深度優先遍歷,深度優先
二叉樹的深度優先遍歷與廣度優先遍歷 [ C++ 實現 ]
深度優先搜索算法(Depth First Search),是搜索算法的一種。是沿著樹的深度遍歷樹的節點,盡可能深的搜索樹的分支。
當節點v的所有邊都己被探尋過,搜索將回溯到發現節點v的那條邊的起始節點。這一過程一直進行到已發現從源節點可達的所有節點為止。
如果還存在未被發現的節點,則選擇其中一個作為源節點並重復以上過程,整個進程反復進行直到所有節點都被訪問為止。
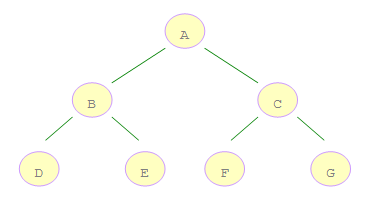
如右圖所示的二叉樹:
A 是第一個訪問的,然後順序是 B、D,然後是 E。接著再是 C、F、G。
那麼,怎麼樣才能來保證這個訪問的順序呢?
分析一下,在遍歷了根結點後,就開始遍歷左子樹,最後才是右子樹。
因此可以借助堆棧的數據結構,由於堆棧是後進先出的順序,由此可以先將右子樹壓棧,然後再對左子樹壓棧,
這樣一來,左子樹結點就存在了棧頂上,因此某結點的左子樹能在它的右子樹遍歷之前被遍歷。
深度優先遍歷代碼片段
//深度優先遍歷
void depthFirstSearch(Tree root){
stack<Node *> nodeStack; //使用C++的STL標准模板庫
nodeStack.push(root);
Node *node;
while(!nodeStack.empty()){
node = nodeStack.top();
printf(format, node->data); //遍歷根結點
nodeStack.pop();
if(node->rchild){
nodeStack.push(node->rchild); //先將右子樹壓棧
}
if(node->lchild){
nodeStack.push(node->lchild); //再將左子樹壓棧
}
}
}
廣度優先搜索算法(Breadth First Search),又叫寬度優先搜索,或橫向優先搜索。
是從根節點開始,沿著樹的寬度遍歷樹的節點。如果所有節點均被訪問,則算法中止。
如右圖所示的二叉樹,A 是第一個訪問的,然後順序是 B、C,然後再是 D、E、F、G。
那麼,怎樣才能來保證這個訪問的順序呢?
借助隊列數據結構,由於隊列是先進先出的順序,因此可以先將左子樹入隊,然後再將右子樹入隊。
這樣一來,左子樹結點就存在隊頭,可以先被訪問到。
廣度優先遍歷代碼片段
//廣度優先遍歷
void breadthFirstSearch(Tree root){
queue<Node *> nodeQueue; //使用C++的STL標准模板庫
nodeQueue.push(root);
Node *node;
while(!nodeQueue.empty()){
node = nodeQueue.front();
nodeQueue.pop();
printf(format, node->data);
if(node->lchild){
nodeQueue.push(node->lchild); //先將左子樹入隊
}
if(node->rchild){
nodeQueue.push(node->rchild); //再將右子樹入隊
}
}
}
完整代碼:
/**
* <!--
* File : binarytree.h
* Author : fancy
* Email :
[email protected] * Date : 2013-02-03
* --!>
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <Stack>
#include <Queue>
using namespace std;
#define Element char
#define format "%c"
typedef struct Node {
Element data;
struct Node *lchild;
struct Node *rchild;
} *Tree;
int index = 0; //全局索引變量
//二叉樹構造器,按先序遍歷順序構造二叉樹
//無左子樹或右子樹用'#'表示
void treeNodeConstructor(Tree &root, Element data[]){
Element e = data[index++];
if(e == '#'){
root = NULL;
}else{
root = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
root->data = e;
treeNodeConstructor(root->lchild, data); //遞歸構建左子樹
treeNodeConstructor(root->rchild, data); //遞歸構建右子樹
}
}
//深度優先遍歷
void depthFirstSearch(Tree root){
stack<Node *> nodeStack; //使用C++的STL標准模板庫
nodeStack.push(root);
Node *node;
while(!nodeStack.empty()){
node = nodeStack.top();
printf(format, node->data); //遍歷根結點
nodeStack.pop();
if(node->rchild){
nodeStack.push(node->rchild); //先將右子樹壓棧
}
if(node->lchild){
nodeStack.push(node->lchild); //再將左子樹壓棧
}
}
}
//廣度優先遍歷
void breadthFirstSearch(Tree root){
queue<Node *> nodeQueue; //使用C++的STL標准模板庫
nodeQueue.push(root);
Node *node;
while(!nodeQueue.empty()){
node = nodeQueue.front();
nodeQueue.pop();
printf(format, node->data);
if(node->lchild){
nodeQueue.push(node->lchild); //先將左子樹入隊
}
if(node->rchild){
nodeQueue.push(node->rchild); //再將右子樹入隊
}
}
}
/**
* <!--
* File : BinaryTreeSearch.h
* Author : fancy
* Email :
[email protected] * Date : 2013-02-03
* --!>
*/
#include "binarytree.h"
int main() {
//上圖所示的二叉樹先序遍歷序列,其中用'#'表示結點無左子樹或無右子樹
Element data[15] = {'A', 'B', 'D', '#', '#', 'E', '#', '#', 'C', 'F','#', '#', 'G', '#', '#'};
Tree tree;
treeNodeConstructor(tree, data);
printf("深度優先遍歷二叉樹結果: ");
depthFirstSearch(tree);
printf("\n\n廣度優先遍歷二叉樹結果: ");
breadthFirstSearch(tree);
return 0;
}

