1. Hash概論
在理解Poco中的Hash代碼之前,首先需要了解一下Hash的基本理論。下面的這些內容和教課書上的內容並沒有太大的差別。
1.1 定義
下面這幾段來自於百度百科:
Hash:一般翻譯做"散列",也有直接音譯為"哈希"的,就是把任意長度的輸入(又叫做預映射, pre-image),通過散列算法,變換成固定長度的輸出,該輸出就是散列值。這種轉換是一種壓縮映射,也就是,散列值的空間通常遠小於輸入的空間,不同的輸入可能會散列成相同的輸出,而不可能從散列值來唯一的確定輸入值。簡單的說就是一種將任意長度的消息壓縮到某一固定長度的消息摘要的函數。
Hash table:散列表,也叫哈希表,是根據關鍵碼值(Key value)而直接進行訪問的數據結構。也就是說,它通過把關鍵碼值映射到表中一個位置來訪問記錄,以加快查找的速度。這個映射函數叫做散列函數,存放記錄的數組叫做散列表。
* 若結構中存在關鍵字和K相等的記錄,則必定存儲在f(K)的位置上。由此,不需比較便可直接取得所查記錄。這個對應關系f稱為散列函數(Hash function),按這個思想建立的表為散列表。
* 對不同的關鍵字可能得到同一散列地址,即key1≠key2,而f(key1)=f(key2),這種現象稱沖突。具有相同函數值的關鍵字對該散列函數來說稱做同義詞。
* 綜上所述,根據散列函數H(key)和處理沖突的方法將一組關鍵字映象到一個有限的連續的地址集(區間)上,並以關鍵字在地址集中的“象”, 作為這條記錄在表中的存儲位置,這種表便稱為散列表,這一映象過程稱為散列造表或散列,所得的存儲位置稱散列地址。這個現象也叫散列桶,在散列桶中,只能通過順序的方式來查找,一般只需要查找三次就可以找到。科學家計算過,當重載因子不超過75%,查找效率最高。
* 若對於關鍵字集合中的任一個關鍵字,經散列函數映象到地址集合中任何一個地址的概率是相等的,則稱此類散列函數為均勻散列函數(Uniform Hash function),這就是使關鍵字經過散列函數得到一個“隨機的地址”,從而減少沖突。
1.2 Hash table查找效率
對於Hash table來言,理論上查找效率為O(1)。但在現實世界中,查找的過程存在沖突現象。產生的沖突少,查找效率就高,產生的沖突多,查找效率就低。因此,影響產生沖突多少的因素,也就是影響查找效率的因素。影響產生沖突多少有以下三個因素:
1. 散列函數是否均勻;
2. 處理沖突的方法;
3. 散列表的裝填因子。
散列表的裝填因子定義為:α= 填入表中的元素個數 / 散列表的長度
實際上,散列表的平均查找長度是裝填因子α的函數,只是不同處理沖突的方法有不同的函數。
1.3 Poco中的Hash內容
Poco中的hash內容主要關注於Hash表的應用。下面是Poco中相關於Hash的類圖:
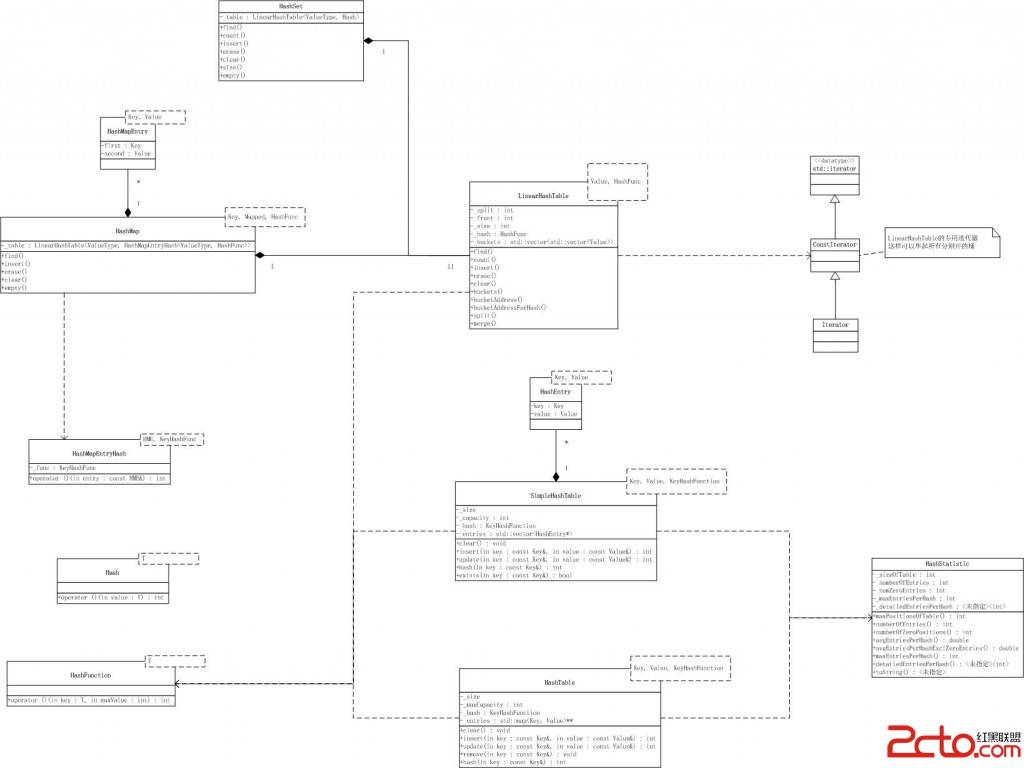 我們看到Poco的Hash內容主要被分成3部分:
1. Hash函數。Poco提供了一組Hash函數用於,生成hash值。同時提供了模板類HashFunction,通過仿函式提供對任意數據結構生成hash值的功能。
2. Hash table(哈希表)。Poco中實現了3種哈希表,分別是SimpleHashTable, HashTable,LinearHashTable。
3. 在哈希表上的應用,封裝出hash map和hash set。
2. Hash函數
Hash函數是解決hash沖突的第一個要素。
Poco中提供了一組Hash函數,用於產生hash值。其定義如下:
[cpp]
inline std::size_t hash(Int8 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt8 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(Int16 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt16 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(Int32 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt32 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(Int64 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt64 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
std::size_t hash(const std::string& str)
