1.Array.h,Array<T>的定義
template <class T>
class Array
{
protected:
T *data; //一個指向數組數據的指針
unsigned int base; //base為數組的起始下表
unsigned int length; //length為數組的長度
public:
Array(); //缺省的構造函數
Array(unsigned int, unsigned int = 0); //數組構造函數
~Array(); //析構函數
Array(Array const&); //拷貝構造函數
Array& operator = (Array const&); //重載等號操作符,用於一個數組給另外一個數組賦值
T const& operator [] (unsigned int) const; //重載中括號操作符,返回一個T數值常量,返回值不能被改變,在函數末尾加const表示this指針指向const
T& operator [] (unsigned int); //重載中括號操作符,返回一個T數值常量,其返回值可以被改變
T* Data() const; //返回數組數據的指針data
unsigned int Base() const; //返回成員base
unsigned int Length() const; //返回成員length
void SetBase(unsigned int); //設置成員變量base的數值
void SetLength(unsigned int); //設置成員變量length的數值
};
//動態數組所占空間S(n)=sizeof(T*)+2sizeof(unsigned int)+nsizeof(T),假定T類型所占用空間為一個常數,故S(n)=O(n)
2.Array<T>中成員函數的實現
#include "Array.h"
template <class T>
Array<T>::Array() :
data(new T[10]),
base(0),
length(0)
{}
//缺省的構造函數不含變量,只需要給對象的變量一個初始值,時間復雜度O(1)
template <class T>
Array<T>::Array(unsigned int n, unsigned int m) :
data(new T[n]),
base(m),
length(n)
{}
//初始化數組,n為數組的長度,時間復雜度常量O(1)
template <class T>
Array<T>::Array(Array<T> const& array) :
data(new T[array.length]),
base(array.base),
length(array.length)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
data[i] = array.data[i];
}
//備份構造函數,將一個數組從賦值到另外一個數組,時間復雜度為O(n)
template <class T>
Array<T>::~Array()
{
delete[] data;
}
//析構函數,刪除數組所占用的內存空間
template <class T>
T* Array<T>::Data() const
{
return data;
}
template <class T>
unsigned int Array<T>::Base() const
{
return base;
}
template <class T>
unsigned int Array<T>::Length() const
{
return length;
}
//這三個為存取器函數,用來返回成員,時間復雜度都為O(1)
template <class T>
T const& Array<T>::operator[] (unsigned int position) const
{
unsigned int const offset = position - base;
if (offset >= length)
throw out_of_range("invalid position");
return data[offset];
}
template <class T>
T& Array<T>::operator[] (unsigned int position)
{
unsigned int const offset = position - base;
if (offset >= length)
throw out_of_range("invalid position");
return data[offset];
}
//這兩個都為取下表操作符的重載,區別是第一個返回值不可以作為左值,第二個返回值可以作為左值,時間復雜度都為O(1)
template <class T>
void Array<T>::SetBase(unsigned int newBase)
{
base = newBase;
}
template <class T>
void Array<T>::SetLength(unsigned int newLength)
{
T* const newData = new T[newLength];
unsigned int const min = length < newLength ? length : newLength;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < min; ++i)
newData[i] = data[i];
delete[] data;
data = newData;
length = newLength;
}
//這兩個函數來重設對象的成員,時間復雜度為T(m,n)=min(m,n)*T(T::T(T&))+O(1)
template <class T>
Array<T>& Array<T>::operator = (Array<T> const& array)
{
if (this != &array)
{
delete[] data;
base = array.base;
length = array.length;
