本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes/p/cpp-primer-chapter1-ans.html,轉載請注明源地址。
【習題 1.3】
編一個程序,在標准輸出上打印“Hello, World”。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"Hello, World\n";
return 0;
}
【習題 1.4】
我們的程序利用內置加法操作符“+”來產生兩個數的和。編寫程序,使用乘法操作符“*”產生兩個數的積。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
cout<<"Enter two numbers: "<<endl;
int v1, v2;
cin>>v1>>v2;
cout<<"The product of"<<v1<<" and "<<v2<<" is "<<v1 * v2<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
【習題 1.5】
我們的程序使用了一條較長的輸出語句。重寫程序,使用單獨的語句打印每一個操作數。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
cout<<"Enter two numbers: "<<endl;
int v1, v2;
cin>>v1>>v2;
cout<<"The sum of";
cout<<v1;
cout<<" and ";
cout<<v2;
cout<<" is ";
cout<<v1 + v2;
cout<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
【習題 1.10】
用 for 循環編程,求從 50~100 的所有自然數的和。然後用 while 循環重寫該程序。
用for循環:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int i, sum=0;
for(i=50; i<=100; ++i)
sum+=i;
cout<<"sum of 50 to 100 is "<<sum<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
用 while 循環:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int i, sum;
i=50;
sum=0;
while(i++<=100)
sum+=i;
cout<<"sum of 50 to 100 is "<<sum<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return
【習題 1.11】
用 while 循環編程,輸出 10~0 遞減的自然數。然後用 for循環重寫該程序。
用 while 循環:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int i=10;
while(i>=0)
cout<<i--<<endl;
return 0;
}
用 for循環:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
for(int i=10; i >=0; --i)
cout<<i<<endl;
return 0;
}
【習題 1.16】
編寫程序,輸出用戶輸入的兩個數中的較大者。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a, b;
cout<<"請輸入兩個數: ";
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<"較大的一個數是: "<< ((a >= b)? a : b)<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
【習題 1.17】
編寫程序,要求用戶輸入一組數。輸出信息說明其中有多少個負數
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int num, a;
num=0;
while(cin>>a)
if(a < 0) num++;
cout<<"輸入的負數數量為: "<<num<<endl;
return 0;
}
【習題 1.18】
編寫程序,提示用戶輸入兩個數幵將這兩個數范圍內的每個數寫到標准輸出。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(int a, int b)
{
a++;
while(a < b)
cout<<a++<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
int main( )
{
int a,b,i;
cout<<"請輸入兩個數: ";
cin>>a>>b;
if(a < b)
print(a,b);
else
print(b,a);
return 0;
}
【習題 1.21】
本書配套網站(http://www.awprofessional.com/cpp_primer)的第1章的代碼目錄下有 Sales_ item.h 源文件。復制該文件到你的工作目錄。編寫程序,循環遍歷一組書的銷售交易, 讀入每筆交易幵將交易寫至標准輸出。
#include <iostream>
#include "Sales_item.h"
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
Sales_item book;
cout<<"輸入交易:"<<endl;
while(cin>>book) {
cout<<"售出書的本數、總收入、平均價格:"
<<endl;
cout<<book<<endl;
}
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
附上 Sales_ item.h 源文件:
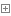
【習題 1.22】
編寫程序,讀入兩個具有相同 ISBN 的 Sales_item 對象幵產生它們的和。
#include <iostream>
#include "Sales_item.h"
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
Sales_item trans1, trans2;
cout<<"讀入交易:"<<endl;
cin>>trans1>>trans2;
if(trans1.same_isbn(trans2))
cout<<"兩筆交易具有相同的ISBN,和為:"<<endl<<trans1 + trans2;
else
cout<<"兩筆交易沒有相同的ISBN";
return 0;
}
【習題 1.23】
編寫程序,讀入幾個具有相同 ISBN 的交易,輸出所有讀入交易的和。
#include <iostream>
#include "Sales_item.h"
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
Sales_item sum, trans;
cout<<"讀入交易:"<<endl;
if(cin>>sum) {
while(cin>>trans) {
if(sum.same_isbn(trans))
sum += trans;
else {
cout<<"不同的ISBN!"<<endl;
return -1;
}
}
} else {
cout<<"no data!"<<endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
【習題 1.24】
編寫程序,讀入幾筆不同的交易。對於每筆新讀入的交易,要確定它的 ISBN 是否和以前的交易的 ISBN 一樣,並且記下每一個 ISBN 的交易的總數。
通過給定多筆不同的交易來測試程序。這些交易必須代表多個不同的 ISBN,但是每個ISBN 的記錄應分在同一組。
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include "Sales_item.h"
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
Sales_item trans;
cout<<"讀入交易:"<<endl;
cin>>trans;
map<string, int> count;
count[trans.getIsbn()]++;
while(cin>>trans) {
++count[trans.getIsbn()];
}
map<string, int>::iterator it;
for(it=count.begin(); it!=count.end(); it++)
cout<<it->first<<":"<<it->second<<endl;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}