{
std::size_t h = 0;
std::string::const_iterator it = str.begin();
std::string::const_iterator end = str.end();
while (it != end)
{
h = h * 0xf4243 ^ *it++;
}
return h;
}
這裡就不對hash函數做過多敘述了,下面列出一些其他的常用hash函數。網上有專門的論述,並對不同的hash函數效果做了比較,有興趣的話可以google一下。
附:各種哈希函數的C語言程序代碼
[cpp]
unsigned int SDBMHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
// equivalent to: hash = 65599*hash + (*str++);
hash = (*str++) + (hash << 6) + (hash << 16) - hash;
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// RS Hash
unsigned int RSHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int b = 378551;
unsigned int a = 63689;
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * a + (*str++);
a *= b;
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// JS Hash
unsigned int JSHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 1315423911;
while (*str)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 5) + (*str++) + (hash >> 2));
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// P. J. Weinberger Hash
unsigned int PJWHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int BitsInUnignedInt = (unsigned int)(sizeof(unsigned int) * 8);
unsigned int ThreeQuarters = (unsigned int)((BitsInUnignedInt * 3) / 4);
unsigned int OneEighth = (unsigned int)(BitsInUnignedInt / 8);
unsigned int HighBits = (unsigned int)(0xFFFFFFFF) << (BitsInUnignedInt - OneEighth);
unsigned int hash = 0;
unsigned int test = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = (hash << OneEighth) + (*str++);
if ((test = hash & HighBits) != 0)
{
hash = ((hash ^ (test >> ThreeQuarters)) & (~HighBits));
}
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// ELF Hash
unsigned int ELFHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 0;
unsigned int x = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = (hash << 4) + (*str++);
if ((x = hash & 0xF0000000L) != 0)
{
hash ^= (x >> 24);
hash &= ~x;
}
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// BKDR Hash
unsigned int BKDRHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313 etc..
