平面最遠點對
Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: 65536K
Total Submissions: 22454 Accepted: 6868
Description
求 N (2 <= N <= 50,000) 個點平面最遠點對距離的平方.
Input
* 第1行:N
接下來每行為點的坐標 x 和 y ,(x,y)(-10,000<=x,y<=10,000的整數).
Output
輸出一行,為平面最遠點對距離平方.
Sample Input
4
0 0
0 1
1 1
1 0
Sample Output
2
Hint
(0, 0) a到 (1, 1) 距離平方為 2
Source
USACO 2003 Fall
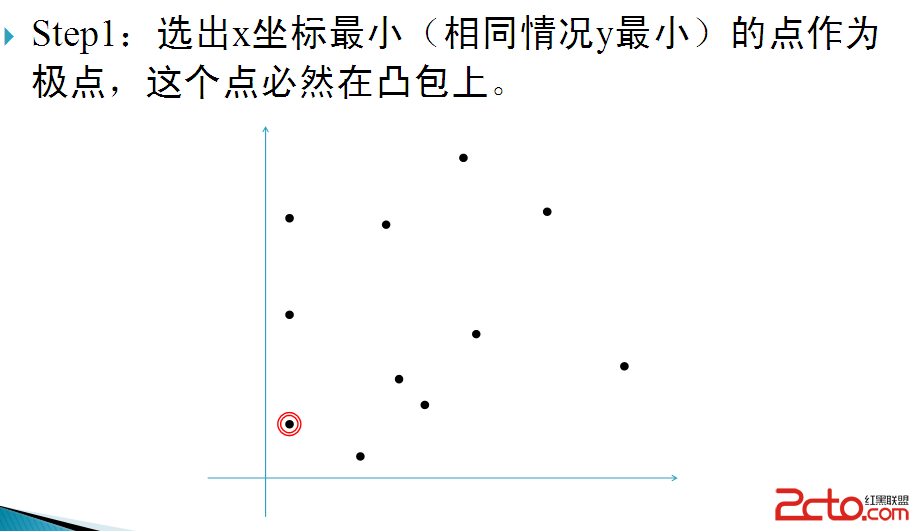
凸包模版題:
先用GrahamScan掃描求凸包,顯然最遠點對在凸包上。
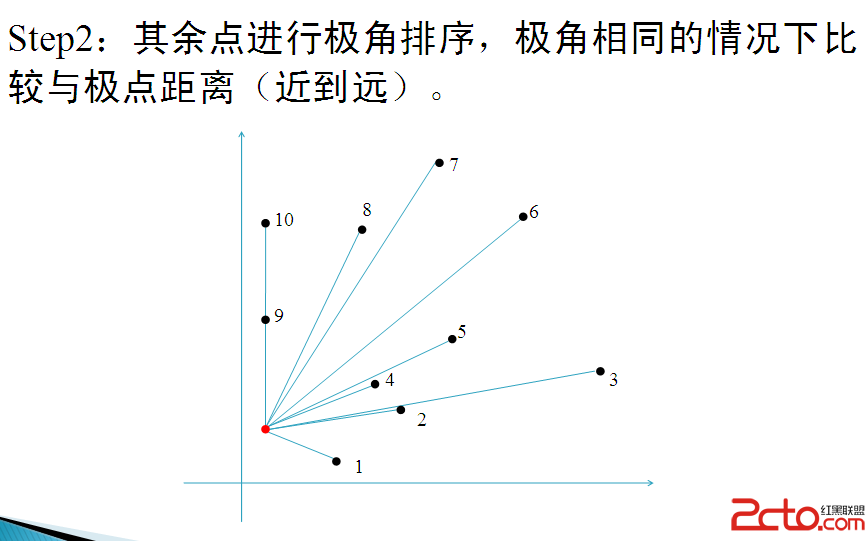
極角排序:
按照逆時針順序給平面上的點集到一個點的距離排序,使得排序後所有點正好繞這個點一圈.(按距離遠近從小到大排
思路:
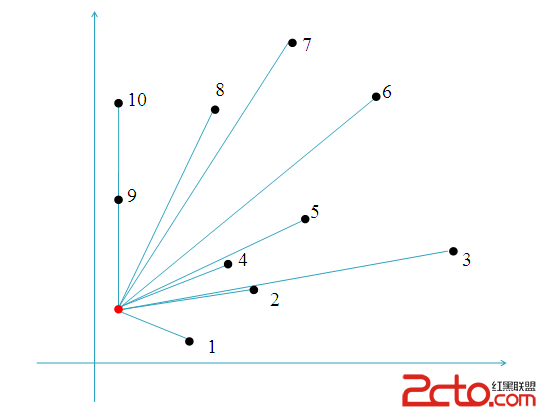 GrahamScan掃描:
GrahamScan掃描:

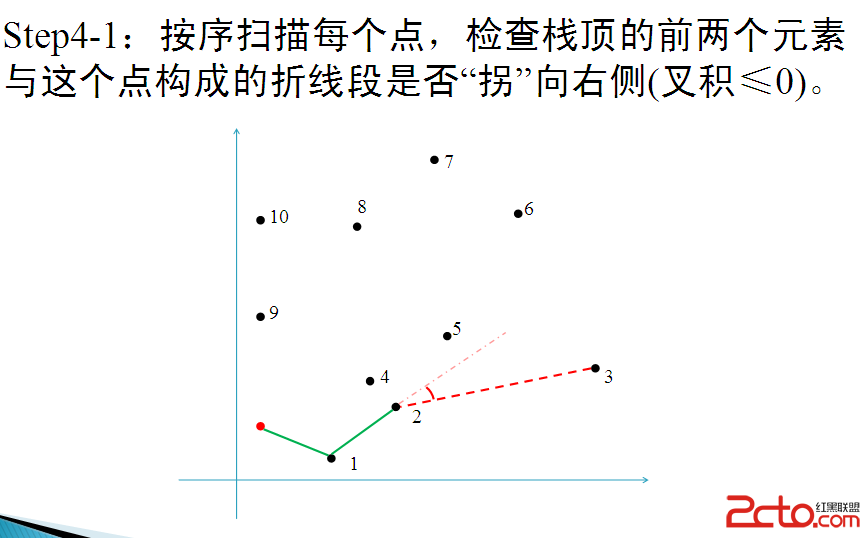
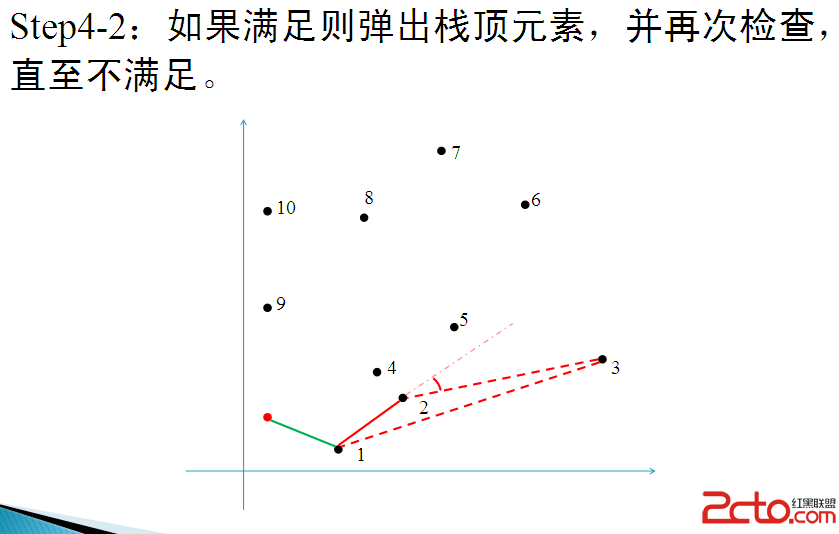
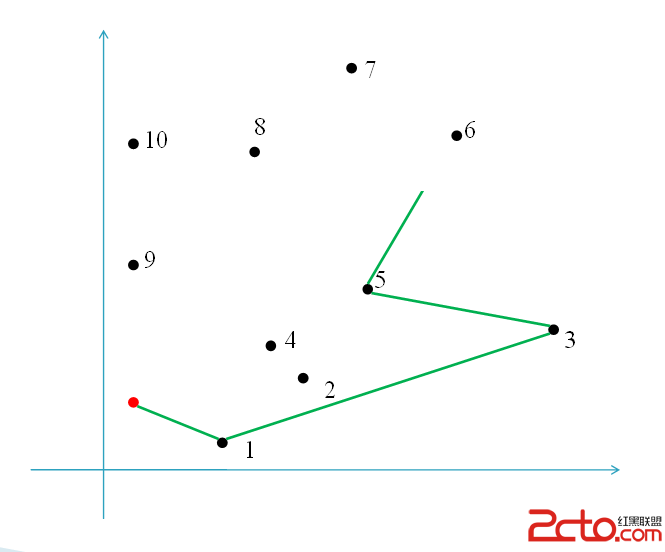
