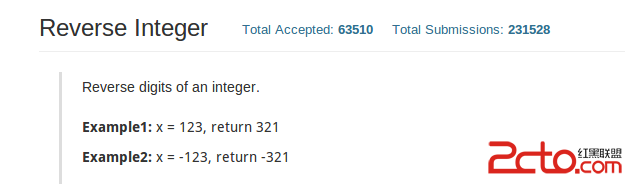
LeetCode #Reverse Number#
剛背了單詞,然後做個題玩玩~挑個軟柿子踩踩~哈哈
很簡單的思路.不過好玩的是我忘記檢查處理完的數據是否符合整形數據返回了.因而好一會兒不能AC.
感謝 @Fantasy. 很快的指出我沒有檢查返回數據的范圍.
先給出我超丑陋的解(python), 而後給出其他高手給出的很優雅的解!!也是用python
最後會給出利用java和C/C++的解.
Programmer : EOF
Date : 2015.03.31
File : reverse_interger.py
class Solution:
# @return an integer
def reverse(self, x):
buffer =[]
INT_MAX = 0x7fffffff
INT_MIN = (-INT_MAX - 1)
if x > INT_MAX or x < INT_MIN :
return 0
if x > 0 :
tmp = x
counter = 1
while tmp > 0 :
counter += 1
buffer.append(tmp % 10);
tmp /= 10
tmp = 0
for i in range(0, len(buffer)) :
tmp *= 10
tmp += buffer[i]
if tmp > INT_MAX or tmp < INT_MIN :
return 0
return tmp
elif x < 0 :
tmp = -x
counter = 1
while tmp > 0 :
counter += 1
buffer.append(tmp % 10);
tmp /= 10
tmp = 0
for i in range(0, len(buffer)) :
tmp *= 10
tmp += buffer[i]
if tmp > INT_MAX or tmp < INT_MIN :
return 0
return -tmp
else:
return 0
#--------------------------just for testing ----------------------------
s = Solution()
print s.reverse(123)
... 確實好搓就很簡單做一下很基礎的數學運算,利用余數和商的特性,把結果保存在list中.而後逆序的組合成整數,最後別忘記重新檢查整數是否符合要求,是否越界!!
下面給出別人很優雅的解:
class Solution:
# @return an integer
def reverse(self, x):
if x<0:
sign = -1
else:
sign = 1
strx=str(abs(x))
r = strx[::-1]
return sign*int(r)
先強轉成字符串,而後在利用python切片的技巧,逆序輸出字符,然後再int()強轉,限定好整數范圍.
最後恢復數據的符號.
java解(來源於@凱旋沖鋒):利用了內置整形的特性
package reverse_integer;
public class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
long r = 0;
while (x != 0) {
r = r * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return r > Integer.MAX_VALUE || r < Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : (int) r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new Solution().reverse(1563847412));
}
}
最後獻上皓神的解答,C語言實現.
自己抽自己一巴掌,擦,居然沒看清楚皓神寫的注釋!!
Did you notice that the reversed integer might overflow? Assume the input is a 32-bit integer,
// Source : https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer/ // Author : Hao Chen // Date : 2014-06-18 /********************************************************************************** * * Reverse digits of an integer. * * Example1: x = 123, return 321 * Example2: x = -123, return -321 * * * Have you thought about this? * * Here are some good questions to ask before coding. Bonus points for you if you have already thought through this! * * > If the integer's last digit is 0, what should the output be? ie, cases such as 10, 100. * * > Did you notice that the reversed integer might overflow? Assume the input is a 32-bit integer, * then the reverse of 1000000003 overflows. How should you handle such cases? * * > Throw an exception? Good, but what if throwing an exception is not an option? * You would then have to re-design the function (ie, add an extra parameter). * * **********************************************************************************/ #include#include //Why need the INT_MIN be defined like that? //Please take a look: // http://stackoverflow.com/questions/14695118/2147483648-0-returns-true-in-c #define INT_MAX 2147483647 #define INT_MIN (-INT_MAX - 1) int reverse(int x) { int y=0; int n; while( x != 0){ n = x%10; //Checking the over/underflow. //Actually, it should be y>(INT_MAX-n)/10, but n/10 is 0, so omit it. if (y > INT_MAX/10 || y < INT_MIN/10){ return 0; } y = y*10 + n; x /= 10; } return y; } #define TEST(n, e) printf(%12d => %-12d %s! , n, reverse(n), e == reverse(n)?passed:failed) int main(int argc, char**argv) { //basic cases TEST( 123, 321); TEST( -123, -321); TEST( -100, -1); TEST( 1002, 2001); //big integer TEST( 1463847412, 2147483641); TEST(-2147447412, -2147447412); TEST( 2147447412, 2147447412); //overflow TEST( 1000000003, 0); TEST( 2147483647, 0); TEST(-2147483648, 0); //customized cases if (argc<2){ return 0; } printf( ); for (int i=1; i %-12d %s! , n, reverse(n), reverse(reverse(n))==n ? passed:failed); } return 0; }