).
Pointwise(m, container)
argument contains the same number of elements as in container, and for all i, (the i-th element in argument, the i-th element in container) match m, which is a matcher on 2-tuples. E.g. Pointwise(Le(), upper_bounds) verifies that each element in argument doesn't exceed the corresponding element in upper_bounds. See more detail below.
SizeIs(m)
argument is a container whose size matches m. E.g. SizeIs(2) or SizeIs(Lt(2)).
UnorderedElementsAre(e0, e1, ..., en)
argument has n + 1 elements, and under some permutation each element matches an ei (for a different i), which can be a value or a matcher. 0 to 10 arguments are allowed.
UnorderedElementsAreArray({ e0, e1, ..., en }), UnorderedElementsAreArray(array), or UnorderedElementsAreArray(array, count)
The same as UnorderedElementsAre() except that the expected element values/matchers come from an initializer list, STL-style container, or C-style array.
WhenSorted(m)
When argument is sorted using the < operator, it matches container matcher m. E.g. WhenSorted(UnorderedElementsAre(1, 2, 3)) verifies that argument contains elements 1, 2, and 3, ignoring order.
WhenSortedBy(comparator, m)
The same as WhenSorted(m), except that the given comparator instead of < is used to sort argument. E.g. WhenSortedBy(std::greater<int>(), ElementsAre(3, 2, 1)).
注意:
這些匹配器也可以匹配:
i. 通過引用傳遞的本地數組(例如在Foo(const int(&a)[5])中)和
ii. 作為指針和計數傳遞的數組(例如,在Bar(const T * buffer,int len) - 參見 Multi-argument Matchers)。
匹配的數組可以是多維的(即其元素可以是數組)。
在Pointwise(m,...)中的m應該是:: testing :: tuple <T,U>的匹配器,其中T和U分別是實際容器和預期容器的元素類型。 例如,要比較兩個Foo容器,其中Foo不支持operator ==但是有一個Equals()方法,可以寫:
using ::testing::get;
MATCHER(FooEq, "") {
return get<0>(arg).Equals(get<1>(arg));
}
...
EXPECT_THAT(actual_foos, Pointwise(FooEq(), expected_foos));
Field(&class::field, m)argument.field (or argument->field when argument is a plain pointer) matches matcher m, where argument is an object of type class.Key(e)
argument.first matches e, which can be either a value or a matcher. E.g. Contains(Key(Le(5))) can verify that a map contains a key <= 5.
Pair(m1, m2)
argument is an std::pair whose first field matches m1 and second field matches m2.
Property(&class::property, m)
argument.property() (or argument->property() when argument is a plain pointer) matches matcher m, where argument is an object of type class.
ResultOf(f, m)f(argument) matches matcher m, where f is a function or functor.Pointee(m)
argument (either a smart pointer or a raw pointer) points to a value that matches matcher m.
WhenDynamicCastTo<T>(m)
when argument is passed through dynamic_cast<T>(), it matches matcher m.
從技術上講,完全匹配器匹配單個值。 “多參數”匹配器只是匹配元組的匹配器。 以下匹配器可用於匹配元組(x,y):
Eq()x == yGe()
x >= y
Gt()
x > y
Le()
x <= y
Lt()
x < y
Ne()
x != y
您可以使用以下選擇器來選擇參數的子集(或對其重新排序)以參與匹配:
AllArgs(m)m. Useful as syntactic sugar in .With(AllArgs(m)).Args<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(m)
The tuple of the k selected (using 0-based indices) arguments matches m, e.g. Args<1, 2>(Eq()).
你可以從一個或多個其他匹配器做一個匹配器:
AllOf(m1, m2, ..., mn)argument matches all of the matchers m1 to mn.AnyOf(m1, m2, ..., mn)
argument matches at least one of the matchers m1 to mn.
Not(m)
argument doesn't match matcher m.
MatcherCast<T>(m)m to type Matcher<T>.SafeMatcherCast<T>(m)
safely casts matcher m to type Matcher<T>.
Truly(predicate)
predicate(argument) returns something considered by C++ to be true, where predicate is a function or functor.
