引言
讀寫鎖 是為了 解決, 大量 ''讀'' 和 少量 ''寫'' 的業務而設計的.
讀寫鎖有3個特征:
1.當讀寫鎖是寫加鎖狀態時,在這個鎖被解鎖之前,所有試圖對這個鎖加鎖的線程都會被阻塞
2.當讀寫鎖在讀加鎖狀態時,再以讀模式對它加鎖的線程都能得到訪問權,但以寫模式加鎖的線程將會被阻塞
3.當讀寫鎖在讀加鎖狀態時,如果有線程試圖以寫模式加鎖,讀寫鎖通常會阻塞隨後的讀模式加鎖
我們先舉一段標准庫構建的讀寫鎖demo來了解讀寫鎖api 的使用 .
pthread_rwlock.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define _INT_BZ (13)
#define _INT_WTH (2)
#define _INT_RTH (10)
struct rwarg {
pthread_t id;
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock; // 加鎖用的
int idx; // 指示buf中寫道那了
char buf[BUFSIZ]; // 存儲臨時數據
};
// 寫線程, 主要隨機寫字符進去
void twrite(struct rwarg * arg);
// 讀線程
void treads(struct rwarg * arg);
/*
* 主函數測試線程讀寫邏輯
* 少量寫線程, 大量讀線程測試
*/
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
// 初始化定義需要使用的量
struct rwarg arg = { 0, PTHREAD_RWLOCK_INITIALIZER, 0, "" };
int i;
// 讀線程跑起來
for(i=0; i<_INT_RTH; ++i)
pthread_create((pthread_t *)&arg, NULL, (void * (*)(void *))treads, &arg);
// 寫線程再跑起來
for(i=0; i<_INT_WTH; ++i)
pthread_create((pthread_t *)&arg, NULL, (void * (*)(void *))twrite, &arg);
// 簡單等待一下
printf("sleep input enter:");
getchar();
return 0;
}
// 寫線程, 主要隨機寫字符進去
void
twrite(struct rwarg * arg) {
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&arg->rwlock);
while(arg->idx < _INT_BZ) {
arg->buf[arg->idx] = 'a' + arg->idx;
++arg->idx;
}
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&arg->rwlock);
}
// 讀線程
void
treads(struct rwarg * arg) {
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
while(arg->idx < _INT_BZ) {
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&arg->rwlock);
puts(arg->buf);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&arg->rwlock);
}
}
編譯
gcc -Wall -ggdb2 -o pthread_rwlock.out pthread_rwlock.c -lpthread
執行的結果
linux上執行沒反應, 這代碼放在window 同樣沒有反應. 主要原因是 大量讀加鎖阻塞了寫加鎖.
預估主要原因是 pthread 實現的 rwlock 讀寫鎖, 沒有粗暴支持讀寫鎖特性3 . 這也是其讀寫鎖一個潛在bug(寫鎖沒有阻塞後續的讀鎖).
是不是有些收獲, 底層API有問題也不少的. 哈哈.
這裡扯一點C基礎語法 中 I 對於 美得 感受與寫法. 希望大家有思考.
a) 指針一般 寫法
int *piyo;
// 聲明部分
int *heoo(int a, int *pi);
// 定義部分
int *
heoo(int a, int b) {
...
}
上面是一種通用寫法. 缺點在 聲明和 定義 不統一, 不協調, 不爽.
b) 指針仿照OOP 寫法
int* piyo;
// 聲明部分
int* heoo(int a, int* pi);
//定義部分
int*
heoo(int a, int b){
...
}
這種寫法很好理解, 也很好看. 可惜這是C, (C++也是). 因為C出現比較早, 存在缺陷. 上面致命缺點是
int* piyo, *hoge;
特別丑.
c) 請用下面寫法, 都是從無數別人代碼中磨出來的.
int * piyo;
// 聲明部分
int * heoo(int a, int * pi);
//定義部分
int *
heoo(int a, int b){
...
}
到這裡扯淡結束了. 編程 希望是 實用->設計好->有美感->自然 . 而不是 屎一樣的實現而妄想優雅的接口. 如果有一天能為自己寫代碼的話.
前言
到這裡我們按照上面讀寫鎖的3條特性, 自己實現一個讀寫鎖. 首先看數據結構
// init need 0
struct rwlock {
int rlock;
int wlock;
};
當我們需要使用讀寫鎖時候只需要 struct rwlock lock = { 0 , 0 }; 很清潔
後面先在linux 使用gcc 提供的原子操作特性實現一個 讀鎖 實現
// 加讀鎖
static void rwlock_rlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
for(;;) {
// 看是否有人在試圖讀, 得到並防止代碼位置優化
while(lock->wlock)
__sync_synchronize();
__sync_add_and_fetch(&lock->rlock, 1);
// 沒有寫占用, 開始讀了
if(!lock->wlock)
break;
// 還是有寫, 刪掉添加的讀
__sync_add_and_fetch(&lock->rlock, -1);
}
}
在加寫鎖時候, 先判斷讀鎖是否沒有人在使用了. __sync_synchronize 是為了防止進行代碼位置優化. 後面邏輯是
開始加讀鎖, 但是在加讀鎖瞬間如果有寫鎖那麼立馬釋放剛申請的讀鎖. 一切為讀鎖為核心設計.
