Toy Storage
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 131072/65536K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 5 Accepted Submission(s) : 5
Problem Description
Mom and dad have a problem: their child, Reza, never puts his toys away when he is finished playing with them. They gave Reza a rectangular box to put his toys in. Unfortunately, Reza is rebellious and obeys his parents by simply throwing his toys into the box. All the toys get mixed up, and it is impossible for Reza to find his favorite toys anymore.
Reza's parents came up with the following idea. They put cardboard partitions into the box. Even if Reza keeps throwing his toys into the box, at least toys that get thrown into different partitions stay separate. The box looks like this from the top:
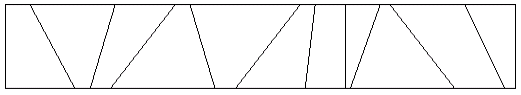
We want for each positive integer t, such that there exists a partition with t toys, determine how many partitions have t, toys.
Input
The input consists of a number of cases. The first line consists of six integers n, m, x1, y1, x2, y2. The number of cardboards to form the partitions is n (0 < n <= 1000) and the number of toys is given in m (0 < m <= 1000). The coordinates of the upper-left corner and the lower-right corner of the box are (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), respectively. The following n lines each consists of two integers Ui Li, indicating that the ends of the ith cardboard is at the coordinates (Ui, y1) and (Li, y2). You may assume that the cardboards do not intersect with each other. The next m lines each consists of two integers Xi Yi specifying where the ith toy has landed in the box. You may assume that no toy will land on a cardboard.
A line consisting of a single 0 terminates the input.
Output
For each box, first provide a header stating "Box" on a line of its own. After that, there will be one line of output per count (t > 0) of toys in a partition. The value t will be followed by a colon and a space, followed the number of partitions containing t toys. Output will be sorted in ascending order of t for each box.
Sample Input
4 10 0 10 100 0
20 20
80 80
60 60
40 40
5 10
15 10
95 10
25 10
65 10
75 10
35 10
45 10
55 10
85 10
5 6 0 10 60 0
4 3
15 30
3 1
6 8
10 10
2 1
2 8
1 5
5 5
40 10
7 9
0
Sample Output
Box
2: 5
Box
1: 4
2: 1
Source
PKU
[cpp]
// 765.cpp : 定義控制台應用程序的入口點。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define MAX 1010
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int x,y;
bool operator <(const Node K) const
{
if(x!=K.x) return x<K.x;
return y<K.y;
}
}a[MAX];
int b[MAX],c[MAX];
int n,m,x1,yy1,x2,y2;
bool chaji(int m,int x,int y)
{
int c[2][2];
c[0][0]=a[m].x-a[m].y; //p.x
c[0][1]=yy1-y2; //p.y
c[1][0]=x-a[m].y;//q.x
c[1][1]=y-y2; //q.y
if(c[0][0]*c[1][1]-c[0][1]*c[1][0]>0) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,x,y;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&m,&x1,&yy1,&x2,&y2);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y);
a[n+1].x=x2,a[n+1].y=x2;
sort(a+1,a+n+1);
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
int l=1,r=n+1,mid;
while(l<=r)
{
mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(chaji(mid,x,y)) r=mid-1;
else l=mid+1;
}
if(chaji(mid,x,y)>0)b[mid]++;
else b[mid+1]++;
}
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
for(i=1;i<=n+1;i++)
c[b[i]]++;
printf("Box\n");
for(i=1;i<=n+1;i++)
if(c[i]) printf("%d: %d\n",i,c[i]);
}
return 0;
}