在Windows下我們可以利用ipconfig命令獲取網卡的相關信息,在Linux下命令是ifconfig
我們可以 獲取的信息更為豐富,其中包括網卡接收和發送的流量,用C語言實現這個命令並不是一件簡單的事,由此, 博主經查閱相關資料,得知,網卡的相關信息保存在 /proc/net/dev 這個文件夾下,所以,我們可以 通過讀取這個文件裡的信息獲取相應網卡的信息。
這個文件包含四部分內容,分別是:發送包的個數 ,發送的流量,接收包的個數,接收的流量,同時,由於網絡環境在不斷的變化之中,所以,這個文件的內容 也是在實時更新的。
下面這張圖片顯示的是 ifconfig 命令的實現結果
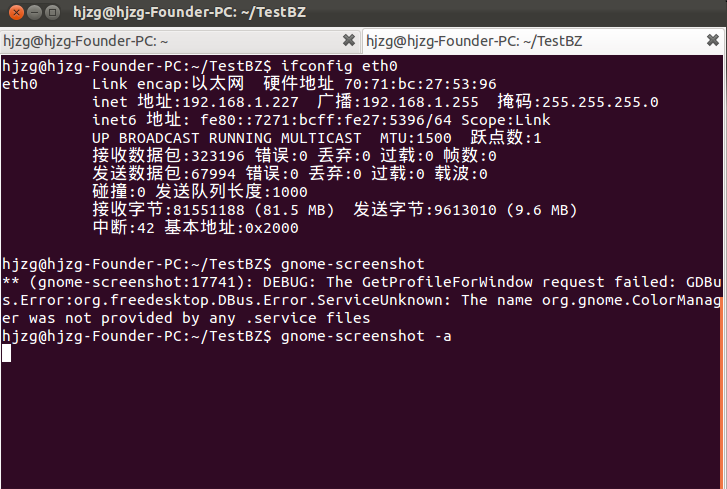
注意,其中有許多參數,這些參數並不保存在文件中
下面是博主實現的一段C語言代碼獲取接收和 發送的流量
重要的地方已經給出了注釋
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
long *my_ipconfig(char *ath0)
{
int nDevLen = strlen(ath0);
if (nDevLen < 1 || nDevLen > 100)
{
printf("dev length too long\n");
return NULL;
}
int fd = open("/proc/net/dev", O_RDONLY | O_EXCL);
if (-1 == fd)
{
printf("/proc/net/dev not exists!\n");
return NULL;
}
char buf[1024*2];
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
int nBytes = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)-1);
if (-1 == nBytes)
{
perror("read error");
close(fd);
return NULL;
}
buf[nBytes] = '\0';
//返回第一次指向ath0位置的指針
char* pDev = strstr(buf, ath0);
if (NULL == pDev)
{
printf("don't find dev %s\n", ath0);
return NULL;
}
char *p;
char *ifconfig_value;
int i = 0;
static long rx2_tx10[2];
/*去除空格,制表符,換行符等不需要的字段*/
for (p = strtok(pDev, " \t\r\n"); p; p = strtok(NULL, " \t\r\n"))
{
i++;
ifconfig_value = (char*)malloc(20);
strcpy(ifconfig_value, p);
/*得到的字符串中的第二個字段是接收流量*/
if(i == 2)
{
rx2_tx10[0] = atol(ifconfig_value);
}
/*得到的字符串中的第十個字段是發送流量*/
if(i == 10)
{
rx2_tx10[1] = atol(ifconfig_value);
break;
}
free(ifconfig_value);
}
return rx2_tx10;
}
int main()
{
long *ifconfig_result;
double re_mb;
/*eth0 是博主計算機上的網卡的名字*/
ifconfig_result = my_ipconfig("eth0");
/*保存在文件中的數值的單位是B,經過計算換算成MB*/
re_mb = (double)ifconfig_result[0]/(1024*1024);
printf("接收流量:%0.2f MB\n",re_mb);
/*保存在文件中的數值的單位是B,經過計算換算成MB*/
re_mb = (double)ifconfig_result[1]/(1024*1024);
printf("發送流量:%0.2f MB\n",re_mb);
}
保存文件的名字為 dele.c
運行相關的命令:
gcc -o dele dele.c
./dele
得到結果如下圖所示
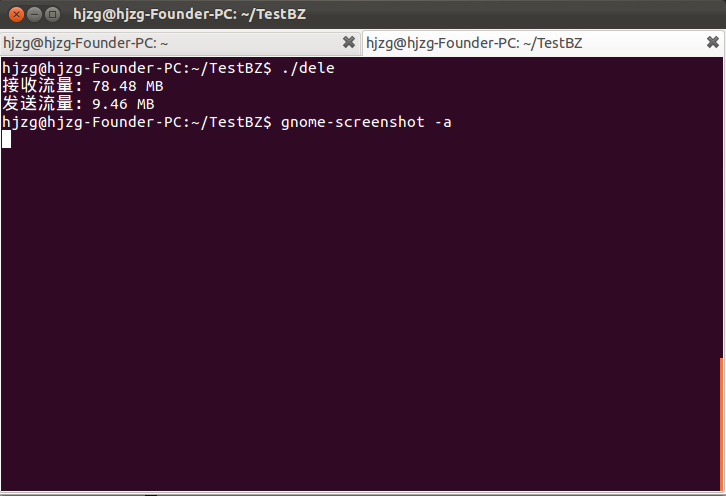
由此得到了網卡的接收和發送流量