引言
今天我們要講述和構建的是一個跨平台多線程C的定時器對象,粒度是毫秒級別.可以稱之為簡易的timer, sctimer.h 庫.
首先看總的接口,看門見客. sctimer.h
#ifndef _H_SCTIMER #define _H_SCTIMER #include <schead.h> /* * 簡單的定時器代碼.跨平台,線程安全 *關鍵是使用簡單. *例如 * 1. 啟動一次,不要求多線程, 1s後執行 * st_add(1, 1, 0, timer, arg, 0) * 2. 啟動輪詢事件, 要求多線程,立即啟動,並且每隔200ms執行一次 * st_add(0, -1, 200, timer, arg, 1) * *這些參數具體含義,講述的很清楚. 你看明白後再用.或者把你常用的封裝好 */ /* * 添加定時器事件,雖然設置的屬性有點多但是都是必要的 . * start : 延遲啟動的時間, 0表示立即啟動, 單位是毫秒 * cut : 表示執行次數, 0表示永久時間, 一次就為1 * intval : 每次執行的時間間隔, 單位是毫秒 * timer : 定時器執行函數 * arg : 定時器參數指針 * fb : 0表示不啟用多線程, 1表示啟用多線程 * : 返回這個定時器的 唯一id */ extern int st_add(int start, int cut, int intval, vdel_f timer, void* arg, bool fb); /* * 刪除指定事件 * st : st_add 返回的定時器id */ extern inline void st_del(int st); #endif // !_H_SCTIMER
基礎數據結構確定
不用慌. 這個應該是最簡單的接口了.一個創建一個嘗試取消接口. 很符合使用習慣. 這個部分不討論代碼細節.
簡單認為 st_add 中 參數 timer理解為注冊的事件器. schead.h 中提供一些跨平台使用的代碼. 到這裡那我們盡情的討論設計.
使用過很多定時器庫. 個人感覺 最爽的是
.net framework 中提供的 Timer定時器. 真幾把傻瓜化好用. 可惜 .net framework 效率不高,太依賴VS IDE並且Linux
平台上起步太晚. 這裡可能扯偏了.
那繼續 討論定時器. 當我第一次考慮定時器的時候, 想到的的數據結構是 最小堆結構(自行Google). 當前最快執行的對象在堆頂,
後面就直接 sleep(min(t)) => run. 插入性能log級別, 執行性能是常量級別, 調整也是O(log). 最優了.
後來投入設計的時候發現,不說這種設計需要大量的交換, 關鍵在於加入 存在大量時間相同執行timer. 這種數據結構會大量交換.
因為普世性小環境,直接否了這種最小二叉堆結構.
後面想到一種特殊堆結構, 升序鏈表 . 完全符合最小堆定義. 插入是O(n) 執行效率是 O(1),調整是O(1). 總的而言
也很好. 最後決定采用 升序鏈表結構. 那我們的數據結構 設計基本敲定了.
(真希望, 有圖, 圖比語言更好理解. 希望有人盜鏈的時候幫我加上圖吧.)
業務流程初步結構設計
首先第一個業務是 st_add 有個參數是 cut,限定這個定時器timer執行的次數. cut == 0的時候表示永久循環的定時器.
我這裡采用的算法思路是.
0.在定時器鏈表中添加這個定時器對象, 將cut + 1, 塞入, 0的時候不動
1.當執行這個定時器對象時候, 將其從定時器鏈表中彈出
2.如果是 cut ==0 ,永久事件. 執行完畢後, 修改一下時間量,再 add進定時器鏈表中,再次輪序
2.1 如果 cut > 1, 表示繼續執行, 將cut-- 之後add進去
3 .如果cut == 1的時候表示這個定時器對象可以 關閉了, 那麼就釋放.