data = new T[length];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
data[i] = array.data[i];
}
return this;
}
//重載賦值操作符,時間復雜度為O(n)
3.測試主函數main.cpp
#include "Array.cpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T> void Output(Array<T> array);
template <class T>
void Output(Array<T> array)
{
cout << "data:";
for (unsigned int i = array.Base(); i < array.Length(); i++)
{
cout << array.Data()[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "length:" << array.Length()<<endl;
cout << "base:" << array.Base() <<endl;
}
int main()
{
cout << "Array()正在執行。。。" << endl;
Array<int> array0 = Array<int>();
Output(array0);
cout << "Array(unsigned int, unsigned int = 0)正在執行。。。" << endl;
Array<int> array1 = Array<int>(10);
Output(array1);
cout << "Array(Array const&)正在執行。。。" << endl;
Array<int> array2(array1);
Output(array2);
cout << "~Array()正在執行。。。" << endl;
array2.~Array();
Output(array2);
cout << "T const* Data() const,unsigned int Base() const,unsigned int Length() const,"
<< "T const& operator [] (unsigned int) const在Output函數中執行。。。" << endl;
cout << "T& operator [] (unsigned int)正在執行。。。" << endl;
Array<int> array3(10);
for (unsigned int i = array1.Base(); i < array1.Length() - array1.Base(); i++)
{
array3.Data()[i] = i;
}
Output(array3);
cout << "void SetBase(unsigned int)正在執行。。。" << endl;
array3.SetBase(2);
Output(array3);
cout << "void SetLength(unsigned int)正在執行。。。" << endl;
array3.SetLength(7);
Output(array3);
getchar();
return 0;
}
4.測試結果
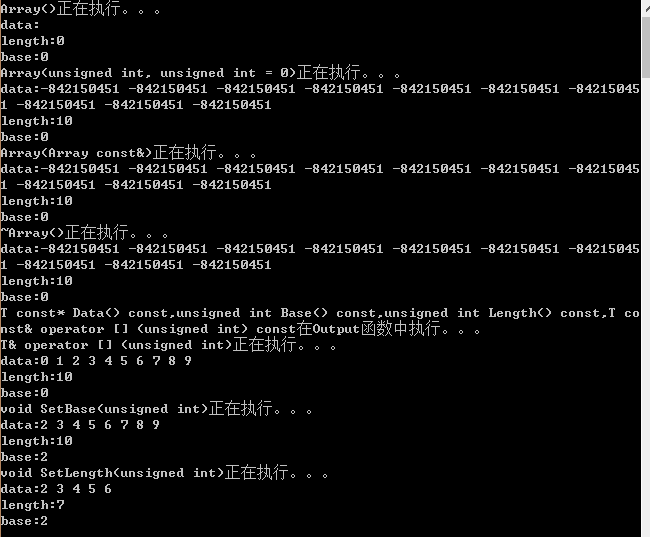
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node//循環節點的定義
{
int number;//編號
Node *next;
};
Node *CreateList(Node *L,int &n,int &m);//建立約瑟夫環函數
void Joseph(Node *L,int n,int m);//輸出每次出列號數函數
Node *DeleteList(Node **L,int i,Node *q);//尋找每次出列人的號數
int LengthList(Node *L);//計算環上所有人數函數
void main()//主函數
{
Node *L;
L=NULL;//初始化尾指針
int n, m;
cout<<"請輸入人數N:";
cin>>n;//環的長度
if(n<1){cout<<"請輸入正整數!";}//人數異常處理
else
{
cout<<"請輸入所報數M:";
cin>>m;
if(m<1){cout<<"請輸入正整數!";}//號數異常處理
else
{
L=CreateList(L,n,m);//重新給尾指針賦值
Joseph(L,n,m);
}
}
system("pause");
}
Node *CreateList(Node *L,int &n,int &m)//建立一個約瑟夫環(尾插法)
{
Node *q;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
Node *p;
p=new Node;
p->number=i;
p->next=NULL;
if(i==1) L=q=p;//工作指針的初始化
else
{
q->next=p;
q=q->next;
}
}
q->next=L;
if(L!=NULL){return(L);}//返回尾指針
else cout<<"尾指針異常!"<<endl;//尾指針異常處理
}
void Joseph(Node *L,int n,int m)//輸出每次出列的人
{
int k;
cout<<"請輸入第一個報數人:";
cin>>k;
if(k<1||k>n){cout<<"請輸入1-"<<n<<"之間的數"<<endl;}
else
{
cout<<"\n出列順序:\n";
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
Node *q = new Node;
if(i==1) q=DeleteList(&L,k+m-1,q);//第一個出列人的號數
else q=DeleteList(&L,m,q);
cout<<&quo......余下全文>>
B。。。
首先:棧是不可能的,棧是先進後出,沒法子任意插入和刪除
鏈表的話比較低效
靜態數組的話插入刪除的話需要移動其他位置數據
所以我個人覺得應該選B