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// DJB Hash
unsigned int DJBHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 5381;
while (*str)
{
hash += (hash << 5) + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// AP Hash
unsigned int APHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 0;
int i;
for (i=0; *str; i++)
{
if ((i & 1) == 0)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 7) ^ (*str++) ^ (hash >> 3));
}
else
{
hash ^= (~((hash << 11) ^ (*str++) ^ (hash >> 5)));
}
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
unsigned int hash(char *str)
{
register unsigned int h;
register unsigned char *p;
for(h=0, p = (unsigned char *)str; *p ; p++)
h = 31 * h + *p;
return h;
}
[cpp]
// PHP中出現的字符串Hash函數
static unsigned long hashpjw(char *arKey, unsigned int nKeyLength)
{
unsigned long h = 0, g;
char *arEnd=arKey+nKeyLength;
while (arKey < arEnd) {
h = (h << 4) + *arKey++;
if ((g = (h & 0xF0000000))) {
h = h ^ (g >> 24);
h = h ^ g;
}
}
return h;
}
[cpp]
// OpenSSL中出現的字符串Hash函數
unsigned long lh_strhash(char *str)
{
int i,l;
unsigned long ret=0;
unsigned short *s;
if (str == NULL) return(0);
l=(strlen(str)+1)/2;
s=(unsigned short *)str;
for (i=0; i
ret^=(s[i]<<(i&0x0f));
return(ret);
}
/* The following hash seems to work very well on normal text strings
* no collisions on /usr/dict/words and it distributes on %2^n quite
* well, not as good as MD5, but still good.
*/
unsigned long lh_strhash(const char *c)
{
unsigned long ret=0;
long n;
unsigned long v;
int r;
if ((c == NULL) || (*c == '\0'))
return(ret);
/*
unsigned char b[16];
MD5(c,strlen(c),b);
return(b[0]|(b[1]<<8)|(b[2]<<16)|(b[3]<<24));
*/
n=0x100;
while (*c)
{
v=n|(*c);
n+=0x100;
r= (int)((v>>2)^v)&0x0f;
ret=(ret(32-r));
ret&=0xFFFFFFFFL;
ret^=v*v;
c++;
}
return((ret>>16)^ret);
}
[cpp]
// MySql中出現的字符串Hash函數
#ifndef NEW_HASH_FUNCTION
/* Calc hashvalue for a key */
static uint calc_hashnr(const byte *key,uint length)
{
register uint nr=1, nr2=4;
while (length--)
{
nr^= (((nr & 63)+nr2)*((uint) (uchar) *key++))+ (nr << 8);
nr2+=3;
}
return((uint) nr);
}
/* Calc hashvalue for a key, case indepenently */
static uint calc_hashnr_caseup(const byte *key,uint length)
{
register uint nr=1, nr2=4;
while (length--)
{
nr^= (((nr & 63)+nr2)*((uint) (uchar) toupper(*key++)))+ (nr << 8);
nr2+=3;
}
return((uint) nr);
}
#else
/*
* Fowler/Noll/Vo hash
*
* The basis of the hash algorithm was taken from an idea sent by email to the
* IEEE Posix P1003.2 mailing list from Phong Vo ([email protected]) and
* Glenn Fowler ([email protected]). Landon Curt Noll ([email protected])
* later improved on their algorithm.
*
* The magic is in the interesting relationship between the special prime
* 16777619 (2^24 + 403) and 2^32 and 2^8.
*
* This hash produces the fewest collisions of any function that we've seen so
* far, and works well on both numbers and strings.
