A soldier wants to buy w bananas in the shop. He has to pay k dollars for the first banana, 2k dollars for the second one and so on (in other words, he has to pay i·k dollars for the i-th banana).
He has n dollars. How many dollars does he have to borrow from his friend soldier to buy w bananas?
InputThe first line contains three positive integers k, n, w (1 ≤ k, w ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ n ≤ 109), the cost of the first banana, initial number of dollars the soldier has and number of bananas he wants.
OutputOutput one integer — the amount of dollars that the soldier must borrow from his friend. If he doesn't have to borrow money, output 0.
Sample test(s) input3 17 4output
13
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <string.h>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 #define LL __int64
7 LL n,k,w;
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 int i;
12 LL sum = 0;
13 scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&k,&n,&w);
14 for(i = 1;i<=w;i++)
15 sum +=i*k;
16 if(n>=sum)
17 printf("0\n");
18 else
19 printf("%I64d\n",sum-n);
20
21 return 0;
22 }
Colonel has n badges. He wants to give one badge to every of his n soldiers. Each badge has a coolness factor, which shows how much it's owner reached. Coolness factor can be increased by one for the cost of one coin.
For every pair of soldiers one of them should get a badge with strictly higher factor than the second one. Exact values of their factors aren't important, they just need to have distinct factors.
Colonel knows, which soldier is supposed to get which badge initially, but there is a problem. Some of badges may have the same factor of coolness. Help him and calculate how much money has to be paid for making all badges have different factors of coolness.
InputFirst line of input consists of one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000).
Next line consists of n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ n), which stand for coolness factor of each badge.
OutputOutput single integer — minimum amount of coins the colonel has to pay.
Sample test(s) input4output
1 3 1 4
1input
5output
1 2 3 2 5
2Note
In first sample test we can increase factor of first badge by 1.
In second sample test we can increase factors of the second and the third badge by 1.
題意:給你n堆價值,要求得到每堆價值是獨一無二的,問你往每堆加多少,最少加多少。
思路:(貪心)先排序,然後以第一個為基准,後面的不大於前面的,就加加;
轉載請注明出處:尋找&星空の孩子
題目鏈接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/B
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <string>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <map>
8 #include <set>
9 #include <vector>
10 #include <math.h>
11 #include <bitset>
12 #include <list>
13 #include <algorithm>
14 #include <climits>
15 using namespace std;
16
17 #define lson 2*i
18 #define rson 2*i+1
19 #define LS l,mid,lson
20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson
21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
24 #define W(a) while(a)
25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
26 #define LL long long
27 #define N 5000005
28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
29 #define EXP 1e-8
30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
31 const int mod = 1e9+7;
32 #define LL __int64
33 int n,a[3005];
34 int main()
35 {
36 int i,j,ans;
37 while(~scanf("%d",&n))
38 {
39 ans = 0;
40 int sum1 = 0,sum2 = 0;
41 for(i = 1; i<=n; i++)
42 {
43 scanf("%d",&a[i]);
44 sum1+=a[i];
45 }
46 sort(a+1,a+1+n);
47 sum2 = a[1];
48 for(i = 2; i<=n; i++)
49 {
50 if(a[i] == a[i-1])
51 a[i]++;
52 else if(a[i]<a[i-1])
53 a[i] +=(a[i-1]-a[i])+1;
54 sum2+=a[i];
55 }
56 printf("%d\n",sum2-sum1);
57 }
58
59 return 0;
60 }
Two bored soldiers are playing card war. Their card deck consists of exactly n cards, numbered from 1 to n, all values are different. They divide cards between them in some manner, it's possible that they have different number of cards. Then they play a "war"-like card game.
The rules are following. On each turn a fight happens. Each of them picks card from the top of his stack and puts on the table. The one whose card value is bigger wins this fight and takes both cards from the table to the bottom of his stack. More precisely, he first takes his opponent's card and puts to the bottom of his stack, and then he puts his card to the bottom of his stack. If after some turn one of the player's stack becomes empty, he loses and the other one wins.
You have to calculate how many fights will happen and who will win the game, or state that game won't end.
InputFirst line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10), the number of cards.
