Description
The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the mayoral election campaign have been placing their electoral posters at all places at their whim. The city council has finally decided to build an electoral wall for placing the posters and introduce the following rules:Input
The first line of input contains a number c giving the number of cases that follow. The first line of data for a single case contains number 1 <= n <= 10000. The subsequent n lines describe the posters in the order in which they were placed. The i-th line among the n lines contains two integer numbers li and ri which are the number of the wall segment occupied by the left end and the right end of the i-th poster, respectively. We know that for each 1 <= i <= n, 1 <= li <= ri <= 10000000. After the i-th poster is placed, it entirely covers all wall segments numbered li, li+1 ,... , ri.Output
For each input data set print the number of visible posters after all the posters are placed.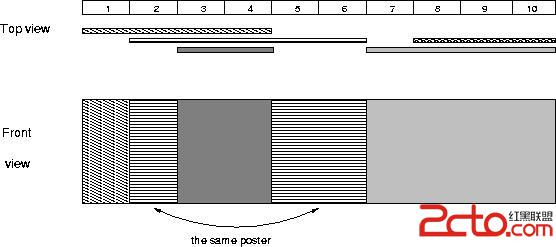
Sample Input
1 5 1 4 2 6 8 10 3 4 7 10
Sample Output
4
題意:給出一面牆,給出n張海報貼在牆上,每張海報都覆蓋一個范圍,問最後可以看到多少張海報
海報覆蓋的范圍很大,直接使用數組存不下,但是只有最多10000張海報,也就是說最多出現20000個點,所以可以使用離散化,將每個點離散後,重新對給出控制的區間,這樣區間最大就是1到20000.可以直接使用線段樹,成段更新,每次更新一個顏色,最後遍歷所有的段,將還可以遍歷的顏色儲存,統計
將-1 定義為沒有顏色,0代表有多種顏色,1到m代表各自的顏色,線段樹只要在0時向下深入,其他的直接統計顏色。
但是這個題中的離散化有問題,會擠掉中間的顏色,不過poj好像也是這麼做的,沒有考慮中間的顏色。
如 1 ,10 1,4 7,10 這三組數的正確結果應該是還可以看到3種顏色,但是如果直接排列點的話就會擠掉5到6這一種顏色。
真正的這種成段的離散化,一定要將兩個節點中還有值的話,要多加一個節點,代表兩個節點中間的值。
#include#include #include using namespace std; #define maxn 30000 #define lmin 1 #define rmax n #define lson l,(l+r)/2,rt<<1 #define rson (l+r)/2+1,r,rt<<1|1 #define root lmin,rmax,1 #define now l,r,rt #define int_now int l,int r,int rt int cl[maxn<<2] , lazy[maxn<<2] , a[maxn] ; struct node{ int id1 , id2 , k ; }p[maxn]; bool cmp(node a,node b) { return a.k < b.k ; } void push_up(int_now) { if( !cl[rt<<1] || !cl[rt<<1|1] || cl[rt<<1] != cl[rt<<1|1] ) cl[rt] = 0 ; else cl[rt] = cl[rt<<1|1] ; } void push_down(int_now) { if( lazy[rt] != -1 ) { lazy[rt<<1] = lazy[rt<<1|1] = lazy[rt] ; cl[rt<<1] = cl[rt<<1|1] = lazy[rt] ; lazy[rt] = -1 ; } } void update(int ll,int rr,int x,int_now) { if( ll > r || rr < l ) return ; if( ll <= l && r <= rr ) { cl[rt] = lazy[rt] = x ; return ; } push_down(now); update(ll,rr,x,lson); update(ll,rr,x,rson); push_up(now); } void query(int ll,int rr,int_now,int *a) { if( cl[rt] == -1 ) return ; else if(cl[rt] > 0) { a[ cl[rt] ] = 1 ; return ; } push_down(now); query(ll,rr,lson,a); query(ll,rr,rson,a); } int main() { int t , i , n , m , l , r , x ; scanf("%d", &t); while(t--) { scanf("%d", &m); for(i = 0 ; i < m ; i++) { scanf("%d %d", &p[i].k, &p[i+m].k); p[i].id1 = i ; p[i+m].id1 = i+m ; } sort(p,p+2*m,cmp); int temp = -1 ; n = 0 ; for(i = 0 ; i < 2*m ; i++) { if( p[i].k == temp ) p[i].id2 = n ; else { p[i].id2 = ++n ; temp = p[i].k ; } a[ p[i].id1 ] = p[i].id2 ; } memset(cl,-1,sizeof(cl)); memset(lazy,-1,sizeof(lazy)); for(i = 0 ; i < m ; i++) { update(a[i],a[i+m],i+1,root); } memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); query(1,n,root,a); int num = 0; for(i = 1 ; i <= m ; i++) if(a[i]) num++ ; printf("%d\n", num); } return 0; }