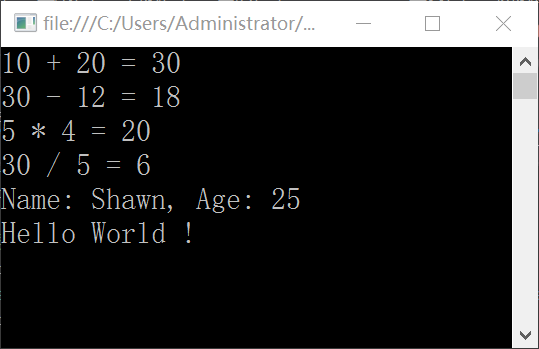
首先創建一個C++解決方案;其次在下面的選項裡面選擇win32項目,這個一定注意;不要選控制台或者MFC程序;
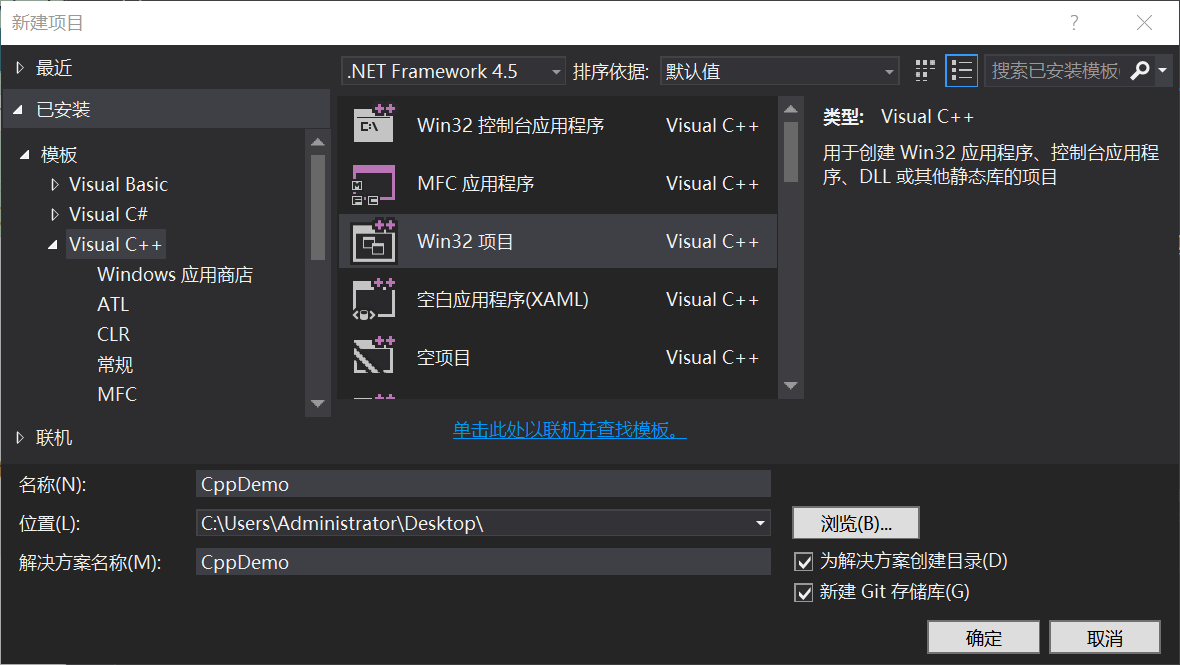
然後再程序設置中選擇DLL;其他默認即可;
最後得到了下面的界面;
我們可以看到這裡有一些文件,其中dllmain.cpp作為定義DLL應用程序的入口點,它的作用跟exe文件有個main或者WinMain入口函數是一樣的,它就是作為DLL的一個入口函數,實際上它是個可選的文件。它是在靜態鏈接時或動態鏈接時調用LoadLibrary和FreeLibrary時都會被調用。
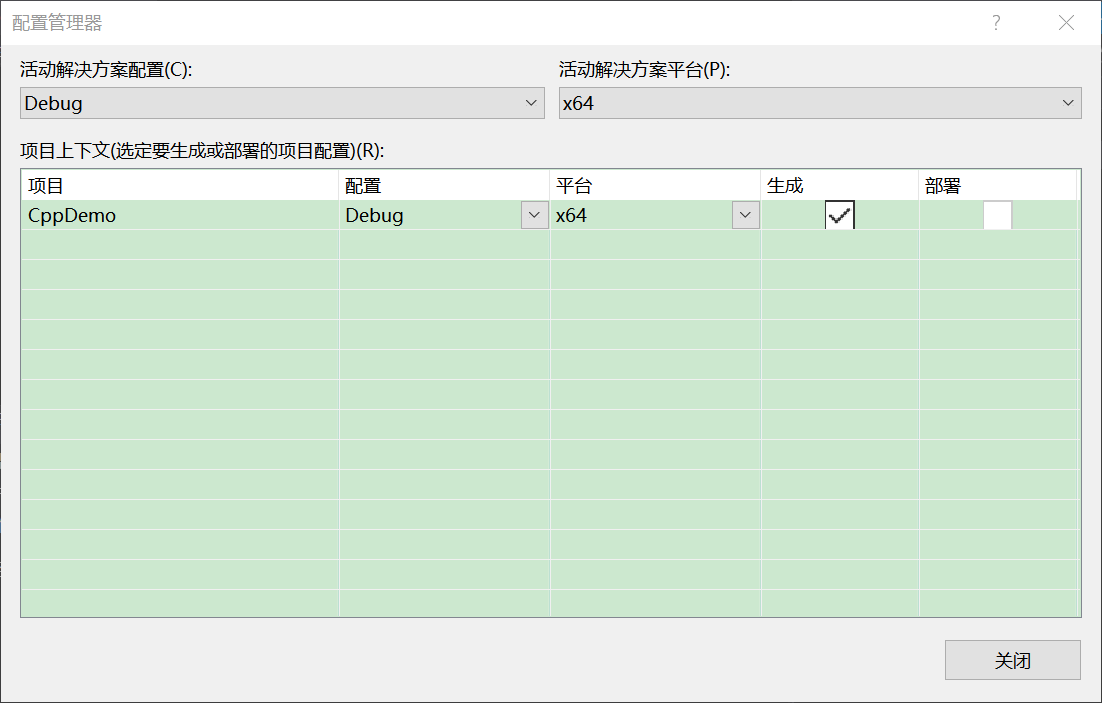
以下是要注意的部分了:一定要對下面的Debug部分進行更改;這一點就是X64配合的主要步驟;

配置管理器更改如下圖;
然後再CppDemo.cpp中輸入以下代碼:
//以下是我寫的程序;
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) int Multiply(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) int Divide(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
extern "C" 包含雙重含義,從字面上即可得到:首先,被它修飾的目標是“extern”的;其次,被它修飾的目標是“C”的。而被extern "C"修飾的變量和函數是按照C語言方式編譯和連接的。
__declspec(dllexport)的目的是為了將對應的函數放入到DLL動態庫中。
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport)加起來的目的是為了使用DllImport調用非托管C++的DLL文件。因為使用DllImport只能調用由C語言函數做成的DLL。
下面創建C#控制台程序;
賦值CppDemo中的dll文件到 C#程序目錄的X64的運行目錄中
並且添加類:
public class CPPDLL
{
[DllImport("CppDemo.dll")]
public static extern int Add(int x,int y);
[DllImport("CppDemo.dll")]
public static extern int Sub(int x, int y);
