Description
A power network consists of nodes (power stations, consumers and dispatchers) connected by power transport lines. A node u may be supplied with an amount s(u) >= 0 of power, may produce an amount 0 <= p(u) <= pmax(u) of power, may consume an amount 0 <= c(u) <= min(s(u),cmax(u)) of power, and may deliver an amount d(u)=s(u)+p(u)-c(u) of power. The following restrictions apply: c(u)=0 for any power station, p(u)=0 for any consumer, and p(u)=c(u)=0 for any dispatcher. There is at most one power transport line (u,v) from a node u to a node v in the net; it transports an amount 0 <= l(u,v) <= lmax(u,v) of power delivered by u to v. Let Con=Σuc(u) be the power consumed in the net. The problem is to compute the maximum value of Con.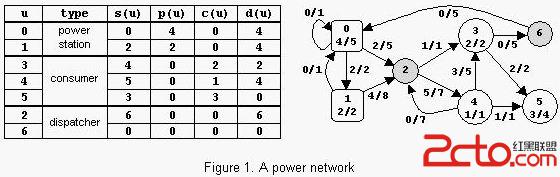
Output
For each data set from the input, the program prints on the standard output the maximum amount of power that can be consumed in the corresponding network. Each result has an integral value and is printed from the beginning of a separate line.Sample Input
2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20
7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 (2,4)7
(3,5)2 (3,6)5 (4,2)7 (4,3)5 (4,5)1 (6,0)5
(0)5 (1)2 (3)2 (4)1 (5)4
Sample Output
15 6
Hint
The sample input contains two data sets. The first data set encodes a network with 2 nodes, power station 0 with pmax(0)=15 and consumer 1 with cmax(1)=20, and 2 power transport lines with lmax(0,1)=20 and lmax(1,0)=10. The maximum value of Con is 15. The second data set encodes the network from figure 1.Source
Southeastern Europe 2003#include#include #include #include using namespace std; int const INF = 0x3fffffff; int const MAX = 105; int c[MAX][MAX]; int f[MAX][MAX]; int a[MAX]; int pre[MAX]; int n, np, nc, m; int Edmonds_Karp(int s, int t) { int ans = 0; queue q; while(true) { memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); a[s] = INF; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int v = 0; v <= n + 1; v++) { if(!a[v] && c[u][v] > f[u][v]) { a[v] = min(a[u], c[u][v] - f[u][v]); pre[v] = u; q.push(v); } } } if(a[t] == 0) break; for(int u = t; u != s; u = pre[u]) { f[pre[u]][u] += a[t]; f[u][pre[u]] -= a[t]; } ans += a[t]; } return ans; } int main() { while(scanf("%d %d %d %d", &n, &np, &nc, &m) != EOF) { memset(c, 0, sizeof(c)); memset(f, 0, sizeof(f)); for(int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int u, v, w; scanf(" (%d,%d)%d", &u, &v, &w); c[u + 1][v + 1] += w; } for(int i = 0; i < np; i++) { int v, w; scanf(" (%d)%d", &v, &w); c[0][v + 1] += w; } for(int i = 0; i < nc; i++) { int u, w; scanf(" (%d)%d", &u, &w); c[u + 1][n + 1] += w; } printf("%d\n", Edmonds_Karp(0, n + 1)); } }