業務模型多線程部分設計
這裡需要處理一個問題, 定時器必須是異步的. 否則主線程就阻塞了. 我的思路是
1.當我們st_add 第一次添加對象進去的時候. 開啟 loop 函數一直輪序 定時器鏈表對象
2.當我們st_add 添加對象 剛好是當前最小的對象, 對象 取消掉已經輪序的 線程. 重新構建關系再一次 開啟新線程輪序
業務刪除模塊
思路就是在定時器鏈表中查詢,找到後直接彈出. 後面釋放.
這裡需要注意的是 上面三個模塊都需要是互斥的. 就是需要用到鎖. 我們這裡使用的是原子鎖.
好了到這裡基本思路都說清楚了. 至少大致方向有了. 這裡還有一個業務, 就是阻塞怎麼設計. 我采用的是最優阻塞, 缺點是需要取消
重建.還有一種思路是小單位阻塞, 大量輪序.就看取捨了.
思路比代碼重要. 只有思路清晰了,裝逼才容易. 會說的比會做的,感覺更吊.留下的都是思想家.沒聽說過行動家.
好那我們開始行動吧.
前言
這裡會簡單的分析一些實現細節.
跨平台部分
首先看阻塞部分
/*
* 2.0 如果定義了 __GNUC__ 就假定是 使用gcc 編譯器,為Linux平台
* 否則 認為是 Window 平台,不可否認宏是丑陋的
*/
#if defined(__GNUC__)
//下面是依賴 Linux 實現,等待毫秒數
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#define SLEEPMS(m) \
usleep(m * 1000)
#else
// 這裡創建等待函數 以毫秒為單位 , 需要依賴操作系統實現
#include <Windows.h>
#include <direct.h> // 加載多余的頭文件在 編譯階段會去掉
#define rmdir _rmdir
/**
* Linux sys/time.h 中獲取時間函數在Windows上一種移植實現
**tv : 返回結果包含秒數和微秒數
**tz : 包含的時區,在window上這個變量沒有用不返回
** : 默認返回0
**/
extern int gettimeofday(struct timeval* tv, void* tz);
//為了解決 不通用功能
#define localtime_r(t, tm) localtime_s(tm, t)
#define SLEEPMS(m) \
Sleep(m)
#endif /*__GNUC__ 跨平台的代碼都很丑陋 */
主要看 SLEEPMS宏, linux上采用usleep 停頓微妙級別. window上使用Sleep 停頓毫秒級別. 這裡就沒事了.
獲取時間部分
對於gettimerofday 這個函數linux上提供了, window上沒有, 它返回時間單位. window實現如下
#if defined(_MSC_VER)
/**
* Linux sys/time.h 中獲取時間函數在Windows上一種移植實現
**tv : 返回結果包含秒數和微秒數
**tz : 包含的時區,在window上這個變量沒有用不返回
** : 默認返回0
**/
int
gettimeofday(struct timeval* tv, void* tz)
{
time_t clock;
struct tm tm;
SYSTEMTIME wtm;
GetLocalTime(&wtm);
tm.tm_year = wtm.wYear - 1900;
tm.tm_mon = wtm.wMonth - 1; //window的計數更好寫
tm.tm_mday = wtm.wDay;
tm.tm_hour = wtm.wHour;
tm.tm_min = wtm.wMinute;
tm.tm_sec = wtm.wSecond;
tm.tm_isdst = -1; //不考慮夏令時
clock = mktime(&tm);
tv->tv_sec = (long)clock; //32位使用,接口已經老了
tv->tv_usec = wtm.wMilliseconds * 1000;
return _RT_OK;
}
#endif
利用GetLocalTime 實現的.比較粗暴. 這裡扯一點, 關於schead.h 是simple c 開源基礎框架中一個基本頭文件. 最近優化了一處判斷系統大小端代碼如下
//12.0 判斷是大端序還是小端序,大端序返回true
bool
sh_isbig(void)
{
static union {
unsigned short _s;
unsigned char _c;
} __u = { 1 };
return __u._c == 0;
}
更清爽了一點.以前是 unsigned char _cs[sizeof(unsigned short)]; 結構. 這裡少了幾個字符.快了一點.