Matches(m)(value)true if value matches m. You can use Matches(m) alone as a unary functor.ExplainMatchResult(m, value, result_listener)
evaluates to true if value matches m, explaining the result to result_listener.
Value(value, m)
evaluates to true if value matches m.
MATCHER(IsEven, "") { return (arg % 2) == 0; }IsEven() to match an even number.MATCHER_P(IsDivisibleBy, n, "") { *result_listener << "where the remainder is " << (arg % n); return (arg % n) == 0; }
Defines a macher IsDivisibleBy(n) to match a number divisible by n.
MATCHER_P2(IsBetween, a, b, std::string(negation ? "isn't" : "is") + " between " + PrintToString(a) + " and " + PrintToString(b)) { return a <= arg && arg <= b; }
Defines a matcher IsBetween(a, b) to match a value in the range [a, b].
筆記:
ASSERT_THAT(expression, m)expression doesn't match matcher m.EXPECT_THAT(expression, m)
Generates a non-fatal failure if the value of expression doesn't match matcher m.
操作指定了mock函數在調用時應該執行的操作。
Return()void mock function.Return(value)
Return value. If the type of value is different to the mock function's return type, value is converted to the latter type at the time the expectation is set, not when the action is executed.
ReturnArg<N>()
Return the N-th (0-based) argument.
ReturnNew<T>(a1, ..., ak)
Return new T(a1, ..., ak); a different object is created each time.
ReturnNull()
Return a null pointer.
ReturnPointee(ptr)
Return the value pointed to by ptr.
ReturnRef(variable)
Return a reference to variable.
ReturnRefOfCopy(value)
Return a reference to a copy of value; the copy lives as long as the action.
Assign(&variable, value)value to variable.DeleteArg<N>()
Delete the N-th (0-based) argument, which must be a pointer.
SaveArg<N>(pointer)
Save the N-th (0-based) argument to *pointer.
SaveArgPointee<N>(pointer)
Save the value pointed to by the N-th (0-based) argument to *pointer.
SetArgReferee<N>(value)
Assign value to the variable referenced by the N-th (0-based) argument.
SetArgPointee<N>(value)
Assign value to the variable pointed by the N-th (0-based) argument.
SetArgumentPointee<N>(value)
Same as SetArgPointee<N>(value). Deprecated. Will be removed in v1.7.0.
SetArrayArgument<N>(first, last)
Copies the elements in source range [first, last) to the array pointed to by the N-th (0-based) argument, which can be either a pointer or an iterator. The action does not take ownership of the elements in the source range.
SetErrnoAndReturn(error, value)
Set errno to error and return value.
Throw(exception)
Throws the given exception, which can be any copyable value. Available since v1.1.0.
Invoke(f)f with the arguments passed to the mock function, where f can be a global/static function or a functor.Invoke(object_pointer, &class::method)
Invoke the {method on the object with the arguments passed to the mock function.
InvokeWithoutArgs(f)
Invoke f, which can be a global/static function or a functor. f must take no arguments.
InvokeWithoutArgs(object_pointer, &class::method)
Invoke the method on the object, which takes no arguments.
InvokeArgument<N>(arg1, arg2, ..., argk)
Invoke the mock function's N-th (0-based) argument, which must be a function or a functor, with the k arguments.
被調用函數的返回值被用作動作的返回值。
定義要與Invoke *()一起使用的函數或函數時,可以將任何未使用的參數聲明為未使用:
double Distance(Unused, double x, double y) { return sqrt(x*x + y*y); }
...
EXPECT_CALL(mock, Foo("Hi", _, _)).WillOnce(Invoke(Distance));
在Invoke Argument <N>(...)中,如果一個參數需要通過引用傳遞,則將其包裝在ByRef()中。 例如,
InvokeArgument<2>(5, string("Hi"), ByRef(foo))
調用模擬函數#2參數,通過值傳遞給它5和字符串(“Hi”),並通過引用傳遞foo。
DoDefault()ON_CALL() or the built-in one).Note: due to technical reasons, DoDefault() cannot be used inside a composite action - trying to do so will result in a run-time error.
