淺析:淺拷貝 及 深拷貝的傳統寫法,淺析拷貝傳統寫法
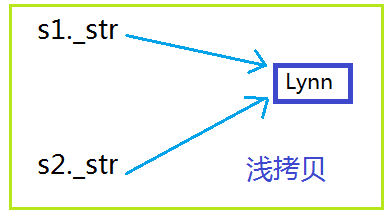
淺拷貝會造成指針懸掛的問題。
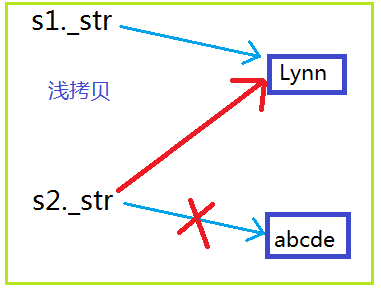
舉個例子:兩個對象是s1和s2的指針_str都指向new開辟的同一塊空間,如下圖,主程序結束時,對象逐個撤銷,先撤銷對象s2,會調用析構函數釋放動態分配的內存;再撤銷對象s1時,s1._str所指向的內存空間已經是無法訪問了,而s2._str原先指向的那塊內存卻無法釋放,出現了所謂的指針懸掛! 兩個對象企圖釋放同一塊內存,從而導致一塊內存被釋放兩次這也是不行的,運行會出錯。
ORT.png)
![]()
1 #include <iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 class String
5 {
6 public:
7 String(char *str)
8 :_str(new char [strlen(str )+1])
9 {
10 strcpy(_str, str);
11 }
12 String(const String & s)
13 {
14 _str = s._str;
15 }
16 String& operator=(const String & s )
17 {
18 if (this !=&s)
19 {
20 _str = s._str;
21 }
22 return *this ;
23 }
24 ~String()
25 {
26 delete[] _str;
27 }
28 private:
29 char* _str;
30 };
31
32 void Test()
33 {
34 String s1("Lynn" );
35 String s2=s1;
36 }
37 int main()
38 {
39 Test();
40 system("pause" );
41 return 0;
42 }
淺拷貝
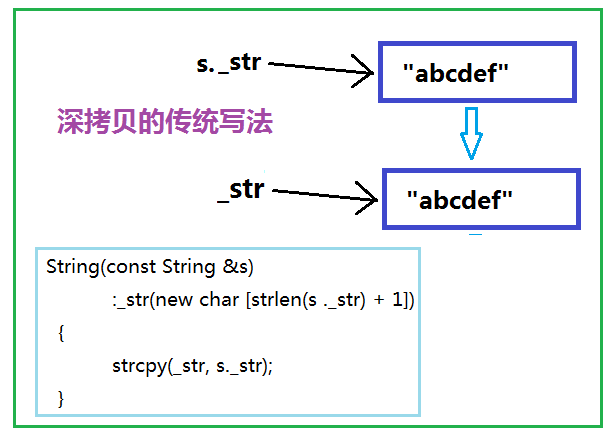
深拷貝 深拷貝解決了指針懸掛的問題,當調用拷貝構造或賦值運算符的重載函數時,程序會生成一份該內存的拷貝,這樣每個指針都會指向一塊相對獨立的空間,撤銷對象時調用析構函數,分別釋放他們自己的動態分配的內存,相互之間不影響。如下圖:
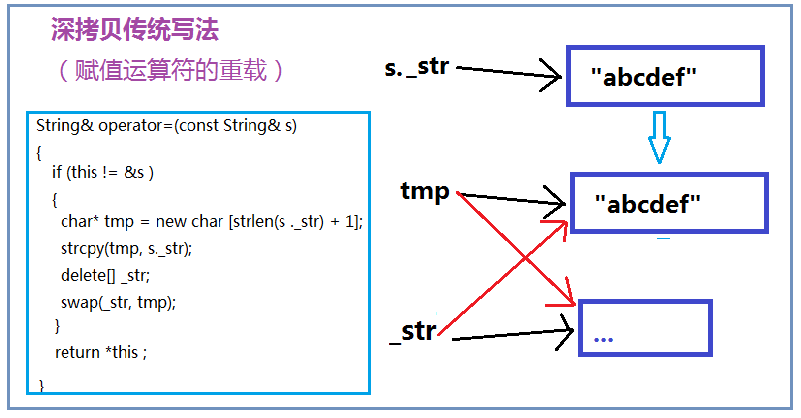

深拷貝
![]()
1 ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
2
3 // 寫String類的構造函數時一定要注意參數問題
4 // 首先要考慮到構造的對象分有參數和無參數兩種情況
5 // 構造對象的時候不能直接賦值,否則一塊內存兩次釋放的話程序會出錯
6 // 無參的構造函數不能將_str指針賦值為NULL,因為不能strlen(NULL)
7 // 賦值運算符的重載要考慮到有可能分配內存失敗的問題
8 // 當然,記得要給'\0'分配空間哦
9 // By:Lynn-Zhang
10 //////////////////////////*****************////////////////////////////////////////////
11
12 #include<iostream>
13 using namespace std;
14
15 class String
16 {
17 public:
18
19 String(char * str="") //不能strlen(NULL)
20 :_str(new char [strlen(str ) + 1])
21 {
22 strcpy(_str, str);
23 }
24 String(const String &s)
25 :_str(new char [strlen(s ._str) + 1])
26 {
27 strcpy(_str, s._str);
28 }
29
30 //賦值運算符的重載
31 String& operator=(const String& s)
32 {
33 if (this != &s )
34 {
35 /* //有可能開辟空間失敗,但是卻破壞了_str的內容
36 delete[] _str;
37 _str = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
38 strcpy(_str, s._str); */
39
40 char* tmp = new char [strlen(s ._str) + 1];
41 strcpy(tmp, s._str);
42 delete[] _str;
43 swap(_str, tmp);
44
45 }
46 return *this ;
47 }
48 char* CStr()
49 {
50 return _str;
51 }
52 ~String()
53 {
54 delete[] _str;
55 }
56 private:
57 char* _str;
58 };
59
60
61 //函數測試
62 void Test()
63 {
64 String s1("aaaaa" );
65 cout << s1.CStr() << endl;
66 String s2(s1);
67 cout << s2.CStr() << endl;
68 String s3 = s1;
69 s3= s2;
70 cout << s3.CStr() << endl;
71 String s4;
72 // s4 = s1;
73 cout << s4.CStr() << endl;
74
75 }
76 int main()
77 {
78 Test();
79 system("pause" );
80 return 0;
81 }


ORT.png)



 深拷貝
深拷貝