本文配套源碼
在如今的網絡應用中,文件的傳送是重要的功能之一,也是共享的基礎。一些重要的協議像HTTP, FTP等都支持文件的傳送。尤其是FTP,它的全稱就是“文件傳送協議”,當初的工程師設計 這一協議就是為了解決網絡間的文件傳送問題,而且以其穩定,高速,簡單而一直保持著很大的生命力 。作為一個程序員,使用這些現有的協議傳送文件相當簡單,不過,它們只適用於服務器模式中。這樣 ,當我們想在點與點之間傳送文件就不適用了或相當麻煩,有一種大刀小用的意味。筆者一直想尋求一 種簡單有效,且具備多線程斷點續傳的方法來實現點與點之間的文件傳送問題,經過大量的翻閱資料與 測試,終於實現了,現把它共享出來,與大家分享。
我寫了一個以此為基礎的實用程序(網絡傳聖,包含源代碼),可用了基於TCP/IP的電腦上,供大家學習。
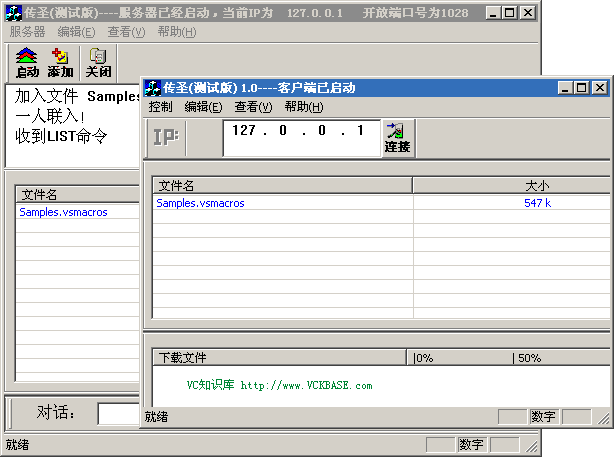
(本文源代碼運行效果圖)
實現方法(VC++,基於TCP/IP協議)如下:
仍釆用服務器與客戶模式,需分別對其設 計與編程。
服務器端較簡單,主要就是加入待傳文件,監聽客戶,和傳送文件。而那些斷點續傳 的功能,以及文件的管理都放在客戶端上。
一、服務器端
首先介紹服務器端:
最 開始我們要定義一個簡單的協議,也就是定義一個服務器端與客戶端聽得懂的語言。而為了把問題簡化 ,我就讓服務器只要聽懂兩句話,一就是客戶說“我要讀文件信息”,二就是“我准備 好了,可以傳文件了”。
由於要實現多線程,必須把功能獨立出來,且包裝成線程,首先 建一個監聽線程,主要負責接入客戶,並啟動另一個客戶線程。我用VC++實現如下:
DWORD WINAPI listenthread(LPVOID lpparam)
{
//由主函數傳來的套接 字
SOCKET pthis=(SOCKET)lpparam;
//開始監聽
int rc=listen (pthis,30);
//如果錯就顯示信息
if(rc<0){
CString aaa;
aaa="listen錯誤\n";
AfxGetMainWnd()- >SendMessageToDescendants(WM_AGE1,(LPARAM)aaa.GetBuffer(0),1);
aaa.ReleaseBuffer();
return 0;
}
//進入循環,並接收到來的套接 字
while(1){
//新建一個套接字,用於客戶端
SOCKET s1;
s1=accept(pthis,NULL,NULL);
//給主函數發有人聯入消息
CString aa;
aa="一人聯入!\n";
AfxGetMainWnd()->SendMessageToDescendants (WM_AGE1,(LPARAM)aa.GetBuffer(0),1);
aa.ReleaseBuffer();
DWORD dwthread;
//建立用戶線程
::CreateThread(NULL,0,clientthread,(LPVOID) s1,0,&dwthread);
}
return 0;
}
接著我們來看用戶線程:
先看文件消息類定義:
struct fileinfo
{
int fileno;//文件號
int type;//客戶端想說什麼(前面那兩句話,用1,2表示)
long len;//文件長度
int seek;//文件開始位置,用於多線程
char name[100];//文件名
};
用戶線程函數:
DWORD WINAPI clientthread(LPVOID lpparam)
{
//文件消息
fileinfo* fiinfo;
//接收緩存
char* m_buf;
m_buf=new char[100];
//監聽函數傳來的用戶套接字
SOCKET pthis=(SOCKET) lpparam;
//讀傳來的信息
int aa=readn(pthis,m_buf,100);
//如果有 錯就返回
if(aa<0){
closesocket (pthis);
return -1;
}
//把傳來的信息轉為定義的文件信息
fiinfo=(fileinfo*)m_buf;
CString aaa;
//檢驗客戶想說什麼
switch(fiinfo->type)
{
//我要讀文件信息
case 0:
//讀文件
aa=sendn(pthis,(char*) zmfile,1080);
//有錯
if(aa<0){
closesocket (pthis);
return -1;
}
//發消息給主函數
aaa="收到LIST命令 \n";
AfxGetMainWnd()->SendMessageToDescendants(WM_AGE1,(LPARAM) aaa.GetBuffer(0),1);
break;
//我准備好了,可以傳文件了
case 2:
//發文件消息給主函數
aaa.Format("%s 文件被請求!% s\n",zmfile[fiinfo->fileno].name,nameph[fiinfo->fileno]);