線程庫仍然是采用ptrhead 通用庫.
通用的原子鎖 scatom.h
這裡展示gcc 部分提供的原子鎖 代碼吧
/*
加鎖等待,知道 ATOM_SET 返回合適的值
_INT_USLEEP 是操作系統等待納秒數,可以優化,看具體操作系統
使用方式
int lock = 0;
ATOM_LOCK(lock);
//to do think ...
ATOM_UNLOCK(lock);
*/
#define _INT_USLEEP (2)
#define ATOM_LOCK(v) \
while(ATOM_SET(v, 1)) \
usleep(_INT_USLEEP)
/*
對ATOM_LOCK 解鎖, 當然 直接調用相當於 v = 0;
*/
#define ATOM_UNLOCK(v) \
__sync_lock_release(&(v))
到這裡基本跨平台部分准備的前戲基本就完成了. 後面最後測試的時候會展示所有的代碼.
正文
到這裡會完整的展示代碼和測試demo.
那我們開始講代碼吧,首先給全部. 學習日本, 雖然無趣, 但脫光再說. sctimer.c
#include <sctimer.h>
#include <scatom.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// 使用到的定時器結點
struct stnode {
int id; //當前定時器的id
time_t stime; //運行的具體時間到秒
int ms; //還需要等待的毫秒數
int cut; //循環執行次數, -1表示一直執行
int intval; //下一次輪詢的時間間隔
int type; //0表示不開啟多線程, 1表示開啟多線程
vdel_f timer; //執行的函數事件
void* arg; //執行函數參數
struct stnode* next; //下一個定時器結點
};
// 當前鏈表對象管理器
struct stlist {
int lock; //加鎖用的
int nowid; //當前使用的最大timer id
int status; //0表示停止態, 1表示主線程loop運行態
pthread_t tid; //主循環線程id, 0表示沒有啟動
struct stnode* head; //定時器鏈表的頭結點
};
// 定時器對象的單例, 最簡就是最復雜
static struct stlist _st;
// 先創建鏈表對象處理函數
static struct stnode* _new_stnode(int start, int cut, int intval, vdel_f timer, void* arg, bool fb)
{
int s = start / 1000;
struct stnode* node = malloc(sizeof(struct stnode));
if (NULL == node)
CERR_EXIT("_new_stnode malloc node is error!");
// 初始化, 首先初始化當前id
node->id = ATOM_ADD_FETCH(_st.nowid, 1);
node->stime = s + time(NULL);
node->ms = start - s*1000;
node->cut = cut > 0 ? cut + 1 : 0; // 執行到1的時候停止,並且兼容永久時間0
node->intval = intval;
node->type = fb;
node->timer = timer;
node->arg = arg;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// 如果stl < str 返回true, 否則返回false
static inline bool _stnode_cmp(struct stnode* stl, struct stnode* str)
{
return (stl->stime < str->stime) ||
(stl->stime == str->stime && stl->ms < str->ms);
}
// 添加鏈表對象, 返回true表示插入的是頭結點, 當你執行的時候需要全額加鎖
static bool _stlist_add(struct stlist* st, struct stnode* node)
{
struct stnode* head;
// 插入為頭結點直接返回
if (!(head=st->head) || _stnode_cmp(node, head)) {
node->next = head;
st->head = node;
ATOM_UNLOCK(st->lock);
return true;
}
// 中間插入了
while (head->next){
if (_stnode_cmp(node, head->next))
break;
head = head->next;
}
node->next = head->next;
head->next = node;
return false;
}
// 根據id,刪除一個timer結點, 返回NULL表示沒有找見不處理,多線程安全的
static struct stnode* _stlist_del(struct stlist* st, int id)
{
struct stnode *head, *tmp = NULL;
if (!(head = st->head)) return NULL;
ATOM_LOCK(st->lock);
// 刪除為頭結點直接返回
if (head->id == id) {
st->head = head->next;
tmp = head;
}
else { // 中間刪除那個結點了
while (head->next) {
if (head->next->id == id)
