Description
In the Fibonacci integer sequence,F0= 0,F1= 1, andFn=Fn? 1+Fn? 2forn≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is
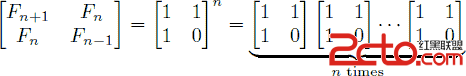 .
.
Given an integern, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits ofFn.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤n≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number ?1.
Output
For each test case, print the last four digits ofFn. If the last four digits ofFnare all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., printFnmod 10000).
Sample Input
0 9 999999999 1000000000 -1
Sample Output
0 34 626 6875
Hint
As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
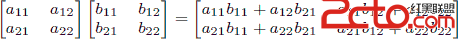 .
.
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:
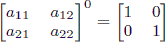 .
.
Source
Stanford Local 2006矩陣乘法裸題,題目已經把題解講的很清楚了...
#include#include #include #include #include #include #define F(i,j,n) for(int i=j;i<=n;i++) #define D(i,j,n) for(int i=j;i>=n;i--) #define ll long long #define mod 10000 using namespace std; int n; struct matrix { int f[2][2]; matrix(){memset(f,0,sizeof(f));} friend matrix operator *(const matrix &a,const matrix &b) { matrix c; F(i,0,1) F(j,0,1) F(k,0,1) c.f[i][j]=(c.f[i][j]+a.f[i][k]*b.f[k][j])%mod; return c; } }; int main() { while (scanf("%d",&n)) { if (n==-1) break; matrix a,b; a.f[0][0]=a.f[0][1]=a.f[1][0]=1;a.f[1][1]=0; b.f[1][0]=b.f[0][1]=0;b.f[0][0]=b.f[1][1]=1; for(;n;n>>=1,a=a*a) if (n&1) b=b*a; printf("%d\n",b.f[1][0]); } return 0; }