UVa1635 - Irrelevant Elements(質因數分解)
Young cryptoanalyst Georgie is investigating different schemes of generating random integer numbers
ranging from 0 to
m - 1.
He thinks that standard random number generators are not good enough, so he has invented his own scheme that is intended to bring more randomness into the generated numbers. First, Georgie chooses
n and
generates
n random integer numbers ranging from 0 to
m -
1. Let the numbers generated be
a1,
a2,...,
an.
After that Georgie calculates the sums of all pairs of adjacent numbers, and replaces the initial array with the array of sums, thus getting
n - 1 numbers:
a1 +
a2,
a2 +
a3,...,
an
- 1 +
an. Then he applies the same procedure to the new array, getting
n - 2 numbers.
The procedure is repeated until only one number is left. This number is then taken modulo
m. That gives the result of the
generating procedure. Georgie has proudly presented this scheme to his computer science teacher, but was pointed out that the scheme has many drawbacks. One important drawback is the fact that the result of the procedure sometimes does not even depend on some
of the initially generated numbers. For example, if
n = 3 and
m =
2, then the result does not depend on
a2. Now Georgie wants
to investigate this phenomenon. He calls the
i-th element of the initial array irrelevant if
the result of the generating procedure does not depend on
ai. He considers various
n and
m and
wonders which elements are irrelevant for these parameters. Help him to find it out.
Input
Input file contains several datasets. Each datasets has
n and
m ( 1
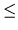 n
n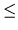
100 000, 2
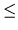 m
m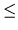
10
9)
in a single line.
Output
On the first line of the output for each dataset print the number of irrelevant elements of the initial array for given
n and
m.
On the second line print all such
ithat
i-th
element is irrelevant. Numbers on the second line must be printed in the ascending order and must be separated by spaces.
Sample Input
3 2
Sample Output
1
2
題意:整個式子的和可以 化簡為 sigma (C(n-1,i-1)*ai)
思路:只要判斷C(n-1,i-1)能否被 m整除即可。
做法是先分解m的質因數,然後計算1!~(n-1)! 包含m的質因數的個數
C(n-1,i-1) = (n-1)!/((i-1)!*(n-i)!)
只要判斷 剩下的質因數的個數是否大於等於m的任一個質因數的個數即可
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxp = 40000+10;
const int maxn = 100000+10;
int n,m;
bool isPrime[maxp];
vector ret,prime,hp,cnt,tmp;
vector g[maxn];
void getPrime(){
memset(isPrime,true,sizeof isPrime);
for(int i = 2; i < maxp; i++){
if(isPrime[i]){
prime.push_back(i);
for(int j = i+i;j < maxp; j += i){
isPrime[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
void getDigit(){
int tk = m;
for(int i = 0; i < prime.size() && prime[i]*prime[i] <= tk; i++){
if(tk%prime[i]==0){
int k = 0;
hp.push_back(prime[i]);
while(tk%prime[i]==0){
tk /= prime[i];
k++;
}
cnt.push_back(k);
}
}
if(tk>1){
hp.push_back(tk);
cnt.push_back(1);
}
}
void init(){
cnt.clear();
hp.clear();
ret.clear();
getDigit();
for(int i = 0; i <= n-1; i++) g[i].clear();
for(int i = 0; i <= n-1; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < hp.size(); j++){
int d = 0,t = i;
while(t) {
d += t/hp[j];
t /= hp[j];
}
g[i].push_back(d);
}
}
}
void solve(){
bool miden = false;
for(int i = 2; i <= (n-1)/2+1; i++){
bool flag = true;
for(int j = 0; j < hp.size(); j++){
int d = g[n-1][j]-g[i-1][j]-g[n-i][j];
if(d < cnt[j]){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
ret.push_back(i);
if(i==(n-1)/2+1 && (n&1)) miden = true;
}
}
tmp.clear();
tmp = ret;
if(n&1){
int i;
if(miden) i = tmp.size()-2;
else i = tmp.size()-1;
for(; i >= 0; i--){
ret.push_back(n+1-tmp[i]);
}
}else{
for(int i = tmp.size()-1; i >= 0; i--){
ret.push_back(n+1-tmp[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n",ret.size());
if(ret.size()){
printf("%d",ret[0]);
for(int i = 1; i < ret.size(); i++){
printf(" %d",ret[i]);
}
}
puts("");
}
int main(){
//freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
getPrime();
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){
init();
solve();
}
return 0;
}