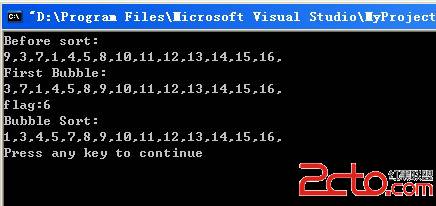
"Bubble Sort" is a simple way to sort elements. This sort employs a "bubbling strategy" to get the largetest element to the right. In a bubbling pass, pairs of adjacent elements are compared, the elements are swapped in case the one on the left is greater than the one on the right. At the end of the bubbling pass, we are assured that the largest element is in the right-most position.
[cpp]
// Bubble.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class T>
//one bubbling pass
bool Bubble(T a[], int n, int &flag){
bool swapped = false;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
if(a[i] > a[i+1]){
swap(a[i],a[i+1]);
swapped = true;
flag = i + 1;
}
}
return swapped;
}
template <class T>
void BubbleSort(T a[], int n){
int flag = n;
for(int i = flag; i > 1 && Bubble(a, i, flag) ; i--);
}
template <class T>
void PrintfNum(T a[], int n);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int a[14]={9,3,7,1,4,5,8,10,11,12,13,14,15,16};
cout << "Before sort:" << endl;
int flag;
PrintfNum(a, 14);
cout << "First Bubble:" << endl;
Bubble(a, 14, flag);
PrintfNum(a, 14);
cout << "flag:" << flag << endl;
cout << "Bubble Sort:" << endl;
BubbleSort(a, 14);
PrintfNum(a, 14);
return 0;
}
template <class T>
void PrintfNum(T a[], int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout << a[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
}