DoAll(a1, a2, ..., an)a1 to an and return the result of an in each invocation. The first n - 1sub-actions must return void.IgnoreResult(a)
Perform action a and ignore its result. a must not return void.
WithArg<N>(a)
Pass the N-th (0-based) argument of the mock function to action a and perform it.
WithArgs<N1, N2, ..., Nk>(a)
Pass the selected (0-based) arguments of the mock function to action a and perform it.
WithoutArgs(a)
Perform action a without any arguments.
ACTION(Sum) { return arg0 + arg1; }Sum() to return the sum of the mock function's argument #0 and #1.ACTION_P(Plus, n) { return arg0 + n; }
Defines an action Plus(n) to return the sum of the mock function's argument #0 and n.
ACTION_Pk(Foo, p1, ..., pk) { statements; }
Defines a parameterized action Foo(p1, ..., pk) to execute the given statements.
The ACTION* macros cannot be used inside a function or class.
這些在Times()中用於指定將調用模擬函數的次數:
AnyNumber()AtLeast(n)
The call is expected at least n times.
AtMost(n)
The call is expected at most n times.
Between(m, n)
The call is expected between m and n (inclusive) times.
Exactly(n) or n
The call is expected exactly n times. In particular, the call should never happen when n is 0.
默認情況下,期望可以按任何順序匹配。如果一些或所有期望必須在給定的順序中匹配,則有兩種方式來指定它們。 它們可以單獨使用或一起使用。
using ::testing::Expectation;
...
Expectation init_x = EXPECT_CALL(foo, InitX());
Expectation init_y = EXPECT_CALL(foo, InitY());
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar())
.After(init_x, init_y);
上邊說,只有在InitX()和InitY()被調用之後才能調用Bar()。
如果你不知道你寫的期望有多少個前提條件,你可以使用ExpectationSet來收集它們:
using ::testing::ExpectationSet;
...
ExpectationSet all_inits;
for (int i = 0; i < element_count; i++) {
all_inits += EXPECT_CALL(foo, InitElement(i));
}
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Bar())
.After(all_inits);
上面說,只有在所有元素都被初始化之後才能調用Bar()。(但我們不關心哪些元素在其他元素之前被初始化)。
在 .After(all_inits)中使用ExpectationSet之後再修改ExpectationSet不會影響.After()的含義。
當你有一個長鏈的順序期望,使用序列指定順序更容易,這不需要給鏈中的每個期望一個不同的名稱。同一序列中的所有預期調用必須按其指定的順序發生。
using ::testing::Sequence;
Sequence s1, s2;
...
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Reset())
.InSequence(s1, s2)
.WillOnce(Return(true));
EXPECT_CALL(foo, GetSize())
.InSequence(s1)
.WillOnce(Return(1));
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Describe(A<const char*>()))
.InSequence(s2)
.WillOnce(Return("dummy"));
上邊說,Reset()必須在GetSize()和Describe()之前調用,後兩個可以以任何順序發生。
在一個序列中方便地提出許多期望:
using ::testing::InSequence;
{
InSequence dummy;
EXPECT_CALL(...)...;
EXPECT_CALL(...)...;
...
EXPECT_CALL(...)...;
}
上邊說,在dummy范圍內的所有預期調用必須以嚴格的順序發生。 名稱dummy是不相關的。)
Google Mock會在模擬對象被破壞時驗證對模擬對象的期望,或者您可以更早地執行:
using ::testing::Mock; ... // Verifies and removes the expectations on mock_obj; // returns true iff successful. Mock::VerifyAndClearExpectations(&mock_obj); ... // Verifies and removes the expectations on mock_obj; // also removes the default actions set by ON_CALL(); // returns true iff successful. Mock::VerifyAndClear(&mock_obj);
您還可以告訴Google Mock模擬對象可以洩漏,無需進行驗證:
Mock::AllowLeak(&mock_obj);
Google Mock定義了一個方便的模擬類模板
class MockFunction<R(A1, ..., An)> {
public:
MOCK_METHODn(Call, R(A1, ..., An));
};
See this recipe for one application of it.