*/
uint calc_hashnr(const byte *key, uint len)
{
const byte *end=key+len;
uint hash;
for (hash = 0; key < end; key++)
{
hash *= 16777619;
hash ^= (uint) *(uchar*) key;
}
return (hash);
}
uint calc_hashnr_caseup(const byte *key, uint len)
{
const byte *end=key+len;
uint hash;
for (hash = 0; key < end; key++)
{
hash *= 16777619;
hash ^= (uint) (uchar) toupper(*key);
}
return (hash);
}
#endif
3. Hash 表
我們接下去分析Poco中Hash表的實現。Poco中實現了3種哈希表,分別是SimpleHashTable, HashTable,LinearHashTable。它們的實現對應了當出現沖突時,解決沖突的不同方法。首先我們看一下通用的解決方法。
1. 線性探測。當出現碰撞時,順序依次查詢後續位置,直到找到空位。《利用線性探測法構造散列表》
2. 雙重散列法。當使用第一個散列Hash函數,出現碰撞時,用第二個散列函數去尋找空位
3. 拉鏈法。出現碰撞的時候,使用list存儲碰撞數據
4. 線性哈希,linear hash。立刻分裂或者延遲分裂。通過分裂,控制桶的高度,每次分裂時,會重新散列碰撞元素。《linear hashing》
SimpleHashTable的實現對應了方法一;HashTable對應了方法3;LinearHashTable對應了方法4。
3.1 SimpleHashTable
從類圖裡我們看到,SimpleHashTable是一個HashEntry容器, 內部定義如下:
[cpp]
std::vector<HashEntry*> _entries
當插入新數據時,首先根據hash值,計算空位,然後存儲;如果發現沖突,順著計算的hash值按地址順序依次尋找空位;如_entries容器無空位,則拋出異常。
[cpp]
UInt32 insert(const Key& key, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
insertRaw(key, hsh, value);
return hsh;
}
Value& insertRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
UInt32 pos = hsh;
if (!_entries[pos])
_entries[pos] = new HashEntry(key, value);
else
{
UInt32 origHash = hsh;
while (_entries[hsh % _capacity])
{
if (_entries[hsh % _capacity]->key == key)
throw ExistsException();
if (hsh - origHash > _capacity)
throw PoolOverflowException("SimpleHashTable full");
hsh++;
}
pos = hsh % _capacity;
_entries[pos] = new HashEntry(key, value);
}
_size++;
return _entries[pos]->value;
}
SimpleHashTable進行搜索時,策略也一致。
[cpp]
const Value& get(const Key& key) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
return getRaw(key, hsh);
}
const Value& getRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
UInt32 origHash = hsh;
while (true)
{
if (_entries[hsh % _capacity])
{
if (_entries[hsh % _capacity]->key == key)
{
return _entries[hsh % _capacity]->value;
}
}
else
throw InvalidArgumentException("value not found");
if (hsh - origHash > _capacity)
throw InvalidArgumentException("value not found");
hsh++;
}
}
SimpleHashTable沒有提供刪除數據的接口,只適用於數據量不大的簡單應用。
3.2 HashTable
HashTable是拉鏈法的一個變種。當沖突數據發生時,存儲的容器是map而不是list。其內部容器定義為:
[cpp]
HashEntryMap** _entries;
同map相比,它實際上是把一個大map分成了很多個小map,通過hash方法尋找到小map,再通過map的find函數尋找具體數據。其插入和搜索數據函數如下:
[cpp]
UInt32 insert(const Key& key, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
insertRaw(key, hsh, value);
return hsh;
}
Value& insertRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
if (!_entries[hsh])
_entries[hsh] = new HashEntryMap();
std::pair<typename HashEntryMap::iterator, bool> res(_entries[hsh]->insert(std::make_pair(key, value)));
if (!res.second)
throw InvalidArgumentException("HashTable::insert, key already exists.");
_size++;
return res.first->second;
}
const Value& get(const Key& key) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
return getRaw(key, hsh);
}
const Value& getRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
if (!_entries[hsh])
throw InvalidArgumentException("key not found");
ConstIterator it = _entries[hsh]->find(key);
if (it == _entries[hsh]->end())
throw InvalidArgumentException("key not found");
return it->second;
}
HashTable支持remove操作。
3.2 LinearHashTable
LinearHashTable按照解決沖突的方法4實現。它內部的容器為vector<vector<Value>>,同時還存在兩個控制量_split和_front:
[cpp]
std::size_t _split;
std::size_t _front;
vector<vector<Value>> _buckets;
它的插入操作如下:
[cpp]
std::pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const Value& value)
/// Inserts an element into the table.
