Description
Background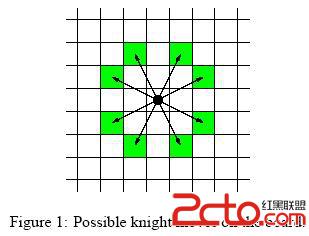
Input
The input begins with the number n of scenarios on a single line by itself.Output
For each scenario of the input you have to calculate the minimal amount of knight moves which are necessary to move from the starting point to the ending point. If starting point and ending point are equal,distance is zero. The distance must be written on a single line.Sample Input
3 8 0 0 7 0 100 0 0 30 50 10 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
5 28 0
#include#include #include #include using namespace std; int n,sx,sy,ex,ey; int vis[305][305]; int to[8][2] = {-1,-2,-2,-1,-2,1,-1,2,1,-2,2,-1,2,1,1,2}; struct node { int x,y,step; }; int check(int x,int y) { if(x<0 || x>=n || y<0 || y>=n) return 1; return vis[x][y]; } void bfs() { memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); node a,next; queue Q; int i; a.x = sx; a.y = sy; a.step = 0; vis[sx][sy] = 1; Q.push(a); while(!Q.empty()) { a = Q.front(); Q.pop(); if(a.x == ex && a.y == ey) { printf("%d\n",a.step); return; } for(i = 0;i<8;i++) { next = a; next.x = a.x+to[i][0]; next.y = a.y+to[i][1]; if(check(next.x,next.y)) continue; next.step = a.step+1; vis[next.x][next.y] = 1; Q.push(next); } } } int main() { int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&n,&sx,&sy,&ex,&ey); bfs(); } return 0; }