題目:用冒泡法從鍵盤輸入10個數字,編寫代碼對他排序
分析:
冒泡法排序將待排序的元素看做是垂直的氣泡,值較小的元素比較輕,往上浮動,在這裡算法中需要對這組“氣泡”出來若干次;每處理一次,就對兩個相鄰的“氣泡”的值進行交換,當位置較高的“氣泡”大於另一個“氣泡”的值,則可以通過臨時變量將兩個“氣泡”的值交換,所以此時,第一次處理後,最輕的“氣泡”值就浮到最高的位置,第二次處理後,第二輕的數據浮到第二高的位置。一般處理N次以後,這時就沒有必要比較第N高位置以上的“氣泡”,因為此時差不多的“氣泡”都正確排好了序.
代碼如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace bubble_sort
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, b,temp;
int[] Bubble_sort_arr = new int[10];//定義類型為int的數組Bubble_sort_arr
Console.WriteLine("請輸入10個整數");
for (a=0; a < 10;a++ )//將輸入的10個數字存儲於數組的子項當中
{
Bubble_sort_arr[a] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
for (b = Bubble_sort_arr.Length - 1;
b > 0;
b-- )//經過2層的循環,將數組中的子項數值進行交換
{
for(a=0;a<b;a++)
{
//當前一項大於後一項的時候,將交換兩項的位置
if (Bubble_sort_arr[a] > Bubble_sort_arr[a + 1])
{
temp = Bubble_sort_arr[a];
Bubble_sort_arr[a] = Bubble_sort_arr[a + 1];
Bubble_sort_arr[a + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("排好序的10個整數是");
for (a = 0; a < Bubble_sort_arr.Length;a++ )
{
Console.WriteLine(Bubble_sort_arr[a].ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
結果:

題目:遞歸法對一組的排序規則為:1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34........請求第50位的數值
分析:
從給出的數字序列當中發現規律,第1個數字和第2個數字相加之和為第3個數;第2個數和第3個數的和為第4個數,依次類推,可知道第N-1個數字和第N個數字相加的和為第N+1數字,此時可以得到如下規律:
當N=0;或者N=1時,F(N)=1; 當N>1時,F(N)=F(N-1)+F(N-2);此時不難得到第50個數字是多少了...如圖:
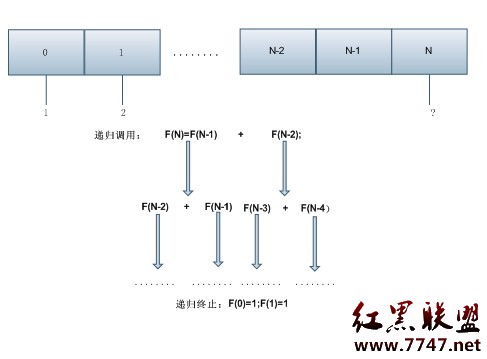
代碼如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Recursion
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("輸出第50為的是{0}",GetNumber(49));
Console.ReadKey();
}
static int GetNumber(int N)
{
if (N <= 1)
{
return 1;
}
return GetNumber(N - 1) + GetNumber(N - 2);
}
}
}
高斯求和:整數1--100求和的問題根據數學家高斯給出著名的解決方法,請用算法實現..
分析:
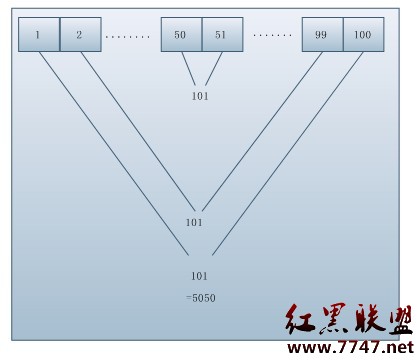
代碼如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Gaussian_summation
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//定義兩個int類型變量 a,sum,a用於計數和索引,sum用於存儲相加結果
int a, sum = 0;
int[] Arr = new int[100];
//定義int類型數組,Arr包括100個子項
for(a=0;a<Arr.Length;a++)//開始循環,從0-99,將a賦予當前數組子項
{
Arr[a]=a+1; &nbs