///
/// If the element already exists in the table,
/// a pair(iterator, false) with iterator pointing to the
/// existing element is returned.
/// Otherwise, the element is inserted an a
/// pair(iterator, true) with iterator
/// pointing to the new element is returned.
{
std::size_t hash = _hash(value);
std::size_t addr = bucketAddressForHash(hash);
BucketVecIterator it(_buckets.begin() + addr);
BucketIterator buckIt(std::find(it->begin(), it->end(), value));
if (buckIt == it->end())
{
split();
addr = bucketAddressForHash(hash);
it = _buckets.begin() + addr;
buckIt = it->insert(it->end(), value);
++_size;
return std::make_pair(Iterator(it, _buckets.end(), buckIt), true);
}
else
{
return std::make_pair(Iterator(it, _buckets.end(), buckIt), false);
}
}
其中split函數是所有操作的關鍵:
[cpp]
void split()
{
if (_split == _front)
{
_split = 0;
_front *= 2;
_buckets.reserve(_front*2);
}
Bucket tmp;
_buckets.push_back(tmp);
_buckets[_split].swap(tmp);
++_split;
for (BucketIterator it = tmp.begin(); it != tmp.end(); ++it)
{
using std::swap;
std::size_t addr = bucketAddress(*it);
_buckets[addr].push_back(Value());
swap(*it, _buckets[addr].back());
}
}
從上面的代碼中我們可以看到,在每次插入新元素的時候,都會增加一個新的桶,並對桶_buckets[_split]進行重新散列;在_split == _front時,會把_buckets的容積擴大一倍。通過動態的增加桶的數量,這種方法降低了每個桶的高度,從而保證了搜索的效率。
4. HashMap和HashSet
HashMap和HashSet是在LinearHashTable上的封裝,使接口同stl::map和stl::set相類似,使用時非常的簡單。下面來看一個例子:
[cpp]
#include "Poco/HashMap.h"
int main()
{
typedef HashMap<int, int> IntMap;
IntMap hm;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
std::pair<IntMap::Iterator, bool> res = hm.insert(IntMap::ValueType(i, i*2));
IntMap::Iterator it = hm.find(i);
}
assert (!hm.empty());
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
IntMap::Iterator it = hm.find(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
std::pair<IntMap::Iterator, bool> res = hm.insert(IntMap::ValueType(i, 0));
}
return 0;
}
我們看到Poco的Hash內容主要被分成3部分:
1. Hash函數。Poco提供了一組Hash函數用於,生成hash值。同時提供了模板類HashFunction,通過仿函式提供對任意數據結構生成hash值的功能。
2. Hash table(哈希表)。Poco中實現了3種哈希表,分別是SimpleHashTable, HashTable,LinearHashTable。
3. 在哈希表上的應用,封裝出hash map和hash set。
2. Hash函數
Hash函數是解決hash沖突的第一個要素。
Poco中提供了一組Hash函數,用於產生hash值。其定義如下:
[cpp]
inline std::size_t hash(Int8 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt8 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(Int16 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt16 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(Int32 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt32 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(Int64 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
inline std::size_t hash(UInt64 n)
{
return static_cast<std::size_t>(n)*2654435761U;
}
std::size_t hash(const std::string& str)
{
std::size_t h = 0;
std::string::const_iterator it = str.begin();
std::string::const_iterator end = str.end();
while (it != end)
{
h = h * 0xf4243 ^ *it++;
}
return h;
}
這裡就不對hash函數做過多敘述了,下面列出一些其他的常用hash函數。網上有專門的論述,並對不同的hash函數效果做了比較,有興趣的話可以google一下。
附:各種哈希函數的C語言程序代碼
[cpp]
unsigned int SDBMHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
// equivalent to: hash = 65599*hash + (*str++);
hash = (*str++) + (hash << 6) + (hash << 16) - hash;
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// RS Hash
unsigned int RSHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int b = 378551;
unsigned int a = 63689;
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * a + (*str++);
a *= b;
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// JS Hash
unsigned int JSHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 1315423911;
while (*str)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 5) + (*str++) + (hash >> 2));
