意圖:允許一個對象在其內部狀態改變時改變它的行為;對象看起來似乎修改了它的類;在一個狀態即將結束的時候啟用下一個狀態,可以是一個按需的連鎖反應;
適用性:
1、一個對象的行為取決於它的狀態,並且它必須在運行過程中可以根據它的狀態改變它的行為;
2、一個操作中含有龐大的多分支的條件語句,並且這些分支依賴於該對象的狀態;這個狀態通常使用一個或多個枚舉常量表示;通常,有多個操作包含這一相同的條件結構;State模式把每一個條件分支放入一個獨立的類中;這使得你可以根據對象自身的情況把對象的狀態作為一個對象,而且這一對象可以不依賴於其它對象而獨立變化;
結構圖:
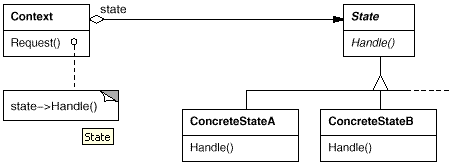
[cpp]
應用:
#ifndef _STATE_H_
#define _STATE_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class TCPStream;
//需要被改變狀態的對象類;它聚合了一個狀態對象:TCPState;依據TCPState對象的變化來改變TCPConnection對象的行為;
class TCPConnection
{
public:
TCPConnection(void);
~TCPConnection(void);
void ActiveOpen(void);
void PassiveOpen(void);
void Close(void);
void Send(void);
void Acknowledge(void);
void Synchronize(void);
void ProcessStream(TCPStream*);
private:
friend class TCPState;
void ChangeState(TCPState*);
private:
TCPState* m_lpState;
};
//TCPConnection類對象的狀態對象:TCPState;它實現為一個純虛基類;
class TCPState
{
public:
TCPState(void);
virtual ~TCPState(void);
virtual void Transmit(TCPConnection*, TCPStream*);
virtual void ActiveOpen(TCPConnection*);
virtual void PassiveOpen(TCPConnection*);
virtual void Close(TCPConnection*);
virtual void Synchronize(TCPConnection*);
virtual void Acknowledge(TCPConnection*);
virtual void Send(TCPConnection*);
protected:
void ChangeState(TCPConnection*, TCPState*);
};
//連接已建立狀態
class TCPEstablished: public TCPState
{
public:
virtual ~TCPEstablished(void);
static TCPState* Instance(void);
virtual void Transmit(TCPConnection*, TCPStream*);
virtual void Close(TCPConnection*);
private:
TCPEstablished(void);
};
//連接關閉狀態
class TCPClosed: public TCPState
{
public:
virtual ~TCPClosed(void);
static TCPState* Instance(void);
virtual void ActiveOpen(TCPConnection*);
virtual void PassiveOpen(TCPConnection*);
private:
TCPClosed(void);
};
//監聽狀態類
class TCPListen: public TCPState
{
public:
~TCPListen(void);
static TCPState* Instance(void);
virtual void Send(TCPConnection*);
private:
TCPListen(void);
};
TCPConnection::TCPConnection(void)
{
this->m_lpState = TCPClosed::Instance();
cout << "call TCPConnection()" << endl;
}
TCPConnection::~TCPConnection(void)
{
cout << "call ~ TCPConnection()" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::ActiveOpen(void)
{
this->m_lpState->ActiveOpen(this);
cout << "TCPConnection active-open state" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::PassiveOpen(void)
{
this->m_lpState->PassiveOpen(this);
cout << "TCPConnection passive-open state" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::Close(void)
{
this->m_lpState->Close(this);
cout << "TCPConnection close state" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::Send(void)
{
this->m_lpState->Send(this);
cout << "TCPConnection send state" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::Acknowledge(void)
{
this->m_lpState->Acknowledge(this);
cout << "TCPConnection ack state" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::Synchronize(void)
{
this->m_lpState->Synchronize(this);
cout << "TCPConnection sync state" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::ProcessStream(TCPStream* st)
{
cout << "TCPConnection ProcessStream" << endl;
}
void TCPConnection::ChangeState(TCPState* state)
{
if(this->m_lpState)
{
delete this->m_lpState;
this->m_lpState = NULL;
}
this->m_lpState = state;
cout << "TCPConnection::ChangeState()" << endl;
}
TCPState::TCPState(void)
{
cout << "call TCPState()" << endl;
}
TCPState::~TCPState(void)
{
cout << "call ~ TCPState()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::Transmit(TCPConnection*, TCPStream*)
{
cout << "TCPState::Transmit()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::ActiveOpen(TCPConnection*)
{
cout << "TCPState::ActiveOpen()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::PassiveOpen(TCPConnection*)
{
cout << "TCPState::PassiveOpen()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::Close(TCPConnection*)
{
cout << "TCPState::Close()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::Synchronize(TCPConnection*)
{
cout << "TCPState::Synchronize()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::Acknowledge(TCPConnection*)
{
cout << "TCPState::Acknowledge()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::Send(TCPConnection*)
{
cout << "TCPState::Send()" << endl;
}
void TCPState::ChangeState(TCPConnection* conn, TCPState* state)
{
cout << "TCPState::ChangeState()" << endl;
conn->ChangeState(state);
}
//監聽狀態類
TCPListen::~TCPListen(void)
{
cout << "call ~ TCPListen()" << endl;
}
TCPState* TCPListen::Instance(void)
{
return new TCPListen();
}
void TCPListen::Send(TCPConnection* conn)
{
//send SYN, recv SYN ACK, etc;
this->ChangeState(conn, TCPEstablished::Instance());
}
TCPListen::TCPListen(void)
{
cout << "call TCPListen()" << endl;
}
TCPClosed::~TCPClosed(void)
{
cout << "call ~ TCPClosed()" << endl;
}
TCPState* TCPClosed::Instance(void)
{
return new TCPClosed();
}
TCPClosed::TCPClosed(void)
{
cout << "call TCPClosed()" << endl;
}
void TCPClosed::ActiveOpen(TCPConnection* conn)
{
//send SYN, receive SYN,ACK; etc.
this->ChangeState(conn, TCPEstablished::Instance());
}
void TCPClosed::PassiveOpen(TCPConnection* conn)
{
// send FIN, receive ACK of FIN, etc;
this->ChangeState(conn, TCPListen::Instance());
}
TCPEstablished::~TCPEstablished(void)
{
cout << "call ~ TCPEstablished()" << endl;
}
TCPState* TCPEstablished::Instance(void)
{
return new TCPEstablished();
}
void TCPEstablished::Transmit(TCPConnection* conn, TCPStream* st)
{
conn->ProcessStream(st);
}
void TCPEstablished::Close(TCPConnection* conn)
{
this->ChangeState(conn, TCPListen::Instance());
}
TCPEstablished::TCPEstablished(void)
{
cout << "call TCPEstablished()" << endl;
}
class StateApplication
{
public:
StateApplication(void);
~StateApplication(void);
int doRun(void);
};
StateApplication::StateApplication(void){}
StateApplication::~StateApplication(void){}
int StateApplication::doRun(void)
{
TCPConnection tcpConn;
tcpConn.ActiveOpen();
tcpConn.Acknowledge();
tcpConn.Send();
tcpConn.Synchronize();
tcpConn.Close();
tcpConn.PassiveOpen();
tcpConn.Close();
return 0;
}
#endif
#include "State.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
StateApplication oApp;
oApp.doRun();
return 0;
}
作者:icechenbing