abcfbc abfcab programming contest abcd mnp
4 2 0
鏈接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1159
題意:求兩個字符串的最長公共子串。
思路:動態規劃。
最長公共子序列是一個很經典的動態規劃問題,最近正在學習動態規劃,所以拿來這裡再整理一下。
這個問題在《算法導論》中作為講動態規劃算法的例題出現。
動態規劃,眾所周知,第一步就是找子問題,也就是把一個大的問題分解成子問題。這裡我們設兩個字符串A、B,A = a0, a1, a2, ..., am-1,B = b0, b1, b2, ..., bn-1。
(1)如果am-1 == bn-1,則當前最長公共子序列為a0, a1, ..., am-2與b0, b1, ..., bn-2的最長公共子序列與am-1的和。長度為a0, a1, ..., am-2與b0, b1, ..., bn-2的最長公共子序列的長度+1。
(2)如果am-1 != bn-1,則最長公共子序列為max(a0, a1, ..., am-2與b0, b1, ..., bn-1的公共子序列,a0, a1, ..., am-1與b0, b1, ..., bn-2的公共子序列)
如果上述描述用數學公式表示,則引入一個二維數組c[][],其中c[i][j]記錄X[i]與Y[j]的LCS長度,b[i][j]記錄c[i][j]是通過哪一個子問題的值求得的,即,搜索方向。
這樣我們可以總結出該問題的遞歸形式表達:
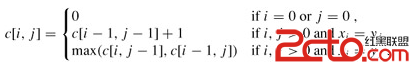
按照動態規劃的思想,對問題的求解,其實就是對子問題自底向上的計算過程。這裡,計算c[i][j]時,c[i-1][j-1]、c[i-1][j]、c[i][j-1]已經計算出來了,這樣,我們可以根據X[i]與Y[j]的取值,按照上面的遞推,求出c[i][j],同時把路徑記錄在b[i][j]中(路徑只有3中方向:左上、左、上,如下圖)。
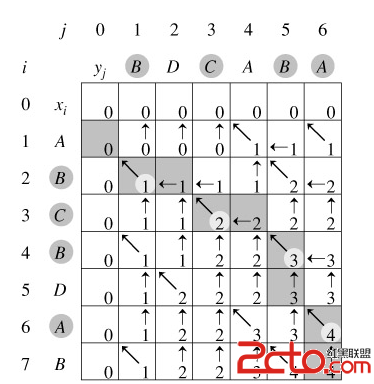
計算c[][]矩陣的時間復雜度是O(m*n);根據b[][]矩陣尋找最長公共子序列的過程,由於每次調用至少向上或向左移動一步,這樣最多需要(m+n)次就會i = 0或j = 0,也就是算法時間復雜度為O(m+n)。
#include#include #include #include using namespace std; int map[10005][10005]; string str1,str2; int len1,len2; //最長公共子序列 /*** 遞歸解法: 0 if(i==0||j==0); map[i][j] = map[i-1][j-1] if(i>0&&j>0&&str1[i]==str2[j]) max(map[i-1][j],map[i][j-1]) if(i>0&&j>0&&str1[i]!=str2[j]) */ /*****遞歸超時了! int LCS(int x,int y) { if(x<0||y<0) return 0; if( str1[x]==str2[y]) return LCS(x-1,y-1)+1; else return max(LCS(x-1,y),LCS(x,y-1)); }*/ int main() { while(cin>>str1>>str2) { len1=str1.length()-1; len2=str2.length()-1; // printf(%d ,LCS(len1,len2)); /***非遞歸解法LCS*/ for(int i=0;i<=len1+1;i++) { for(int j=0;j<=len2+1;j++) { if(i==0||j==0) {map[i][j]=0;continue;} if(str1[i-1]==str2[j-1]) { map[i][j]=map[i-1][j-1]+1; } else { map[i][j]=max(map[i-1][j],map[i][j-1]); } } } printf(%d ,map[len1+1][len2+1]); } return 0; }
還有一種優化空間的方法,利用滾動數組!這裡也附上代碼。在不需要記錄路徑的時候很好用!
#include#include #include #include using namespace std; int map[2][10005]; string str1,str2; int len1,len2; //最長公共子序列 int LCS(int x,int y) { for(int i=0;i<=x;i++) { for(int j=0;j<=y+1;j++) { if(i==0||j==0) {map[i%2][j]=0;continue;} if(str1[i-1]==str2[j-1]) { map[i%2][j]=map[(i-1)%2][j-1]+1; } else { map[i%2][j]=max(map[(i-1)%2][j],map[i%2][j-1]); } } } } int main() { while(cin>>str1>>str2) { len1=str1.length(); len2=str2.length(); LCS(len1,len2); printf(%d ,map[len1%2][len2]); } return 0; }