1 #include<stdlib.h>
2 #include<iostream>
3 #include<stdio.h>
4 #include<string>
5 using namespace std;
6 typedef struct Node{
7 int data;
8 struct Node* next;
9 struct Node* pre;
10 }dnode;
11
12 dnode *create()
13 {
14 dnode*head,*p,*s;
15 int x,cycle=1;
16 head=(dnode*)malloc(sizeof(dnode));
17 p=head;
18 cout<<"\nPlease input the data:"<<endl;
19 while(cycle)
20 {
21 cin>>x;
22 if(x!=0)
23 {
24 s=(dnode*)malloc(sizeof(dnode));
25 s->data=x;
26 p->next=s;
27 s->pre=p;
28 p=s;
29 }
30 else cycle=0;
31 }
32 head=head->next;
33 head->pre=NULL;
34 p->next=NULL;
35 cout<<"\nThe head data is"<<head->data<<endl;
36 return head;
37 }
38
39 dnode* del(dnode* head,int num)
40 {
41 dnode *p1,*p2;
42 p1=head;
43 while(num!=p1->data&&p1->next!=NULL)
44 {
45 p1=p1->next;
46 }
47 if(num==p1->data)
48 {
49 if(p1==head)
50 {
51 head=head->next;
52 head->pre=NULL;
53 free(p1);
54 }
55 else if(p1->next==NULL)
56 {
57 p1->pre->next=NULL;
58 free(p1);
59 }
60 else
61 {
62 p1->next->pre=p1->pre;
63 p1->pre->next=p1->next;
64 free(p1);
65 }
66 }
67 else
68 cout<<"could not been found "<<num<<endl;
69 return head;
70 }
71
72 dnode* insert(dnode* head,int num)
73 {
74 dnode *p0,*p1;
75 p1=head;
76 p0=(dnode*)malloc(sizeof(dnode));
77 p0->data=num;
78 while(p0->data>p1->data&&p1->next!=NULL)
79 {
80 p1=p1->next;
81 }
82 if(p0->data<=p1->data)
83 {
84 if(head==p1)
85 {
86 p0->next=p1->next;
87 p1->pre=p0;
88 head=p0;
89 }
90 else
91 {
92 p0->next=p1;
93 p1->pre->next=p0;
94 p0->pre=p1->pre;
95 p1->pre=p0;
96 }
97 }
98 else
99 {
100 p1->next=p0;
101 p0->pre=p1;
102 p0->next=NULL;
103 }
104 return head;
105 }
106
107 void print(dnode* head)
108 {
109 dnode* p=head;
110 while(p->next!=NULL)
111 {
112 cout<<p->data<<"->";
113 p=p->next;
114 }
115 cout<<endl;
116 }
117 int main()
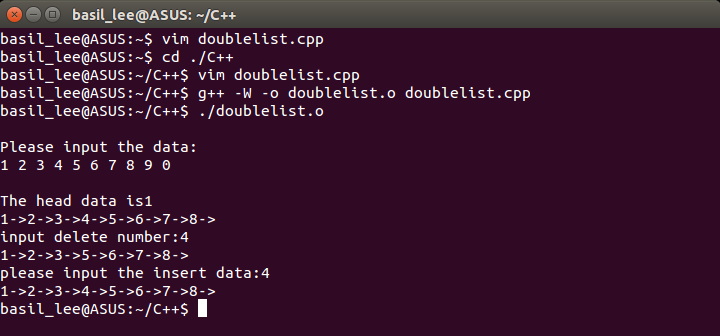
118 {
119 dnode *head,stud;
120 int n,del_num,insert_num;
121 head=create();
122 print(head);
123 cout<<"input delete number:";
124 cin>>del_num;
125 head=del(head,del_num);
126 print(head);
127 cout<<"please input the insert data:";
128 cin>>insert_num;
129 head=insert(head,insert_num);
130 print(head);
131 return 0;
132 }
雙鏈表
1、雙向鏈表(Doubly Linked List)
雙(向)鏈表中有兩條方向不同的鏈,即每個結點中除next域存放後繼結點地址外,還增加一個指向其直接前趨的指針域prior。
注意:
①雙鏈表由頭指針head惟一確定的。
②帶頭結點的雙鏈表的某些運算變得方便。
③將頭結點和尾結點鏈接起來,為雙(向)循環鏈表。
2、雙向鏈表的結點結構和形式描述
①結點結構(見上圖a)
②形式描述
typedef struct dlistnode{
DataType data;
struct dlistnode *prior,*next;
}DListNode;
typedef DListNode *DLinkList;
DLinkList head;
3、雙向鏈表的前插和刪除本結點操作
刻畫雙鏈表結構的對稱性的語句:p→prior→next== p→next→prior;由於雙鏈表的對稱性,在雙鏈表能能方便地完成各種插入、刪除操作。
①雙鏈表的前插操作
void DInsertBefore(DListNode *p,DataType x)
{//在帶頭結點的雙鏈表中,將值為x的新結點插入*p之前,設p≠NULL
DListNode *s=malloc(sizeof(DListNode));//①
s->data=x;//②
s->prior=p->prior;//③
s->next=p;//④
p->prior->next=s;//⑤
p->prior=s;//⑥
}
②雙鏈表上刪除結點*p自身的操作
void DDeleteNode(DListNode *p)
{//在帶頭結點的雙鏈表中,刪除結點*p,設*p為非終端結點
p->prior->next=p->next;//①
p->next->prior=p->prior;//②
free(p);//③
}
注意:
與單鏈表上的插入和刪除操作不同的是,在雙鏈表中插入和刪除必須同時修改兩個方向上的指針。
上述兩個算法的時間復雜度均為O(1)。
參考資料:baike.baidu.com/view/1850617.htm
刪除單鏈表中的某個結點時,一定要得到待刪除結點的前驅,得到該前驅有兩種方法,第一種方法是在定位待刪除結點的同時一路保存當前結點的前驅。第二種方法是在定位到待刪除結點之後,重新從單鏈表表頭開始來定位前驅。盡管通常會采用方法一。但其實這兩種方法的效率是一樣的,指針的總的移動操作都會有2*i次。而如果用雙向鏈表,則不需要定位前驅結點。因此指針總的移動操作為i次。