Second line contains integer k1 (1 ≤ k1 ≤ n - 1), the number of the first soldier's cards. Then follow k1 integers that are the values on the first soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
Third line contains integer k2 (k1 + k2 = n), the number of the second soldier's cards. Then follow k2 integers that are the values on the second soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
All card values are different.
OutputIf somebody wins in this game, print 2 integers where the first one stands for the number of fights before end of game and the second one is 1 or 2 showing which player has won.
If the game won't end and will continue forever output - 1.
Sample test(s) input4output
2 1 3
2 4 2
6 2input
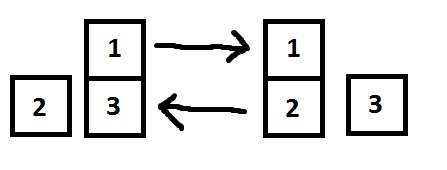
3output
1 2
2 1 3
-1Note
First sample:
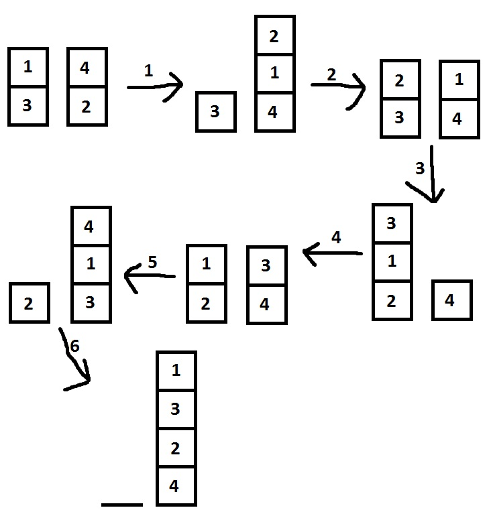
Second sample:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <string>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <map>
8 #include <set>
9 #include <vector>
10 #include <math.h>
11 #include <bitset>
12 #include <list>
13 #include <algorithm>
14 #include <climits>
15 using namespace std;
16
17 #define lson 2*i
18 #define rson 2*i+1
19 #define LS l,mid,lson
20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson
21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
24 #define W(a) while(a)
25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
26 #define LL long long
27 #define N 5000005
28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
29 #define EXP 1e-8
30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
31 const int mod = 1e9+7;
32
33 map<string,map<string,int> > vis;
34 int n;
35 int k1,k2;
36 int a[15],b[15],c[15];
37 char s1[15],s2[15];
38
39 int main()
40 {
41 int i,j,k;
42 scanf("%d",&n);
43 scanf("%d",&k1);
44 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
45 {
46 scanf("%d",&a[i]);
47 c[i] = a[i];
48 }
49 scanf("%d",&k2);
50 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
51 {
52 scanf("%d",&b[i]);
53 c[k1+i] = b[i];
54 }
55 sort(c,c+k1+k2);
56 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
57 {
58 for(j = 0; j<k1+k2; j++)
59 {
60 if(a[i]==c[j])
61 s1[i] = j+'0';
62 }
63 }
64 s1[k1] = '\0';
65 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
66 {
67 for(j = 0; j<k1+k2; j++)
68 {
69 if(b[i]==c[j])
70 s2[i] = j+'0';
71 }
72 }
73 s2[k2] = '\0';
74 vis[s1][s2] = 1;
75 int ans = 0;
76 while(k1&&k2)
77 {
78 int p1 = s1[0],p2 = s2[0];
79 // printf("[%d %d %d %d]\n",p1,p2,k1,k2);
80
81 /* printf("(1):");
82 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
83 printf("%c ",s1[i]);
84 printf("\n");
85 printf("(2):");
86 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
87 printf("%c ",s2[i]);
88 printf("\n");*/
89 if(p1>p2)
90 {
91 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
92 s2[i] = s2[i+1];
93 k2--;
94 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
95 s1[i] = s1[i+1];
96 s1[k1-1] = p2;
97 s1[k1] = p1;
98 k1++;
99 s2[k2] = s1[k1] = '\0';
100 }
101 else
102 {
103 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
104 s1[i] = s1[i+1];
105 k1--;
106 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
107 s2[i] = s2[i+1];
108 s2[k2-1] = p1;
109 s2[k2] = p2;
110 k2++;
111 s2[k2] = s1[k1] = '\0';
112 }
113 /* printf("(1):");
114 for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
115 printf("%c ",s1[i]);
116 printf("\n");
117 printf("(2):");
118 for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
119 printf("%c ",s2[i]);
120 printf("\n");*/
121 if(vis[s1][s2])
122 {
123 ans = -1;
124 break;
125 }
126 //printf("%d %d\n",k1,k2);
127 ans++;
128 vis[s1][s2] = 1;
129 }
130 printf("%d",ans);
131 if(ans!=-1)
132 {
133 if(k1)
134 printf(" 1");
135 else
136 printf(" 2");
137 }
138 printf("\n");
139
140 return 0;
141 }
Two soldiers are playing a game. At the beginning first of them chooses a positive integer n and gives it to the second soldier. Then the second one tries to make maximum possible number of rounds. Each round consists of choosing a positive integer x > 1, such that n is divisible by x and replacing n with n / x. When n becomes equal to 1 and there is no more possible valid moves the game is over and the score of the second soldier is equal to the number of rounds he performed.