break;
head = head->next;
}
if (head->next) {
tmp = head->next;
head->next = tmp->next;
}
}
ATOM_UNLOCK(st->lock);
return tmp;
}
// 得到等待的時間,毫秒, <=0的時候頭時間就可以執行了
static inline int _sleeptime(struct stlist* st)
{
struct stnode* head = st->head;
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return (int)(1000*(head->stime - tv.tv_sec) + head->ms - tv.tv_usec/1000);
}
// timer線程執行的函數
static void* _slnode_timer(struct stnode* sn)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); //設置線程分離,自銷毀
sn->timer(sn->arg);
return NULL;
}
//重新調整, 只能在 _stlist_loop 後面調用, 線程安全,只加了一把鎖
static void _slnode_again_run(struct stlist* st)
{
int s, v;
pthread_t tid;
struct stnode* sn;
ATOM_LOCK(st->lock); // 加鎖防止調整關系覆蓋,可用還是比較重要的
sn = st->head;
st->head = sn->next;
if (sn->cut == 1){ //這時候不需要了,才開始刪除
ATOM_UNLOCK(st->lock);
free(sn);
return;
}
//這裡需要重新組織數據
sn->cut = sn->cut ? sn->cut - 1 : 0;
s = sn->intval + sn->ms;
v = s / 1000;
sn->stime += v;
sn->ms = s - v*1000;
if (sn->type) // 開始處理,先處理異步模式
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, (void* (*)(void*))_slnode_timer, sn);
else //同步模式
sn->timer(sn->arg);
_stlist_add(st, sn);
ATOM_UNLOCK(st->lock);
}
// 運行的主loop,基於timer管理器
static void* _stlist_loop(struct stlist* st)
{
int nowt;
//設置線程屬性, 默認線程屬性 允許退出線程
pthread_setcanceltype(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS, NULL); //設置立即取消
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); //設置線程分離,自銷毀
// 正常輪詢,檢測時間
while (st->head) {
pthread_testcancel(); //添加測試取消點
nowt = _sleeptime(st);
if(nowt <= 0 || st->head->cut == 1)
_slnode_again_run(st); //重新調整關系並且開始執行
else //沒有人到這那就繼續等待
SLEEPMS(nowt);
}
// 已經運行結束
st->status = 0;
return NULL;
}
/*
* 添加定時器事件,雖然設置的屬性有點多但是都是必要的 .
* start : 延遲啟動的時間, 0表示立即啟動, 單位是毫秒
* cut : 表示執行次數, 0表示永久時間, 一次就為1
* intval : 每次執行的時間間隔, 單位是毫秒
* timer : 定時器執行函數
* arg : 定時器參數指針
* fb : 0表示不啟用多線程, 1表示啟用多線程
* : 返回這個定時器的 唯一id
*/
int
st_add(int start, int cut, int intval, vdel_f timer, void* arg, bool fb)
{
struct stnode* now;
DEBUG_CODE({
if(start<0 || cut<0 || intval<0 || !timer)
CERR_EXIT("debug start,cut,intval,timer => %d,%d,%d,%p.", start, cut, intval, timer);
});
// 這裡開始創建對象往 線程隊列中添加
now = _new_stnode(start, cut, intval, timer, arg, fb);
ATOM_LOCK(_st.lock); //核心添加模塊 要等, 添加到鏈表, 看線程能否取消等
_stlist_add(&_st, now);
// 看是否需要取消線程
if(_st.status == 1 && _sleeptime(&_st) < 0){
pthread_cancel(_st.tid);
_st.status = 0;
}
// 這個時候重新開啟線程
if(_st.status == 0){
pthread_create(&_st.tid, NULL, (void* (*)(void*))_stlist_loop, &_st);
_st.status = 1; //延遲真實運行態
}
ATOM_UNLOCK(_st.lock);
return now->id;
}
/*
* 刪除指定事件, 刪除是臨時加上的存在臨界的意外.