--gmock_catch_leaked_mocks=0--gmock_verbose=LEVEL
Sets the default verbosity level (info, warning, or error) of Google Mock messages.
舉一個測試重載函數的匹配器的例子吧,感覺這個挺麻煩的,另外google提供了很多例子,不知道怎麼寫的時候,可以去裡邊找。
//接口類
class Foo {
public:
virtual bool Transform() = 0;
// Overloaded on the types and/or numbers of arguments.
virtual int Add(char x) = 0;
virtual int Add(int x,int y) = 0;
virtual int Add(int times, char x) = 0;
protected:
virtual void Resume() = 0;
private:
virtual int GetTimeOut() = 0;
};
#include "Foo.h"
#include "gmock\gmock.h"
//模擬類
//子類修改父類的訪問權限
class MockFoo : public Foo {
public:
MOCK_METHOD0(Transform, bool());
// The following must be in the public section, even though the
// methods are protected or private in the base class.
MOCK_METHOD0(Resume, void());
MOCK_METHOD0(GetTimeOut, int());
//virtual int Add(char x);
//virtual int Add(int times, char x);
// virtual int Add(int x);
MOCK_METHOD1(Add, int(char x));
//MOCK_METHOD1(Add, int(int x));
MOCK_METHOD2(Add, int(int times, char x));
// virtual int Add(int x,int y) = 0;
MOCK_METHOD2(Add, int(int x, int y));
};
測試用例:
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace std;
using ::testing::Return;
using ::testing::_;
using ::testing::An;
using ::testing::Matcher;
using ::testing::Lt;
using ::testing::TypedEq;
using ::testing::Matches;
using ::testing::Le;
using ::testing::Ne;
using ::testing::AllOf;
//測試模擬private、protected方法:
TEST(TestMockPrivate, TestPrivate) {
MockFoo foo;
//GetTimeOut是private修飾的
EXPECT_CALL(foo, GetTimeOut())
.WillOnce(Return(1));
cout << "test private GetTimeOut:" << foo.GetTimeOut() << endl; //1
}
//測試重載方法
TEST(TestMockOverload, TestOverload) {
MockFoo foo;
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Add(_))
.Times(1)
.WillOnce(Return(1));
cout << "test TestOverload Add:" << foo.Add('c') << endl; //1
}
//測試數量相同,類型不同的情況。
// virtual int Add(int x,int y) = 0;
// virtual int Add(int times, char x) = 0;
TEST(TestMockOverload, TestSameNumArg) {
MockFoo foo;
//兩個都是int
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Add(An<int>(), An<int>()))
.Times(1)
.WillOnce(Return(8));
int c = foo.Add(3, 5);
cout << "test TestOverload Add:" <<c<< endl; //8
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Add(Matcher<int>(Lt(10)), TypedEq<char>('c')))
.Times(1)
.WillOnce(Return(7));
c = foo.Add(2, 'c');
cout << "test TestOverload Add:" << c << endl; //7
}
//測試數量相同,類型不同的情況。
TEST(TestMockOverload, TestSameNumArg2) {
MockFoo foo;
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Add(Matcher<int>(Lt(5)), An<int>()))
.Times(1)
.WillOnce(Return(7));
int c = foo.Add(2, 5);
cout << "test TestOverload Add:" << c << endl; //7
//第一個參數小於5,,第二個參數是'd'
EXPECT_CALL(foo, Add(Matcher<int>(Lt(5)), Matcher<char>('d')))
.Times(1)
.WillOnce(Return(10));
c = foo.Add(2, 'd'); //10
cout << "test TestOverload Add:" << c << endl; //10
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
::testing::InitGoogleMock(&argc, argv);
return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
運行結果:可以看到都成功啦
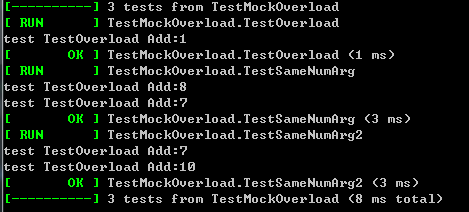
ok。。結束。。
轉載請注明出處:http://www.cnblogs.com/jycboy/p/gmock_cheatsheet.html