To make the game more interesting, first soldier chooses n of form a! / b! for some positive integer a and b (a ≥ b). Here by k! we denote the factorial of k that is defined as a product of all positive integers not large than k.
What is the maximum possible score of the second soldier?
InputFirst line of input consists of single integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 1 000 000) denoting number of games soldiers play.
Then follow t lines, each contains pair of integers a and b (1 ≤ b ≤ a ≤ 5 000 000) defining the value of n for a game.
OutputFor each game output a maximum score that the second soldier can get.
Sample test(s) input2output
3 1
6 3
2
5
題意:n=a!/b!問你n的素數因子的個數。
思路:素數打表;
轉載請注明出處:尋找&星空の孩子
題目鏈接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/D
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <string>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <map>
8 #include <set>
9 #include <vector>
10 #include <math.h>
11 #include <bitset>
12 #include <list>
13 #include <algorithm>
14 #include <climits>
15 using namespace std;
16
17 #define lson 2*i
18 #define rson 2*i+1
19 #define LS l,mid,lson
20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson
21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
24 #define W(a) while(a)
25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
26 #define LL long long
27 #define N 5000005
28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
29 #define EXP 1e-8
30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
31 const int mod = 1e9+7;
32 int p[N];
33 int a[N];
34 int prime[700];
35 LL sum[N];
36 void init()
37 {
38
39 for(int i=0; i<700; ++i)
40 prime[i] = INF;
41 prime[0] = 2;
42 int num = 0;
43 for(int i=3; i<5005; ++i)
44 {
45 int x = 0;
46 while(i%prime[x] && prime[x] <= i) ++x;
47 if( !(i%prime[x]) )
48 a[i] = prime[x];
49 else
50 {
51 prime[++num] = i;
52 a[i] = i;
53 }
54 }
55 a[2] =2;
56 for(int i=5005; i< N; ++i)
57 {
58 int x = 0;
59 while(i%prime[x] && prime[x] <= i) ++x;
60 if( !(i%prime[x]) )
61 a[i] = prime[x];
62 else
63 a[i] = i;
64 }
65 p[2] = 1;
66 for(int i=3; i <N; ++i)
67 p[i] = p[i/a[i]] + 1;
68 }
69 int main()
70 {
71 int i,j,k;
72 init();
73 sum[1] = 0;
74 // printf("%d\n",p[4]);
75 for(i = 2; i<=5000000; i++)
76 {
77 sum[i] = sum[i-1]+p[i];
78 // printf("%d %I64d\n",i,sum[i]);
79 }
80 int t;
81 scanf("%d",&t);
82 while(t--)
83 {
84 scanf("%d%d",&i,&j);
85 // printf("%d %d %I64d %I64d\n",i,j+1,sum[i],sum[j+1]);
86 if(i == j)
87 printf("0\n");
88 else
89 printf("%I64d\n",sum[i]-sum[j]);
90 }
91
92 return 0;
93 }
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <string>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <map>
8 #include <set>
9 #include <vector>
10 #include <math.h>
11 #include <bitset>
12 #include <list>
13 #include <algorithm>
14 #include <climits>
15 using namespace std;
16
17 #define lson 2*i
18 #define rson 2*i+1
19 #define LS l,mid,lson
20 #define RS mid+1,r,rson
21 #define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
22 #define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
23 #define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
24 #define W(a) while(a)