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// P. J. Weinberger Hash
unsigned int PJWHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int BitsInUnignedInt = (unsigned int)(sizeof(unsigned int) * 8);
unsigned int ThreeQuarters = (unsigned int)((BitsInUnignedInt * 3) / 4);
unsigned int OneEighth = (unsigned int)(BitsInUnignedInt / 8);
unsigned int HighBits = (unsigned int)(0xFFFFFFFF) << (BitsInUnignedInt - OneEighth);
unsigned int hash = 0;
unsigned int test = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = (hash << OneEighth) + (*str++);
if ((test = hash & HighBits) != 0)
{
hash = ((hash ^ (test >> ThreeQuarters)) & (~HighBits));
}
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// ELF Hash
unsigned int ELFHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 0;
unsigned int x = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = (hash << 4) + (*str++);
if ((x = hash & 0xF0000000L) != 0)
{
hash ^= (x >> 24);
hash &= ~x;
}
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// BKDR Hash
unsigned int BKDRHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313 etc..
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// DJB Hash
unsigned int DJBHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 5381;
while (*str)
{
hash += (hash << 5) + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
// AP Hash
unsigned int APHash(char *str)
{
unsigned int hash = 0;
int i;
for (i=0; *str; i++)
{
if ((i & 1) == 0)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 7) ^ (*str++) ^ (hash >> 3));
}
else
{
hash ^= (~((hash << 11) ^ (*str++) ^ (hash >> 5)));
}
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
unsigned int hash(char *str)
{
register unsigned int h;
register unsigned char *p;
for(h=0, p = (unsigned char *)str; *p ; p++)
h = 31 * h + *p;
return h;
}
[cpp]
// PHP中出現的字符串Hash函數
static unsigned long hashpjw(char *arKey, unsigned int nKeyLength)
{
unsigned long h = 0, g;
char *arEnd=arKey+nKeyLength;
while (arKey < arEnd) {
h = (h << 4) + *arKey++;
if ((g = (h & 0xF0000000))) {
h = h ^ (g >> 24);
h = h ^ g;
}
}
return h;
}
[cpp]
// OpenSSL中出現的字符串Hash函數
unsigned long lh_strhash(char *str)
{
int i,l;
unsigned long ret=0;
unsigned short *s;
if (str == NULL) return(0);
l=(strlen(str)+1)/2;
s=(unsigned short *)str;
for (i=0; i
ret^=(s[i]<<(i&0x0f));
return(ret);
}
/* The following hash seems to work very well on normal text strings
* no collisions on /usr/dict/words and it distributes on %2^n quite
* well, not as good as MD5, but still good.
*/
unsigned long lh_strhash(const char *c)
{
unsigned long ret=0;
long n;
unsigned long v;
int r;
if ((c == NULL) || (*c == '\0'))
return(ret);
/*
unsigned char b[16];
MD5(c,strlen(c),b);
return(b[0]|(b[1]<<8)|(b[2]<<16)|(b[3]<<24));
*/
n=0x100;
while (*c)
{
v=n|(*c);
n+=0x100;
r= (int)((v>>2)^v)&0x0f;
ret=(ret(32-r));
ret&=0xFFFFFFFFL;
ret^=v*v;
c++;
}
return((ret>>16)^ret);
}
[cpp]
// MySql中出現的字符串Hash函數
#ifndef NEW_HASH_FUNCTION
/* Calc hashvalue for a key */
static uint calc_hashnr(const byte *key,uint length)
{
register uint nr=1, nr2=4;
while (length--)
{
nr^= (((nr & 63)+nr2)*((uint) (uchar) *key++))+ (nr << 8);
nr2+=3;
}
return((uint) nr);
}
/* Calc hashvalue for a key, case indepenently */
static uint calc_hashnr_caseup(const byte *key,uint length)
{
register uint nr=1, nr2=4;
while (length--)
{
nr^= (((nr & 63)+nr2)*((uint) (uchar) toupper(*key++)))+ (nr << 8);
nr2+=3;
}
return((uint) nr);
}
#else
/*
* Fowler/Noll/Vo hash
*
* The basis of the hash algorithm was taken from an idea sent by email to the
* IEEE Posix P1003.2 mailing list from Phong Vo ([email protected]) and
* Glenn Fowler ([email protected]). Landon Curt Noll ([email protected])
* later improved on their algorithm.