* st : st_add 返回的定時器id
*/
inline void
st_del(int st)
{
struct stnode* sn = _stlist_del(&_st, st);
if(sn) free(sn);
}
那我們開始解說吧,從數據結構說起. 先看每個 tiemr 結點結構
// 使用到的定時器結點
struct stnode {
int id; //當前定時器的id
time_t stime; //運行的具體時間到秒
int ms; //還需要等待的毫秒數
int cut; //循環執行次數, -1表示一直執行
int intval; //下一次輪詢的時間間隔
int type; //0表示不開啟多線程, 1表示開啟多線程
vdel_f timer; //執行的函數事件
void* arg; //執行函數參數
struct stnode* next; //下一個定時器結點
};
仔細看看, 這些都是必須的. 鏈表是為了找到下一個結點. (上面//不對其是, 博客園和window上軟件關於 \t 計算代碼不一致造成的.)
再看timer管理器結構
// 當前鏈表對象管理器
struct stlist {
int lock; //加鎖用的
int nowid; //當前使用的最大timer id
int status; //0表示停止態, 1表示主線程loop運行態
pthread_t tid; //主循環線程id, 0表示沒有啟動
struct stnode* head; //定時器鏈表的頭結點
};
寫的很詳細, lock是加鎖用的,每個鏈表一個鎖. nowid 是為了記錄當前已經用的timer對象. 假定用不完. 這個定時器個人代碼估計, 定時器永久循環
對象破了2,3千基本就不行了. 需要重新開線程優化了. 當然了這種情況出現了不僅僅是結構優化就能解決了. 需要系統層優化了.
status標志當前是否有主loop線程在運行. 原本思路是通過pthread_t 判斷.但是 不同平台pthread_t 實現不一樣放棄了.
Linux 上 設計為unsigend long. 但是window上設計為
/*
* Generic handle type - intended to extend uniqueness beyond
* that available with a simple pointer. It should scale for either
* IA-32 or IA-64.
*/
typedef struct {
void * p; /* Pointer to actual object */
unsigned int x; /* Extra information - reuse count etc */
} ptw32_handle_t;
typedef ptw32_handle_t pthread_t;
所以跨平台程序不要假定 pthread_t的實現方式.
說到這. 後面基本都是大白話. 最需要注意的是上面關於加鎖部分. 這些內容是為了防止沖突,都對定時器鏈表修改導致數據意外.
關於 鏈表的插入和刪除都是老套路, 多寫多練習. 算法也許有點吹毛求疵.數據結構真的會用到.
多線程部分, 也不好搞,特別是調試部分. 沒什麼好方法,從同步開始, 慢慢來...
//設置線程屬性, 默認線程屬性 允許退出線程
pthread_setcanceltype(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS, NULL); //設置立即取消
pthread_detach(pthread_self()); //設置線程分離,自銷毀
上面代碼意思,注釋了. 第一個是為了, 在pthread_cancel的時候能夠起到效果. 後面是為了分離. 讓其銷毀時候不再保留對象等待pthread_join來回收.
總的而言多線程編程門道很多. 水很深. 很多選手也就會create 一下, 當然我自己也是. 有機會單獨寫個專題深入講解多線程開發.或多線程業務代碼剖析.
到這裡,基本上講解完了. 代碼短不好理解. 就當看看吧, 了解一種思路總是好的. (可能上面代碼中也存在錯誤,以後再更正吧).
先講講linux 上測試結果. 測試代碼 test_sctimer.c
#include <sctimer.h>
static int _sm;
static void _timer(void* arg)
{
char tstr[64];
sh_times(tstr, LEN(tstr));
printf("%p + %d => %s\n", arg, ++_sm, tstr);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
st_add(0, 5, 2000, _timer, (void*)1, false);
st_add(3000, 2, 2000, _timer, (void*)2, false);
st_add(4000, 1, 2000, _timer, (void*)3, false);
// 開啟一個多線程的永久異步方法
int tid = st_add(0, 0, 1000, _timer, (void*)4, true);
// 等待5秒後關閉 上面永久的定時器事件
SLEEPMS(5000);
st_del(tid);
// 再注冊一個方法
st_add(100, 0, 5000, _timer, (void*)5, false);
sh_pause();
return 0;
}
運行的測試結果如下
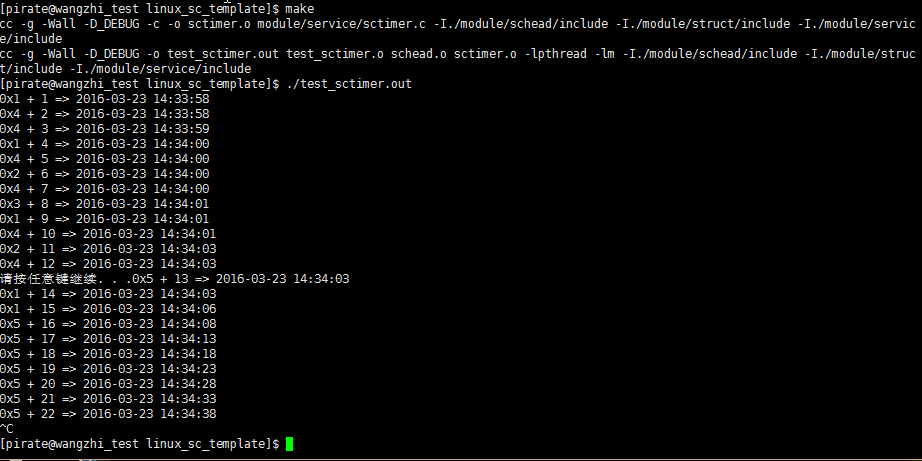
基本上能跑起來.
那好吧. 我貼上 用到的其它代碼圖.
schead.h
schead.c

scatom.h

Makefile

你需要找到從Makefile中找到 關於 test_sctimer.h 的編譯代碼.
目前關於 simple c linux上代碼結構如下
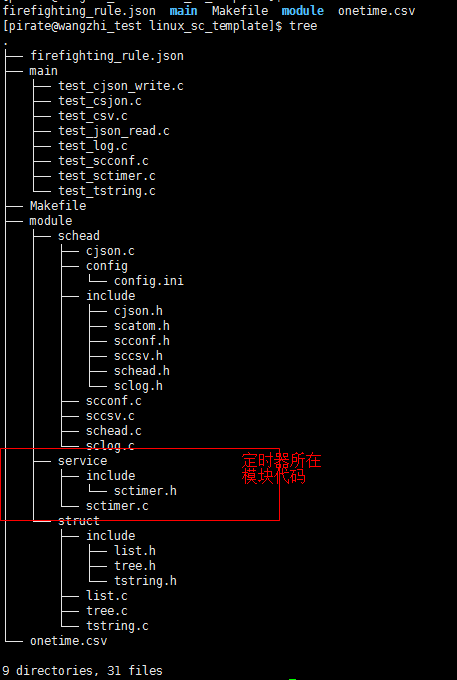
等再搞個大補丁再統一上傳到githup上吧. 目前還是以分享為主, 自己測試測試. 再小的模塊, 都不好做.因為你想做好.
後記
錯誤是難免,歡迎交流指正.結構決定算法,算法優化結構. 環境限制代碼...codeing...
靜靜的看著你裝逼 http://music.163.com/#/song?id=402070795