[DllImport("CppDemo.dll")]
public static extern int Multiply(int x, int y);
[DllImport("CppDemo.dll")]
public static extern int Divide(int x, int y);
}
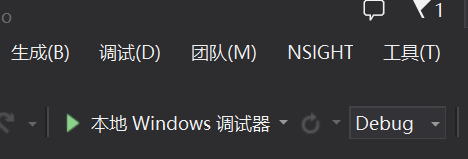
int result = CPPDLL.Add(10, 20);
Console.WriteLine("10 + 20 = {0}", result);
result = CPPDLL.Sub(30, 12);
Console.WriteLine("30 - 12 = {0}", result);
result = CPPDLL.Multiply(5, 4);
Console.WriteLine("5 * 4 = {0}", result);
result = CPPDLL.Divide(30, 5);
Console.WriteLine("30 / 5 = {0}", result);
Console.ReadLine();
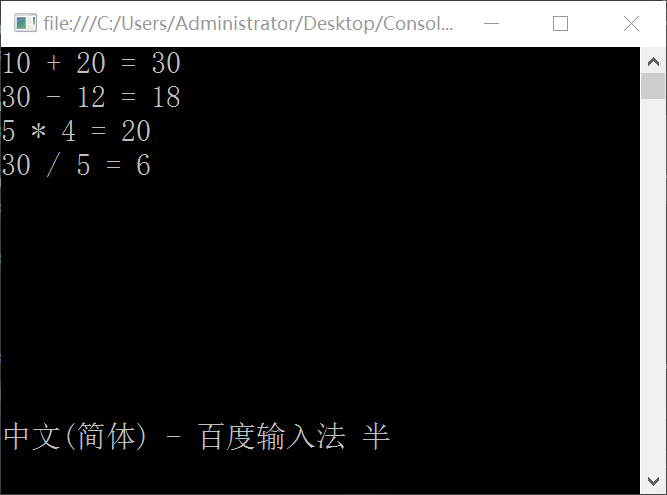
運行結果如下:
下面說說類調用:
首先在CppDemo中添加一個UserInfo這個類:
其中,UserInfo.h 中添加下面程序;
class UserInfo
{
private:
char* m_Name;
int m_Age;
public:
UserInfo(char* name, int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
virtual ~UserInfo(){ } //這裡的virtual是留待以後實現的意思;
int GetAge() { return m_Age; }
char* GetName() { return m_Name; }
};
UserInfo.cpp的內容如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "malloc.h"
#include "UserInfo.h"
typedef struct {
char name[32];
int age;
} User;//定義一個結構體命名為為User;
UserInfo* userInfo;//聲明一個指向UserInfo對象的指針;
//下面這個是接口,返回一個指針指向的地址;
//注意:代碼中的User*是個指針,返回也是一個對象指針,這樣做為了防止方法作用域結束後的局部變量的釋放。