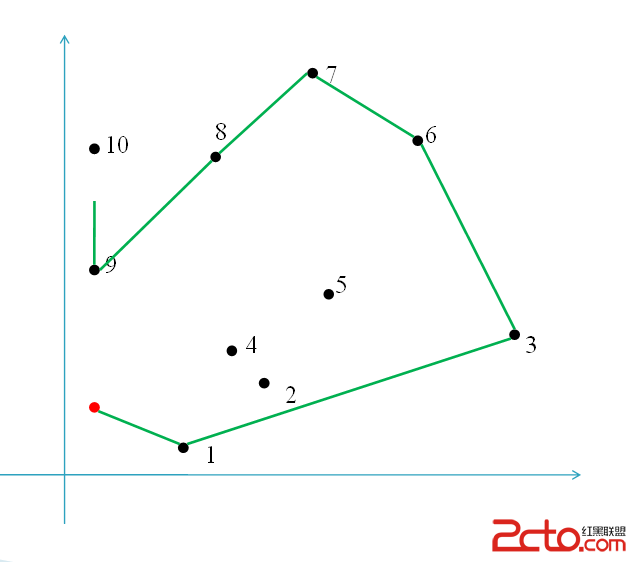
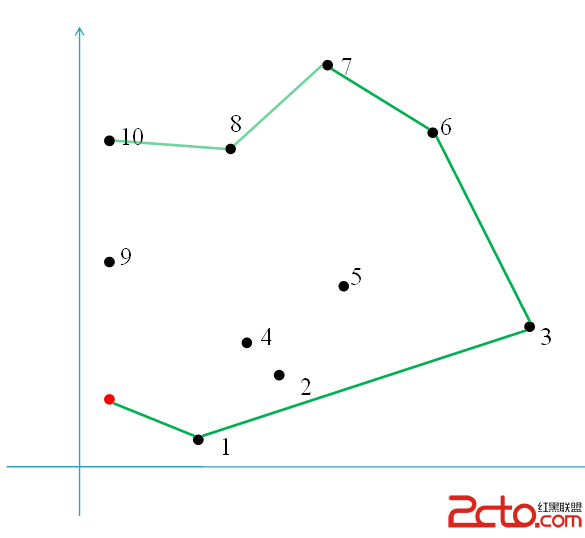
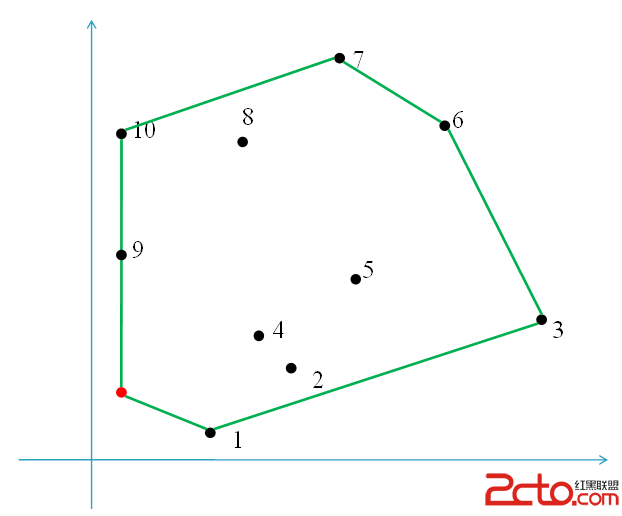
大致如此.
另補:
該題小Bug-有可能所有點在一條直線上。
這樣也能求出:
Ex:
a序列(-1,0) (0,0) (4,0) (9,0)
則st序列重復如下操作:
(-1,1),(0,0)入隊。
(4,0)入隊,不左拐->(0,0)出隊
隊列元素<2 (4,0)入隊
……
[cpp]
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN (50000+10)
double sqr(double x){return x*x;}
struct P
{
double x,y;
P(){}
P(double _x,double _y):x(_x),y(_y){}
}a[MAXN],st[MAXN];
int dis2(P A,P B)
{
return sqr(A.x-B.x)+sqr(A.y-B.y);
}
double dis(P A,P B)
{
return sqrt(double(dis2(A,B)));
}
struct V
{
double x,y;
V(){}
V(double _x,double _y):x(_x),y(_y){}
V(P A,P B):x(B.x-A.x),y(B.y-A.y){}
};
double operator*(V a,V b)
{
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
}
int cmp(P A,P B) //1:a>b 0:a<=b
{
double tmp=V(a[1],A)*V(a[1],B);
if (tmp>0) return 1;
else if (tmp==0) return (-(dis(a[1],A)-dis(a[1],B))>0)?1:0;
else return 0;
}
int n;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y;
int p=1;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) if (a[i].x<a[p].x||a[i].x==a[p].x&&a[i].y<a[p].y) p=i;
if (p>1) swap(a[p],a[1]);
sort(a+2,a+1+n,cmp);
int size=1;
st[1]=a[1];
for (int i=2;i<=n;)
if (size<2||V(st[size-1],st[size])*V(st[size],a[i])>0)
st[++size]=a[i++];
else size--;
int ans=0;
for (int i=1;i<size;i++)
for (int j=i+1;j<=size;j++)
ans=max(ans,dis2(st[i],st[j]));
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
 GrahamScan掃描:
GrahamScan掃描:








