若何用矩形法(梯形法)求定積分。本站提示廣大學習愛好者:(若何用矩形法(梯形法)求定積分)文章只能為提供參考,不一定能成為您想要的結果。以下是若何用矩形法(梯形法)求定積分正文
剖析:
高中的時刻,我們進修過,可以經由過程矩形法或許矩形法來求定積分。
思緒就是將積分區間劃分紅n等份,然後將這n等份近似算作矩形(或梯形),然後對一切的矩形(或梯形)的面積停止乞降。

簡略的例子:
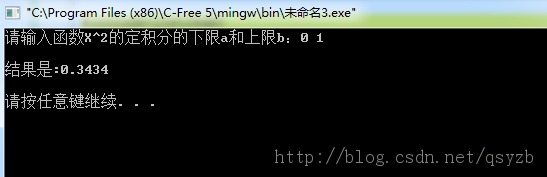
求函數X^2在的定積分
矩形法:
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
float fun(float x);
float a,b;
cout<<"請輸出函數X^2的定積分的上限a和下限b:";
cin>>a>>b;
int n=50;//將區間劃分紅50份
float h=(b-a)/n;//h是每一個區間分年夜小
float s=0;//s是矩形的面積的和
float i=0;
for(i=a;i<b;i+=h){
s=s+fun(i)*h;
}
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<s<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
float fun(float x){
return pow(x,2);
}
梯形法:
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
float fun(float x);
float a,b;
cout<<"請輸出函數X^2的定積分的上限a和下限b:";
cin>>a>>b;
int n=50;//將區間劃分紅50份
float h=(b-a)/n;//h是每一個區間分年夜小
float s=0;//s是矩形的面積的和
float i=0;
for(i=a;i<b;i+=h){
s=s+((fun(i)+fun(i+h))*h)/2;
}
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<s<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
float fun(float x){
return pow(x,2);
}
一個較龐雜的例子
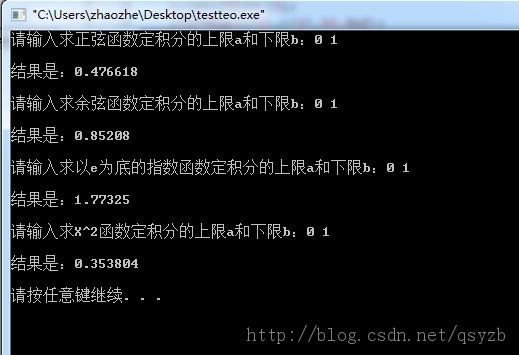
寫一個通用函數,用來求sinx 、 cosx 、 e^x 、 x^2 的定積分
剖析:fun為用來求定積分的通用函數,挪用fun函數的時刻,須要將積分的下限,上限,區間劃分的份數和被積函數的指針傳遞過去。
矩形法:
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
float fsin( float x);
float fcos( float x);
float fe( float x);
float fpf(float x);
float fun(float a,float b, int n,float (*p)(float x));
float a[4],b[4],r[4];
cout<<"請輸出求正弦函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[0]>>b[0];
r[0]=fun(a[0],b[0],50,fsin);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[0]<<endl;
cout<<"\n請輸出求余弦函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[1]>>b[1];
r[1]=fun(a[1],b[1],50,fcos);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[1]<<endl;
cout<<"\n請輸出求以e為底的指數函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[2]>>b[2];
r[2]=fun(a[2],b[2],50,fe);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[2]<<endl;
cout<<"\n請輸出求X^2函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[3]>>b[3];
r[3]=fun(a[3],b[3],50,fpf);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[3]<<endl;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
float fsin(float x){
return sin(x);
}
float fcos(float x){
return cos(x);
}
float fe(float x){
return exp(x);
}
float fpf(float x){
return pow(x,2);
}
float fun(float a,float b,int n,float (*p)(float x)){
float i;
float h=(b-a)/n;
float s=0;
for(i=a;i<b;i+=h){
s=s+p(i)*h;//應用了矩形求面積的公式
}
return s;
}
梯形法:
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
float fsin( float x);
float fcos( float x);
float fe( float x);
float fpf(float x);
float fun(float a,float b, int n,float (*p)(float x));
float a[4],b[4],r[4];
cout<<"請輸出求正弦函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[0]>>b[0];
r[0]=fun(a[0],b[0],50,fsin);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[0]<<endl;
cout<<"\n請輸出求余弦函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[1]>>b[1];
r[1]=fun(a[1],b[1],50,fcos);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[1]<<endl;
cout<<"\n請輸出求以e為底的指數函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[2]>>b[2];
r[2]=fun(a[2],b[2],50,fe);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[2]<<endl;
cout<<"\n請輸出求X^2函數定積分的下限a和上限b:";
cin>>a[3]>>b[3];
r[3]=fun(a[3],b[3],50,fpf);
cout<<"\n成果是:"<<r[3]<<endl;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
float fsin(float x){
return sin(x);
}
float fcos(float x){
return cos(x);
}
float fe(float x){
return exp(x);
}
float fpf(float x){
return pow(x,2);
}
float fun(float a,float b,int n,float (*p)(float x)){
float i;
float h=(b-a)/n;
float s=0;
for(i=a;i<b;i+=h){
s=s+((p(i)+p(i+h))*h)/2;//梯形法求面積
}
return s;
}