Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in-place, do not allocate extra memory.
Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.
1,2,3 → 1,3,2
3,2,1 → 1,2,3
1,1,5 → 1,5,1
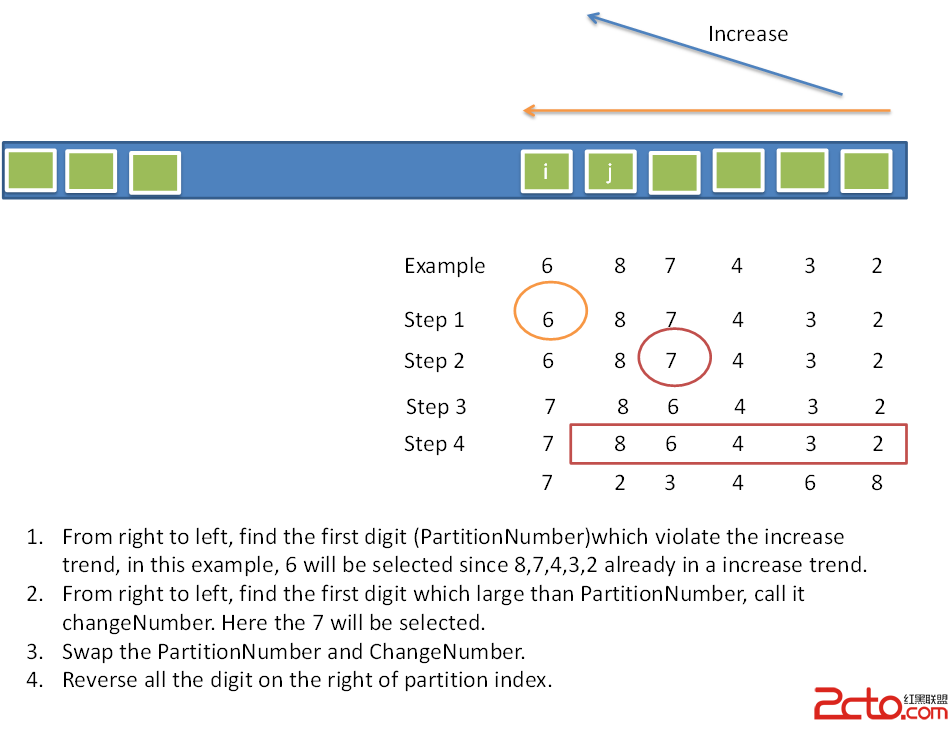
首先需要理解題目的意思:
rearranges 重新排列;permutation 排列;ascending order 升序
求當前排列的下一個排列:
所謂一個排列的下一個排列的意思就是 這一個排列與下一個排列之間沒有其他的排列。
這就要求這一個排列與下一個排列有盡可能長的共同前綴,也即變化限制在盡可能短的後綴上。
//rearranges 重新排列;permutation 排列;ascending order 升序
//所謂一個排列的下一個排列的意思就是 這一個排列與下一個排列之間沒有其他的排列。
//這就要求這一個排列與下一個排列有盡可能長的共同前綴,也即變化限制在盡可能短的後綴上。
// 最差時間復雜度 O(n^2) 空間復雜度 0
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector& nums) {
if (nums.size() == 0)
return;
int k = nums.size()-1;
int last = k;
while (k) {
if (nums[k-1] < nums[k]) {
while (nums[k-1] >= nums[last]) {
last--; //從後往前找(也可從前往後)
}
swap(nums[k-1], nums[last]);
break;
} else {
k--;
}
}
sort(nums.begin()+k, nums.end());
}
private:
void swap(int &a, int &b) {
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
};