對於寫鎖
// 加寫鎖
static void rwlock_wlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
while(__sync_lock_test_and_set(&lock->wlock, 1))
;
// 等待讀占用鎖
while(lock->rlock)
__sync_synchronize();
}
只考慮讀鎖互相競爭, 競爭好了之後, 開始等待讀鎖. 好理解, 後面釋放相對容易. 扯一點對於pthread標准庫讀寫鎖只有一個釋放接口. 估計內存有狀態保持. 才能保證釋放.
使用方便, 但是性能不好. 讀寫鎖實現耦合又大了. 這裡實現
// 解寫鎖
static inline void rwlock_wunlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
__sync_lock_release(&lock->wlock);
}
// 解讀鎖
static inline void rwlock_runlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
__sync_add_and_fetch(&lock->rlock, -1);
}
寫鎖 直接解鎖到底, 讀鎖采用引用減少一處理. 看一個demo simple_rwlock.c
代碼就是上面讀寫鎖實現加上上面例子構建的. 編譯命令
gcc -Wall -ggdb2 -o simple_rwlock.out simple_rwlock.out -lpthread
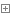
執行結果
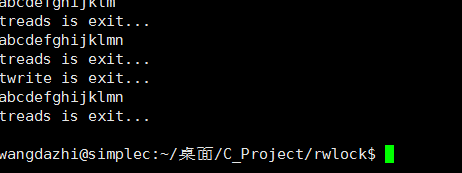
得到我們想要的結果, 說明這個讀寫鎖至少滿足了業務, 比pthread 好用並且功能完整. 後面再看正文擴展成通用庫.
正文
到這裡前戲都已經快完畢, 需要到正文了. 通過上面細說, 我們能夠封裝一個跨品台的讀寫鎖了. 看 scatom.c
#ifndef _H_SIMPLEC_SCATOM
#define _H_SIMPLEC_SCATOM
/*
* 作者 : wz
*
* 描述 : 簡單的原子操作,目前只考慮 VS(CL) 小端機 和 gcc
* 推薦用 posix 線程庫
*/
// 如果 是 VS 編譯器
#if defined(_MSC_VER)
#include <Windows.h>
//忽略 warning C4047: “==”:“void *”與“LONG”的間接級別不同
#pragma warning(disable:4047)
// v 和 a 都是 long 這樣數據
#define ATOM_FETCH_ADD(v, a) InterlockedExchangeAdd((LONG volatile *)&(v), (LONG)(a))
#define ATOM_ADD_FETCH(v, a) InterlockedAdd((LONG volatile *)&(v), (LONG)(a))
#define ATOM_SET(v, a) InterlockedExchange((LONG volatile *)&(v), (LONG)(a))
#define ATOM_CMP(v, c, a) (c == InterlockedCompareExchange((LONG volatile *)&(v), (LONG)(a), (LONG)c))
/*
*對於 InterlockedCompareExchange(v, c, a) 等價於下面
*long tmp = v ; v == a ? v = c : ; return tmp;
*
*咱們的 ATOM_FETCH_CMP(v, c, a) 等價於下面
*long tmp = v ; v == c ? v = a : ; return tmp;
*/
#define ATOM_FETCH_CMP(v, c, a) InterlockedCompareExchange((LONG volatile *)&(v), (LONG)(a), (LONG)c)
#define ATOM_LOCK(v) \
while(ATOM_SET(v, 1)) \
Sleep(0)
#define ATOM_UNLOCK(v) ATOM_SET(v, 0)
// 保證代碼不亂序優化後執行
#define ATOM_SYNC() MemoryBarrier()
// 否則 如果是 gcc 編譯器
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
#include <unistd.h>
/*
* type tmp = v ; v += a ; return tmp ;
* type 可以是 8,16,32,64 bit的類型
*/
#define ATOM_FETCH_ADD(v, a) __sync_fetch_add_add(&(v), (a))
/*
* v += a ; return v;
*/
#define ATOM_ADD_FETCH(v, a) __sync_add_and_fetch(&(v), (a))
/*
* type tmp = v ; v = a; return tmp;
*/
#define ATOM_SET(v, a) __sync_lock_test_and_set(&(v), (a))
/*
* bool b = v == c; b ? v=a : ; return b;
*/
#define ATOM_CMP(v, c, a) __sync_bool_compare_and_swap(&(v), (c), (a))
/*
* type tmp = v ; v == c ? v = a : ; return v;
*/
#define ATOM_FETCH_CMP(v, c, a) __sync_val_compare_and_swap(&(v), (c), (a))
/*
*加鎖等待,知道 ATOM_SET 返回合適的值
*_INT_USLEEP 是操作系統等待納秒數,可以優化,看具體操作系統
*
*使用方式
* int lock = 0;
* ATOM_LOCK(lock);
*
* // to do think ...