*
* The magic is in the interesting relationship between the special prime
* 16777619 (2^24 + 403) and 2^32 and 2^8.
*
* This hash produces the fewest collisions of any function that we've seen so
* far, and works well on both numbers and strings.
*/
uint calc_hashnr(const byte *key, uint len)
{
const byte *end=key+len;
uint hash;
for (hash = 0; key < end; key++)
{
hash *= 16777619;
hash ^= (uint) *(uchar*) key;
}
return (hash);
}
uint calc_hashnr_caseup(const byte *key, uint len)
{
const byte *end=key+len;
uint hash;
for (hash = 0; key < end; key++)
{
hash *= 16777619;
hash ^= (uint) (uchar) toupper(*key);
}
return (hash);
}
#endif
3. Hash 表
我們接下去分析Poco中Hash表的實現。Poco中實現了3種哈希表,分別是SimpleHashTable, HashTable,LinearHashTable。它們的實現對應了當出現沖突時,解決沖突的不同方法。首先我們看一下通用的解決方法。
1. 線性探測。當出現碰撞時,順序依次查詢後續位置,直到找到空位。《利用線性探測法構造散列表》
2. 雙重散列法。當使用第一個散列Hash函數,出現碰撞時,用第二個散列函數去尋找空位
3. 拉鏈法。出現碰撞的時候,使用list存儲碰撞數據
4. 線性哈希,linear hash。立刻分裂或者延遲分裂。通過分裂,控制桶的高度,每次分裂時,會重新散列碰撞元素。《linear hashing》
SimpleHashTable的實現對應了方法一;HashTable對應了方法3;LinearHashTable對應了方法4。
3.1 SimpleHashTable
從類圖裡我們看到,SimpleHashTable是一個HashEntry容器, 內部定義如下:
[cpp]
std::vector<HashEntry*> _entries
當插入新數據時,首先根據hash值,計算空位,然後存儲;如果發現沖突,順著計算的hash值按地址順序依次尋找空位;如_entries容器無空位,則拋出異常。
[cpp]
UInt32 insert(const Key& key, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
insertRaw(key, hsh, value);
return hsh;
}
Value& insertRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
UInt32 pos = hsh;
if (!_entries[pos])
_entries[pos] = new HashEntry(key, value);
else
{
UInt32 origHash = hsh;
while (_entries[hsh % _capacity])
{
if (_entries[hsh % _capacity]->key == key)
throw ExistsException();
if (hsh - origHash > _capacity)
throw PoolOverflowException("SimpleHashTable full");
hsh++;
}
pos = hsh % _capacity;
_entries[pos] = new HashEntry(key, value);
}
_size++;
return _entries[pos]->value;
}
SimpleHashTable進行搜索時,策略也一致。
[cpp]
const Value& get(const Key& key) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
return getRaw(key, hsh);
}
const Value& getRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
UInt32 origHash = hsh;
while (true)
{
if (_entries[hsh % _capacity])
{
if (_entries[hsh % _capacity]->key == key)
{
return _entries[hsh % _capacity]->value;
}
}
else
throw InvalidArgumentException("value not found");
if (hsh - origHash > _capacity)
throw InvalidArgumentException("value not found");
hsh++;
}
}
SimpleHashTable沒有提供刪除數據的接口,只適用於數據量不大的簡單應用。
3.2 HashTable
HashTable是拉鏈法的一個變種。當沖突數據發生時,存儲的容器是map而不是list。其內部容器定義為:
[cpp]
HashEntryMap** _entries;
同map相比,它實際上是把一個大map分成了很多個小map,通過hash方法尋找到小map,再通過map的find函數尋找具體數據。其插入和搜索數據函數如下:
[cpp]
UInt32 insert(const Key& key, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
insertRaw(key, hsh, value);
return hsh;
}
Value& insertRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh, const Value& value)
/// Returns the hash value of the inserted item.