25 #define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
26 #define LL long long
27 #define N 5000005
28 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
29 #define EXP 1e-8
30 #define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
31 const int mod = 1e9+7;
32 int p[N];
33 bool v[N];
34 int a[N];
35 int prime[N/10];
36 LL sum[N];
37 void init()
38 {
39 for(int i=2; i<N; ++i)
40 a[i] = i;
41 int num=-1;
42 for(int i=2; i<N; ++i)
43 {
44 if(!v[i]) prime[++num] = i;
45 for(int j=0; j<=num && i*prime[j] < N; ++j)
46 {
47 int t = i*prime[j];
48 v[t] =1;
49 if(a[t] > prime[j]) a[t] = prime[j];
50 if(i%prime[j] == 0) break;
51 }
52 }
53 p[2] = 1;
54 for(int i=3; i <N; ++i)
55 p[i] = p[i/a[i]] + 1;
56 }
57 int main()
58 {
59 int i,j,k;
60 init();
61 sum[1] = 0;
62 for(i = 2; i<=5000000; i++)
63 {
64 sum[i] = sum[i-1]+p[i];
65 }
66 int t;
67 scanf("%d",&t);
68 while(t--)
69 {
70 scanf("%d%d",&i,&j);
71 if(i == j)
72 printf("0\n");
73 else
74 printf("%I64d\n",sum[i]-sum[j]);
75 }
76
77 return 0;
78 }
In the country there are n cities and m bidirectional roads between them. Each city has an army. Army of the i-th city consists of aisoldiers. Now soldiers roam. After roaming each soldier has to either stay in his city or to go to the one of neighboring cities by at moving along at most one road.
Check if is it possible that after roaming there will be exactly bi soldiers in the i-th city.
InputFirst line of input consists of two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 0 ≤ m ≤ 200).
Next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100).
Next line contains n integers b1, b2, ..., bn (0 ≤ bi ≤ 100).
Then m lines follow, each of them consists of two integers p and q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ n, p ≠ q) denoting that there is an undirected road between cities p and q.
It is guaranteed that there is at most one road between each pair of cities.
OutputIf the conditions can not be met output single word "NO".
Otherwise output word "YES" and then n lines, each of them consisting of n integers. Number in the i-th line in the j-th column should denote how many soldiers should road from city i to city j (if i ≠ j) or how many soldiers should stay in city i (if i = j).
If there are several possible answers you may output any of them.
Sample test(s) input4 4output
1 2 6 3
3 5 3 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 2
YESinput
1 0 0 0
2 0 0 0
0 5 1 0
0 0 2 1
2 0output
1 2
2 1
NO
題意:給你一張無向圖,每個點有一定數量的人,通過移動可以去鄰接點(但是只能移動一次)問你是否能從初始狀態移動到目標狀態;
思路:網絡流+最大流;
轉載請注明出處:尋找&星空の孩子
題目鏈接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/E
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<string.h>
3 #include<queue>
4 #include<algorithm>
5 using namespace std;
6 #define captype int
7
8 const int MAXN = 510; //點的總數
9 const int MAXM = 400010; //邊的總數
10 const int INF = 1<<30;
11 struct EDG{
12 int to,next;
13 captype cap,flow;
14 } edg[MAXM];
15 int eid,head[MAXN];
16 int gap[MAXN]; //每種距離(或可認為是高度)點的個數
17 int dis[MAXN]; //每個點到終點eNode 的最短距離
18 int cur[MAXN]; //cur[u] 表示從u點出發可流經 cur[u] 號邊
19 int pre[MAXN];
20 int mapt[105][105];
21
22 void init(){
