cJSON簡介
JSON基本信息
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一種輕量級的數據交換格式。易於人閱讀和編寫。同時易於機器解析和生成。是一種很好地數據交換語言。
官方信息解讀簡介
JSON構建:基於兩種結構
“名稱/值”對 的集合。
值得有序列表。
JSON具體結構表示
對象:一個”名稱/值"對的集合 {名稱:值,名稱:值}
數組:值得有序集合[值,值]
值:str,num,true,false,null,object,array。可嵌套
字符串:由雙引號包圍的任意數量Unicode字符的集合,反斜槓轉義
數值:類似C,java:沒有8進制和具體的編碼細節
cJSON源碼解讀
首先給出cJSON文件中頭文件函數列表
我們將根據此進行模塊化解讀
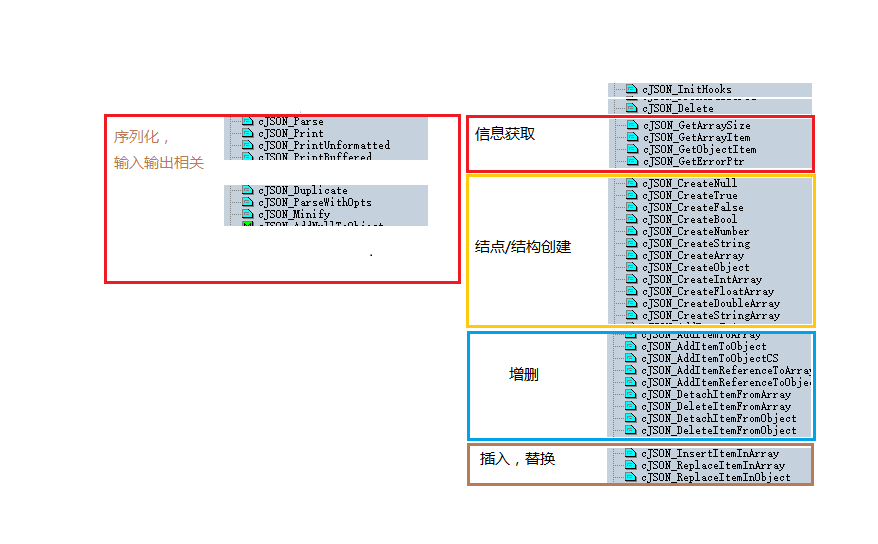
①結構描述
關於具體的結構圖解描述,請參考官方描述
/* cJSON Types: */ #define cJSON_False 0 #define cJSON_True 1 #define cJSON_NULL 2 #define cJSON_Number 3 #define cJSON_String 4 #define cJSON_Array 5 #define cJSON_Object 6 #define cJSON_IsReference 256 #define cJSON_StringIsConst 512
以上是具體的類型區分描述,可以改進為使用enum實現更加安全
/* The cJSON structure: */
typedef struct cJSON {
struct cJSON *next, *prev; /* 如果是同一級別類型元素,使用雙項鏈方式實現 */
struct cJSON *child; /* 如果是具體結構或者數組,第一個指針指向內部鏈 */
int type; /*根據以上定義描述所保存對象類型*/
char *valuestring; /* The item's string, if type==cJSON_String */
int valueint; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
double valuedouble; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
char *string; /* 對於key-value映射結構,表示其key/名稱 */
}cJSON;
②關於內存管理
typedef struct cJSON_Hooks {
void *(*malloc_fn)(size_t sz);
void(*free_fn)(void *ptr);
} cJSON_Hooks;
注:cJSON的內存管理,提供了用戶自主方式的接口。可以通過方法InitHooks來設置自己的內存管理,默認使用malloc,free
static void *(*cJSON_malloc)(size_t sz) = malloc;
static void(*cJSON_free)(void *ptr) = free;
void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks)
{
if (!hooks) { /* Reset hooks */
cJSON_malloc = malloc;
cJSON_free = free;
return;
}
cJSON_malloc = (hooks->malloc_fn) ? hooks->malloc_fn : malloc;
cJSON_free = (hooks->free_fn) ? hooks->free_fn : free;
}
③結點創建,刪除結點
/* Internal constructor. */
static cJSON *cJSON_New_Item(void)
{
cJSON* node = (cJSON*)cJSON_malloc(sizeof(cJSON));
if (node) memset(node, 0, sizeof(cJSON));
return node;
}
/* Delete a cJSON structure. */
//總結一下就是對於 object 和 array 需要先刪除兒子,然後刪除自己。
//對於 字符串, 需要先釋放字符串的內存, 再釋放自己這塊內存。
//對於其他節點,直接釋放自己這塊內存。
void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c)
{
cJSON *next;
while (c)
{
next = c->next;
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->child) cJSON_Delete(c->child); //
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->valuestring) cJSON_free(c->valuestring);
if (!(c->type&cJSON_StringIsConst) && c->string) cJSON_free(c->string);
cJSON_free(c);
c = next;
}
}
有了結點設置,那麼下面就是具體類型結點的實現了:設置類型,設置具體類型的值
/* These calls create a cJSON item of the appropriate type. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void);
/* These utilities create an Array of count items. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers, int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers, int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers, int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char **strings, int count);
/* Create basic types: */
cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void)
{
cJSON *item = cJSON_New_Item();
if (item)
item->type = cJSON_NULL;
return item;
}
/* Create Arrays: */
cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers, int count)
{
int i; cJSON *n = 0, *p = 0,
*a = cJSON_CreateArray();
for (i = 0; a && i < count; i++)
{
n = cJSON_CreateNumber(numbers[i]); //申請N個幾點
if (!i)
a->child = n;//第一個結點鏈接使用child
else
suffix_object(p, n);//其他結點 :連接prev next
p = n;
}return a;
}
④結點操作
/* Append item to the specified array/object. */