AfxGetMainWnd()->SendMessageToDescendants(WM_AGE1,(LPARAM)aaa.GetBuffer(0),1);
//讀文件,並傳送
readfile(pthis,fiinfo->seek,fiinfo->len,fiinfo- >fileno);
//聽不懂你說什麼
default:
aaa="接收協議錯誤! \n";
AfxGetMainWnd()->SendMessageToDescendants(WM_AGE1,(LPARAM) aaa.GetBuffer(0),1);
break;
}
return 0;
}
讀文件函數
void readfile(SOCKET so,int seek,int len,int fino)
{
//文件名
CString myname;
myname.Format("%s",nameph[fino]);
CFile myFile;
//打開文件
myFile.Open(myname, CFile::modeRead | CFile::typeBinary|CFile::shareDenyNone);
//傳到指定位置
myFile.Seek (seek,CFile::begin);
char m_buf[SIZE];
int len2;
int len1;
len1=len;
//開始接收,直到發完整個文件
while(len1>0){
len2=len>SIZE?SIZE:len;
myFile.Read(m_buf, len2);
int aa=sendn(so,m_buf,len2);
if(aa<0){
closesocket (so);
break;
}
len1=len1-aa;
len=len-aa;
}
myFile.Close();
}
服務器端最要的功能各技術就是這些,下面介紹客戶端。
二、客戶端
客戶端最重要,也最復雜,它負責線程的管理,進度的記錄等工作。
大概流程 如下:
先連接服務器,接著發送命令1(給我文件信息),其中包括文件長度,名字等,然後根 據長度決定分幾個線程下載,並初使化下載進程,接著發送命令2(可以給我傳文件了),並記錄文件進 程。最後,收尾。
這其中有一個十分重要的類,就是cdownload類,定義如下:
class cdownload
{
public:
void createthread();//開線程
DWORD finish1();//完成線程
int sendlist();//發命令1
downinfo doinfo;//文件信息 (與服務器定義一樣)
int startask(int n);開始傳文件n
long m_index;
BOOL good[BLACK];
int filerange[100];
CString fname;
CString fnametwo;
UINT threadfunc(long index);//下載進程
int sendrequest (int n);//發文件信息
cdownload(int thno1);
virtual ~cdownload();
};
下面先介紹sendrequest(int n),在開始前,向服務器發獲得文件消息命令,以便讓客 戶端知道有哪些文件可傳
int cdownload::sendrequest(int n)
{
//建套接 字
sockaddr_in local;
SOCKET m_socket;
int rc=0;
//初使 化服務器地址
local.sin_family=AF_INET;
local.sin_port=htons(1028);
local.sin_addr.S_un.S_addr=inet_addr(ip);
m_socket=socket (AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
int ret;
//聯接服務器
ret=connect(m_socket,(LPSOCKADDR)&local,sizeof(local));
//有錯的話
if(ret<0){
AfxMessageBox("聯接錯誤");
closesocket (m_socket);
return -1;
}
//初使化命令
fileinfo fileinfo1;
fileinfo1.len=n;
fileinfo1.seek=50;
fileinfo1.type=1;
//發送命令
int aa=sendn(m_socket,(char*) &fileinfo1,100);
if(aa<0){
closesocket(m_socket);
return -1;
}
//接收服務器傳來的信息
aa=readn(m_socket, (char*)&fileinfo1,100);
if(aa<0){
closesocket(m_socket);
return -1;
}
//關閉
shutdown(m_socket,2);
closesocket(m_socket);
return 1;
}
有了文件消息後我們就可以下載文件 了。在主函數中,用法如下:
//下載第clno個文件,並為它建一個新cdownload類
down[clno]=new cdownload(clno);
//開始下載,並初使化
type=down[clno]- >startask(clno);
//建立各線程
createthread(clno);
下面介紹開始方法:
//開始方法
int cdownload::startask(int n)
{
//讀入文件長度
doinfo.filelen=zmfile[n].length;
//讀入名字
fname=zmfile [n].name;
CString tmep;
//初使化文件名
tmep.Format ("\\temp\\%s",fname);
//給主函數發消息
CString aaa;
aaa="正在讀取 "+fname+" 信息,馬上開始下載。。。\n";
AfxGetMainWnd()->SendMessageToDescendants(WM_AGE1,(LPARAM)aaa.GetBuffer(0),1);
aaa.ReleaseBuffer();
//如果文件長度小於0就返回
if(doinfo.filelen<=0) return -1;
//建一個以.down結尾的文件記錄文件信息
CString m_temp;
m_temp=fname+".down";
doinfo.name=m_temp;
FILE* fp=NULL;
CFile myfile;
//如果是第一次下載文件,初使化各記錄文件
if((fp=fopen(m_temp,"r"))==NULL){
filerange[0]=0;
//文件分塊
for(int i=0;i<BLACK;i++)
{
if(i>0)
filerange[i*2]=i*(doinfo.filelen/BLACK+1);
filerange[i*2+1] =doinfo.filelen/BLACK+1;
}
filerange[BLACK*2-1]=doinfo.filelen-filerange [BLACK*2-2];
myfile.Open(m_temp,CFile::modeCreate|CFile::modeWrite | CFile::typeBinary);
//寫入文件長度
myfile.Write (&doinfo.filelen,sizeof(int));
myfile.Close();
CString temp;
for(int ii=0;ii<BLACK;ii++){
//初使化各進程記錄文件信息(以.downN結尾)
temp.Format(".down%d",ii);
m_temp=fname+temp;
myfile.Open(m_temp,CFile::modeCreate|CFile::modeWrite | CFile::typeBinary);
//寫入 各進程文件信息
myfile.Write(&filerange[ii*2],sizeof(int));
myfile.Write(&filerange[ii*2+1],sizeof(int));
myfile.Close();
}
((CMainFrame*)::AfxGetMainWnd())->m_work.m_ListCtrl->AddItemtwo (n,2,0,0,0,doinfo.threadno);
}
else{
//如果文件已存在,說明是續 傳,讀上次信息
CString temp;
m_temp=fname+".down0";
if((fp=fopen(m_temp,"r"))==NULL)
return 1;
else fclose (fp);
int bb;
bb=0;
//讀各進程記錄的信息
for(int ii=0;ii<BLACK;ii++)
{
temp.Format(".down%d",ii);
m_temp=fname+temp;
myfile.Open(m_temp,CFile::modeRead | CFile::typeBinary);
myfile.Read(&filerange[ii*2],sizeof(int));
myfile.Read(&filerange[ii*2+1],sizeof(int));
myfile.Close();
bb = bb+filerange[ii*2+1];
CString temp;
}
if(bb==0) return 1;
doinfo.totle=doinfo.filelen-bb;
((CMainFrame*)::AfxGetMainWnd())->m_work.m_ListCtrl->AddItemtwo (n,2,doinfo.totle,1,0,doinfo.threadno);
}
//建立下載結束進程timethread ,以管現各進程結束時間。
DWORD dwthread;