23 eid=0;
24 memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
25 memset(mapt,0,sizeof(mapt));
26 }
27 //有向邊 三個參數,無向邊4個參數
28 void addEdg(int u,int v,captype c,captype rc=0){
29 edg[eid].to=v; edg[eid].next=head[u];
30 edg[eid].cap=c; edg[eid].flow=0; head[u]=eid++;
31
32 edg[eid].to=u; edg[eid].next=head[v];
33 edg[eid].cap=rc; edg[eid].flow=0; head[v]=eid++;
34 }
35 captype maxFlow_sap(int sNode,int eNode, int n){//n是包括源點和匯點的總點個數,這個一定要注意
36 memset(gap,0,sizeof(gap));
37 memset(dis,0,sizeof(dis));
38 memcpy(cur,head,sizeof(head));
39 pre[sNode] = -1;
40 gap[0]=n;
41 captype ans=0; //最大流
42 int u=sNode;
43 while(dis[sNode]<n){ //判斷從sNode點有沒有流向下一個相鄰的點
44 if(u==eNode){ //找到一條可增流的路
45 captype Min=INF ;
46 int inser;
47 for(int i=pre[u]; i!=-1; i=pre[edg[i^1].to]) //從這條可增流的路找到最多可增的流量Min
48 if(Min>edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow){
49 Min=edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow;
50 inser=i;
51 }
52 for(int i=pre[u]; i!=-1; i=pre[edg[i^1].to]){
53
54 edg[i].flow+=Min;
55 edg[i^1].flow-=Min; //可回流的邊的流量
56
57 if(edg[i].to==eNode||edg[i].to==sNode||edg[i^1].to==eNode||edg[i^1].to==sNode)
58 continue;
59 if(edg[i].cap>0){
60 int tu, tv;
61 tu=edg[i^1].to; tv=edg[i].to-(n-1)/2;
62 mapt[tu][tv]+=Min;
63 }
64 else{
65 int tu, tv;
66 tu=edg[i].to; tv=edg[i^1].to-(n-1)/2;
67 mapt[tu][tv]-=Min;
68 }
69
70 }
71 ans+=Min;
72 u=edg[inser^1].to;
73 continue;
74 }
75 bool flag = false; //判斷能否從u點出發可往相鄰點流
76 int v;
77 for(int i=cur[u]; i!=-1; i=edg[i].next){
78 v=edg[i].to;
79 if(edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow>0 && dis[u]==dis[v]+1){
80 flag=true;
81 cur[u]=pre[v]=i;
82 break;
83 }
84 }
85 if(flag){
86 u=v;
87 continue;
88 }
89 //如果上面沒有找到一個可流的相鄰點,則改變出發點u的距離(也可認為是高度)為相鄰可流點的最小距離+1
90 int Mind= n;
91 for(int i=head[u]; i!=-1; i=edg[i].next)
92 if(edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow>0 && Mind>dis[edg[i].to]){
93 Mind=dis[edg[i].to];
94 cur[u]=i;
95 }
96 gap[dis[u]]--;
97 if(gap[dis[u]]==0) return ans; //當dis[u]這種距離的點沒有了,也就不可能從源點出發找到一條增廣流路徑
98 //因為匯點到當前點的距離只有一種,那麼從源點到匯點必然經過當前點,然而當前點又沒能找到可流向的點,那麼必然斷流
99 dis[u]=Mind+1;//如果找到一個可流的相鄰點,則距離為相鄰點距離+1,如果找不到,則為n+1
100 gap[dis[u]]++;
101 if(u!=sNode) u=edg[pre[u]^1].to; //退一條邊
102 }
103 return ans;
104 }
105 int main(){
106 int n,m ,s , t , u,v,c[105],tc;
107 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>0){
108 init();
109 s=0;
110 t=2*n+1;
111 int ans=0;
112 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
113 scanf("%d",&c[i]);
114 ans+=c[i];
115 addEdg(s,i,c[i]);
116 addEdg(i,i+n,c[i]);
117 }
118 int sum=0;
119 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
120 {
121 scanf("%d",&tc); sum+=tc;
122 addEdg(i+n,t,tc);
123 }
124 while(m--){
125 scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
126 addEdg(u,v+n,c[u]);
127 addEdg(v,u+n,c[v]);
128 }
129 if(ans!=sum){
130 printf("NO\n"); continue;
131 }
132 ans -= maxFlow_sap(s,t,t+1);
133 if(ans==0){
134 printf("YES\n");
135 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
136 for(int j=1; j<n; j++)
137 printf("%d ",mapt[i][j]);
138 printf("%d\n",mapt[i][n]);
139 }
140 }
141 else
142 printf("NO\n");
143 }
144 }