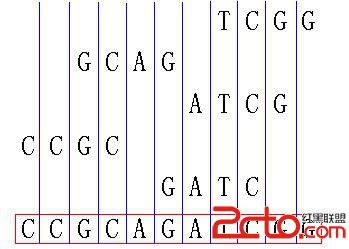
Best Sequence Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 4198 Accepted: 1662 Description The twenty-first century is a biology-technology developing century. One of the most attractive and challenging tasks is on the gene project, especially on gene sorting program. Recently we know that a gene is made of DNA. The nucleotide bases from which DNA is built are A(adenine), C(cytosine), G(guanine), and T(thymine). Given several segments of a gene, you are asked to make a shortest sequence from them. The sequence should use all the segments, and you cannot flip any of the segments. For example, given 'TCGG', 'GCAG', 'CCGC', 'GATC' and 'ATCG', you can slide the segments in the following way and get a sequence of length 11. It is the shortest sequence (but may be not the only one).
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#define INF 0x7ffffff
using namespace std;
char s1[20][30],s2[20][30];
int len[20],pos[20][20],pt[20];
bool status[20];
int n,Min;
int main()
{
//freopen("data1.in","r",stdin);
bool check(char str1[30],char str2[30]);
void dfs(int k);
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int Top=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++)
{
scanf("%s",s2[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++)
{
int j;
for(j=i+1;j<=n-1;j++)
{
int l1,l2;
l1 = strlen(s2[i]);
l2 = strlen(s2[j]);
if(l1==l2&&strcmp(s2[i],s2[j])==0)
{
break;
}else if(l1<l2&&check(s2[i],s2[j]))
{
break;
}
}
if(j==n)
{
strcpy(s1[Top++],s2[i]);
}
}
n=Top;
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++)
{
len[i] = strlen(s1[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=n-1;j++)
{
if(i==j)
{
continue;
}
int x;
for(x=0;x<=len[i]-1;x++)
{
int y;
for(y = x;y<=len[i]-1;y++)
{
if(s1[i][y] != s1[j][y-x])
{
break;
}
}
if(y==len[i])
{
break;
}
}
pos[i][j] = x;
}
}
memset(status,false,sizeof(status));
Min=INF;
dfs(0);
printf("%d\n",Min);
}
return 0;
}
//str1是否在str2中
bool check(char str1[30],char str2[30])
{
int l1 = strlen(str1);
int l2 = strlen(str2);
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<=l2-1;i++)
{
for(j=i;j-i<=l1-1;j++)
{
if(str2[j]!=str1[j-i])
{
break;
}
}
if(j-i==l1)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void dfs(int k)
{
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++)
{
if(!status[i])
{
pt[k] = i;
status[i] = true;
if(k==n-1)
{
int s = len[pt[0]];
for(int j=1;j<=n-1;j++)
{
int sum1 = len[pt[j]] - (len[pt[j-1]]-pos[pt[j-1]][pt[j]]);
s+=sum1;
}
Min=min(Min,s);
}else
{
dfs(k+1);
}
status[i] = false;
}
}
}