*
* ATOM_UNLOCK(lock);
*
*/
#define _INT_USLEEP_LOCK (2)
#define ATOM_LOCK(v) \
while(ATOM_SET(v, 1)) \
usleep(_INT_USLEEP_LOCK)
// 對ATOM_LOCK 解鎖, 當然 直接調用相當於 v = 0;
#define ATOM_UNLOCK(v) __sync_lock_release(&(v))
// 保證代碼不亂序
#define ATOM_SYNC() __sync_synchronize()
#endif // !_MSC_VER && !__GNUC__
#ifndef _STRUCT_RWLOCK
#define _STRUCT_RWLOCK
/*
* 這裡構建simple write and read lock
* struct rwlock need zero.
*/
// init need all is 0
struct rwlock {
int rlock;
int wlock;
};
// add read lock
static void rwlock_rlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
for (;;) {
// 看是否有人在試圖讀, 得到並防止代碼位置優化
while (lock->wlock)
ATOM_SYNC();
ATOM_ADD_FETCH(lock->rlock, 1);
// 沒有寫占用, 開始讀了
if (!lock->wlock)
break;
// 還是有寫, 刪掉添加的讀
ATOM_ADD_FETCH(lock->rlock, -1);
}
}
// add write lock
static void rwlock_wlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
ATOM_LOCK(lock->wlock);
// 等待讀占用鎖
while (lock->rlock)
ATOM_SYNC();
}
// unlock write
static inline void rwlock_wunlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
ATOM_UNLOCK(lock->wlock);
}
// unlock read
static inline void rwlock_runlock(struct rwlock * lock) {
ATOM_ADD_FETCH(lock->rlock, -1);
}
#endif // !_STRUCT_RWLOCK
#endif // !_H_SIMPLEC_SCATOM
我們是可以直接在window上測試, 對於window上線程模型同樣采用 pthread for win32.
測試文件 sc_template/sc_console_template/main/test_atom_rwlock.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <scatom.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define _INT_BZ (13)
#define _INT_WTH (2)
#define _INT_RTH (10)
struct rwarg {
pthread_t id;
struct rwlock lock; // 加鎖用的
int idx; // 指示buf中寫道那了
char buf[BUFSIZ]; // 存儲臨時數據
};
// 寫線程, 主要隨機寫字符進去
void twrite(struct rwarg * arg);
// 讀線程
void treads(struct rwarg * arg);
/*
* 自己寫讀寫鎖底層
*/
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
// 初始化定義需要使用的量
int i;
struct rwarg arg = { 0 };
// 讀線程跑起來
for (i = 0; i<_INT_RTH; ++i)
pthread_create((pthread_t *)&arg, NULL, (void * (*)(void *))treads, &arg);
// 寫線程再跑起來
for (i = 0; i<_INT_WTH; ++i)
pthread_create((pthread_t *)&arg, NULL, (void * (*)(void *))twrite, &arg);
// 簡單等待一下
printf("sleep input enter:");
getchar();
return 0;
}
// 寫線程, 主要隨機寫字符進去
void
twrite(struct rwarg * arg) {
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
while (arg->idx < _INT_BZ) {
rwlock_wlock(&arg->lock);
arg->buf[arg->idx] = 'a' + arg->idx;
++arg->idx;
rwlock_wunlock(&arg->lock);
}
puts("twrite is exit...");
}
// 讀線程
void
treads(struct rwarg * arg) {
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
while (arg->idx < _INT_BZ) {
rwlock_rlock(&arg->lock);
puts(arg->buf);
rwlock_runlock(&arg->lock);
}
puts("treads is exit...");
}
F7 -> Ctrl + F5 運行結果
一切正常. 後面將代碼放入linux 上測試一下. 先看下面目錄結構
編譯命令
gcc -Wall -ggdb2 -I. -o test_atom_rwlock.out test_atom_rwlock.c -lpthread
執行結果 也是一切正常

這裡 -I是為了附加指定的查找路徑, -ggdb2 啟用宏調試等級. 代碼中存在 struct rwarg arg = { 0 };
其實使用了C初始化特性, 標注的按照標注的初始化, 未標注的直接按照零初始化.
後記
錯誤是難免歡迎吐糙~~ (● ̄(エ) ̄●)
爛泥 http://music.163.com/#/song?id=411314656