/// Throws an exception if the entry was already inserted
{
if (!_entries[hsh])
_entries[hsh] = new HashEntryMap();
std::pair<typename HashEntryMap::iterator, bool> res(_entries[hsh]->insert(std::make_pair(key, value)));
if (!res.second)
throw InvalidArgumentException("HashTable::insert, key already exists.");
_size++;
return res.first->second;
}
const Value& get(const Key& key) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
UInt32 hsh = hash(key);
return getRaw(key, hsh);
}
const Value& getRaw(const Key& key, UInt32 hsh) const
/// Throws an exception if the value does not exist
{
if (!_entries[hsh])
throw InvalidArgumentException("key not found");
ConstIterator it = _entries[hsh]->find(key);
if (it == _entries[hsh]->end())
throw InvalidArgumentException("key not found");
return it->second;
}
HashTable支持remove操作。
3.2 LinearHashTable
LinearHashTable按照解決沖突的方法4實現。它內部的容器為vector<vector<Value>>,同時還存在兩個控制量_split和_front:
[cpp]
std::size_t _split;
std::size_t _front;
vector<vector<Value>> _buckets;
它的插入操作如下:
[cpp]
std::pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const Value& value)
/// Inserts an element into the table.
///
/// If the element already exists in the table,
/// a pair(iterator, false) with iterator pointing to the
/// existing element is returned.
/// Otherwise, the element is inserted an a
/// pair(iterator, true) with iterator
/// pointing to the new element is returned.
{
std::size_t hash = _hash(value);
std::size_t addr = bucketAddressForHash(hash);
BucketVecIterator it(_buckets.begin() + addr);
BucketIterator buckIt(std::find(it->begin(), it->end(), value));
if (buckIt == it->end())
{
split();
addr = bucketAddressForHash(hash);
it = _buckets.begin() + addr;
buckIt = it->insert(it->end(), value);
++_size;
return std::make_pair(Iterator(it, _buckets.end(), buckIt), true);
}
else
{
return std::make_pair(Iterator(it, _buckets.end(), buckIt), false);
}
}
其中split函數是所有操作的關鍵:
[cpp]
void split()
{
if (_split == _front)
{
_split = 0;
_front *= 2;
_buckets.reserve(_front*2);
}
Bucket tmp;
_buckets.push_back(tmp);
_buckets[_split].swap(tmp);
++_split;
for (BucketIterator it = tmp.begin(); it != tmp.end(); ++it)
{
using std::swap;
std::size_t addr = bucketAddress(*it);
_buckets[addr].push_back(Value());
swap(*it, _buckets[addr].back());
}
}
從上面的代碼中我們可以看到,在每次插入新元素的時候,都會增加一個新的桶,並對桶_buckets[_split]進行重新散列;在_split == _front時,會把_buckets的容積擴大一倍。通過動態的增加桶的數量,這種方法降低了每個桶的高度,從而保證了搜索的效率。
4. HashMap和HashSet
HashMap和HashSet是在LinearHashTable上的封裝,使接口同stl::map和stl::set相類似,使用時非常的簡單。下面來看一個例子:
[cpp]
#include "Poco/HashMap.h"
int main()
{
typedef HashMap<int, int> IntMap;
IntMap hm;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
std::pair<IntMap::Iterator, bool> res = hm.insert(IntMap::ValueType(i, i*2));
IntMap::Iterator it = hm.find(i);
}
assert (!hm.empty());
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
IntMap::Iterator it = hm.find(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
std::pair<IntMap::Iterator, bool> res = hm.insert(IntMap::ValueType(i, 0));
}
return 0;
}