::CreateThread (NULL,0,timethread,(LPVOID)this,0,&dwthread);
return 0;
}
下面介紹建立各進程函數,很簡單:
void CMainFrame::createthread(int threadno)
{
DWORD dwthread;
//建立BLACK個進程
for(int i=0;i<BLACK;i++)
{
m_thread[threadno][i]= ::CreateThread(NULL,0,downthread,(LPVOID)down [threadno],0,&dwthread);
}
}
downthread進程函數
DWORD WINAPI downthread(LPVOID lpparam)
{
cdownload* pthis=(cdownload*)lpparam;
//進程引索+1
InterlockedIncrement(&pthis->m_index);
//執行 下載進程
pthis->threadfunc(pthis->m_index-1);
return 1;
}
下面介紹下載進程函數,最最核心的東西了
UINT cdownload::threadfunc(long index)
{
//初使化聯接
sockaddr_in local;
SOCKET m_socket;
int rc=0;
local.sin_family=AF_INET;
local.sin_port=htons(1028);
local.sin_addr.S_un.S_addr=inet_addr(ip);
m_socket=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
int ret;
//讀入緩存
char* m_buf=new char[SIZE];
int re,len2;
fileinfo fileinfo1;
// 聯接
ret=connect(m_socket,(LPSOCKADDR)&local,sizeof(local));
//讀入各 進程的下載信息
fileinfo1.len=filerange[index*2+1];
fileinfo1.seek=filerange[index*2];
fileinfo1.type=2;
fileinfo1.fileno=doinfo.threadno;
re=fileinfo1.len;
//打開文 件
CFile destFile;
FILE* fp=NULL;
//是第一次傳的話
if((fp=fopen(fname,"r"))==NULL)
destFile.Open(fname, CFile::modeCreate|CFile::modeWrite | CFile::typeBinary|CFile::shareDenyNone);
else
//如果文件存在,是續傳
destFile.Open(fname,CFile::modeWrite | CFile::typeBinary|CFile::shareDenyNone);
//文件指針移到指定位置
destFile.Seek(filerange[index*2],CFile::begin);
//發消息給服務器,可以傳文件了
sendn(m_socket,(char*)&fileinfo1,100);
CFile myfile;
CString temp;
temp.Format(".down%d",index);
m_temp=fname+temp;
//當各段長度還不為0時
while(re>0){
len2=re>SIZE?SIZE:re;
//讀各段內容
int len1=readn(m_socket,m_buf,len2);
//有錯的話
if(len1<0){
closesocket(m_socket);
break;
}
//寫入文件
destFile.Write(m_buf, len1);
//更改記錄進度信息
filerange[index*2+1]-=len1;
filerange [index*2]+=len1;
//移動記錄文件指針到頭
myfile.Seek(0,CFile::begin);
//寫入記錄進度
myfile.Write(&filerange[index*2],sizeof(int));
myfile.Write(&filerange[index*2+1],sizeof(int));
//減去這次讀的長度
re=re-len1;
//加文件長度
doinfo.totle=doinfo.totle+len1;
};
//這塊下載完成,收尾
myfile.Close();
destFile.Close ();
delete [] m_buf;
shutdown(m_socket,2);
if (re<=0) good[index]=TRUE;
return 1;
}
到這客戶端的主要模塊和機制 已基本介紹完。希望好好體會一下這種多線程斷點續傳的方法。