extern void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item); /* Use this when string is definitely const (i.e. a literal, or as good as), and will definitely survive the cJSON object */
/* Append reference to item to the specified array/object. Use this when you want to add an existing cJSON to a new cJSON,
but don't want to corrupt your existing cJSON. */
extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *item);
/* Remove/Detatch items from Arrays/Objects. */
//Detatch脫離,使item從arr鏈中脫離,便於delete
extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which);
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which);
extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object, const char *string);
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object, const char *string);
/* Update array items. */
extern void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem); /* Shifts pre-existing items to the right. */
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem);
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object, const char *string, cJSON *newitem);
注:①
Detach 是什麼東西呢?
我們把一個節點從 json 樹中刪除, 但是不釋放內存,而是先保留這個節點的指針, 這樣儲存在這個節點的信息都保留了下來。
接下來我們就可以做很多事了, 合適的時候添加到其他對象中, 合適的時候釋放內存。
比如上面的 delete 函數, 就需要真實的刪除了, 這個時候我們刪除即可。
而 detach 實現也比較簡單, 只是少了一步刪除操作。
//將結點從結構中脫離
cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
while (c && which>0)
c = c->next, which--;
if (!c)
return 0;
if (c->prev)
c->prev->next = c->next;
if (c->next)
c->next->prev = c->prev;
if (c == array->child)
array->child = c->next;
c->prev = c->next = 0;
return c;
}
void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array, int which)
{
cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(array, which));
}
②關於以上相關方法,簡單的增加結點就是個鏈表操作了,然後對於
cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray這個方法說明
cJSON除了實現簡單的增加結點到結構之外,還有簡單考慮效率問題。
比如同時增加一個結點到兩棵樹中,那麼如果有深淺拷貝問題時,cJSON做法是,增加一個結點為Reference類型,在另一棵樹中。這裡的做法可以是引用計數,寫實拷貝等
我們來看看cJSON實現吧
/* Utility for handling references. */
static cJSON *create_reference(cJSON *item)
{
cJSON *ref = cJSON_New_Item();
if (!ref)
return 0;
memcpy(ref, item, sizeof(cJSON)); //淺拷貝所有值-->最終保存了結點的value部分
ref->string = 0; //k-v中的值清空,以便於重新設置
ref->type |= cJSON_IsReference; //結點類性是具體item類型的同時也是reference
ref->next = ref->prev = 0; //只是當前節點的引用,去除引用的鏈接
return ref;
}
void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item)
{
cJSON_AddItemToArray(array, create_reference(item)); //創建應用結點之後加入目的數組
}
void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array, int which, cJSON *newitem)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
while (c && which>0)
c = c->next, which--; //找到具體位置
if (!c)
return;
newitem->next = c->next;
newitem->prev = c->prev; //連入結構中
if (newitem->next)
newitem->next->prev = newitem;//修改後指針
if (c == array->child) //如果是個孩子,
array->child = newitem;
else
newitem->prev->next = newitem; //修改後指針
c->next = c->prev = 0;//釋放被代替的結點
cJSON_Delete(c);
}
⑤查找相關
/* Get Array size/item / object item. */
int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
int i = 0;
while (c)
i++, c = c->next;
return i;
}
cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array, int item)
{
cJSON *c = array->child;
while (c && item>0)
item--, c = c->next;
return c;
}
//結構中結點的設置,需要通過變量名來查找
cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object, const char *string)
{
cJSON *c = object->child;
while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string, string))
c = c->next;
return c;
}
⑥總結部分:
通過以上對於cJSON結構的簡單學習和剖析,我們不難聯想到廣義表。其實這個結構的實現就是類似廣義表實現:由child遞歸為廣義結構
關於具體的cJSON數據解析部分,請參考博客《cJONS序列化工具解讀②(數據解析)》