題目:
Einbahnstrasse
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1117 Accepted Submission(s): 316
Problem Description
Einbahnstra e (German for a one-way street) is a street on which vehicles should only move in one direction. One reason for having one-way streets is to facilitate a smoother flow of traffic through crowded areas. This is useful in city centers, especially old cities like Cairo and Damascus. Careful planning guarantees that you can get to any location starting from any point. Nevertheless, drivers must carefully plan their route in order to avoid prolonging their trip due to one-way streets. Experienced drivers know that there are multiple paths to travel between any two locations. Not only that, there might be multiple roads between the same two locations. Knowing the shortest way between any two locations is a must! This is even more important when driving vehicles that are hard to maneuver (garbage trucks, towing trucks, etc.)
You just started a new job at a car-towing company. The company has a number of towing trucks parked at the company's garage. A tow-truck lifts the front or back wheels of a broken car in order to pull it straight back to the company's garage. You receive calls from various parts of the city about broken cars that need to be towed. The cars have to be towed in the same order as you receive the calls. Your job is to advise the tow-truck drivers regarding the shortest way in order to collect all broken cars back in to the company's garage. At the end of the day, you have to report to the management the total distance traveled by the trucks.
Input
Your program will be tested on one or more test cases. The first line of each test case specifies three numbers (N , C , and R ) separated by one or more spaces. The city has N locations with distinct names, including the company's garage. C is the number of broken cars. R is the number of roads in the city. Note that 0 < N < 100 , 0<=C < 1000 , and R < 10000 . The second line is made of C + 1 words, the first being the location of the company's garage, and the rest being the locations of the broken cars. A location is a word made of 10 letters or less. Letter case is significant. After the second line, there will be exactly R lines, each describing a road. A road is described using one of these three formats:
A -v -> B
A <-v - B
A <-v -> B
A and B are names of two different locations, while v is a positive integer (not exceeding 1000) denoting the length of the road. The first format specifies a one-way street from location A to B , the second specifies a one-way street from B to A , while the last specifies a two-way street between them. A , ``the arrow", and B are separated by one or more spaces. The end of the test cases is specified with a line having three zeros (for N , C , and R .)
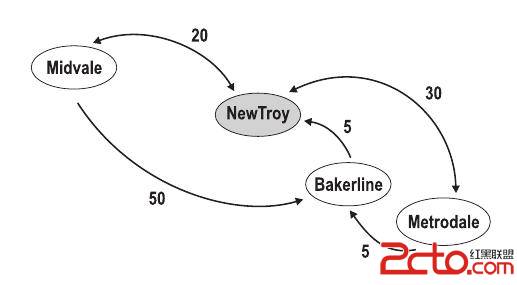
The test case in the example below is the same as the one in the figure.
Output
For each test case, print the total distance traveled using the following format:
k . V
Where k is test case number (starting at 1,) is a space, and V is the result.
Sample Input
4 2 5
NewTroy Midvale Metrodale
NewTroy <-20-> Midvale
Midvale --50-> Bakerline
NewTroy <-5-- Bakerline
Metrodale <-30-> NewTroy
Metrodale --5-> Bakerline
0 0 0
Sample Output
1. 80
題目大意:
路上有c輛壞車, 要從拖車要一個個依次地從車庫裡出發到目的地再把壞車拖回來到車庫裡。求所有壞車都托回來的最短總距離。
分析與總結:
這題對於輸入處理較麻煩( "<-20->"這一部分), 比較好的方法是利用sscanf, 先把這部分輸入到一個字符串,然後中間的數字用因為是從第3個開始的,所以sscanf(str+2, "%d", &w), 便可以提取出中間的數字保存到w了。
然後判斷是雙向還是單向, 只跟這個字符串的第一個和最後一個字符有關,也很容易實現。
輸入處理完成之後, 就用Floyd算法, 然後把那些路徑都加起來就是答案了。
代碼:
[cpp]
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef char State[12];
const int VN = 105;
const int EN = 10105;
const int HashSize = 10003;
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;
int n,c,r;
int size;
int head[VN];
int car[VN*10];
int pos;
int w[VN][VN];
class Hash{
public:
void init(){
rear = 1;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
}
int insert(State &s){
int h = hash(s);
int u = head[h];
while(u!=-1){
if(strcmp(st[u], s)==0) return u;
u = next[u];
}
strcpy(st[rear], s);
next[rear] = head[h];
head[h] = rear;
return rear++;
}
private:
int hash(char *p){
int sum=0;
while(*p){ sum = sum*131 + *p++; }
return (sum&0x7fffffff)%HashSize;
}
int rear;
int head[HashSize];
int next[VN];
State st[VN];
}hash;
inline void init(){
size=pos=0;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
hash.init();
for(int i=0; i<=n; ++i){
w[i][i] = INF;
for(int j=i+1; j<=n; ++j)
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = INF;
}
}
inline void Floyd(){
for(int k=1; k<=n; ++k)
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i)
for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j){
if(w[i][k]!=INF && w[k][j]!=INF)
w[i][j] = min(w[i][j],w[i][k]+w[k][j]);
}
}
int main(){
State name1, name2;
char str1[20];
int u,v,cost,cas=1;
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&c,&r)&&n+c+r){
init();
scanf("%s",name1);
hash.insert(name1);
for(int i=0; i<c; ++i){
scanf("%s",name1);
car[pos++] = hash.insert(name1);
}
for(int i=0; i<r; ++i){
scanf("%s %s %s", name1, str1, name2);
u = hash.insert(name1), v = hash.insert(name2);
sscanf(str1+2, "%d", &cost);
if(str1[0]=='<'&&str1[strlen(str1)-1]=='>'){
if(w[u][v]>cost) w[u][v] = cost;
if(w[v][u]>cost) w[v][u] = cost;
}
else if(str1[0]=='-'&&str1[strlen(str1)-1]=='>'){
if(w[u][v]>cost) w[u][v] = cost;
}
else{
if(w[v][u]>cost)w[v][u] = cost;
}
}
Floyd();
int ans=0;
for(int i=0; i<pos; ++i){
ans += w[1][car[i]]+w[car[i]][1];
}
printf("%d. %d\n",cas++,ans);
}
return 0;
}