extern "C" __declspec(dllexport) User* Create(char* name, int age)
{
//malloc 向系統申請分配指定size個字節的內存空間。
//返回類型是 void* 類型。void* 表示未確定類型的指針。
User* user = (User*)malloc(sizeof(User));//分配給user一塊內存;再用User進行格式化;
userInfo = new UserInfo(name, age);
//復制;
strcpy(user->name, userInfo->GetName());
user->age = userInfo->GetAge();
return user;
}
在項目中CPPDLL類中添加代碼:
//類調用程序塊;
[DllImport("CppDemo.dll")]
public static extern IntPtr Create(string name, int age); //IntPtr是表示平台特定指針,使用時指定;
//StructLayout特性允許我們控制Structure語句塊的元素在內存中的排列方式,
//以及當這些元素被傳遞給外部DLL時,運行庫排列這些元素的方式。
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)] //控制結構體字段的物理布局;括號中的意思是按出現順序依次布局;
public struct User
{
//MarshalAs屬性指示如何在托管代碼和非托管代碼之間封送數據。
//下面說明兩個字段的數據占的能存大小,第一個是字符類型;第二個是32位int類型;
//它有兩個參數,所以能管到下面兩行;
[MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.ByValTStr, SizeConst = 32)]
public string Name;
public int Age;
}
在主程序中添加如下代碼:
//下面是類的調用
IntPtr ptr = CPPDLL.Create("Shawn", 25);
//轉換指針為User類型;因為返回的是一個object,所以要格式化成User;
CPPDLL.User user = (CPPDLL.User)Marshal.PtrToStructure(ptr, typeof(CPPDLL.User));
Console.WriteLine("Name: {0}, Age: {1}", user.Name, user.Age);
運行結果如下;