1.1.1 摘要
相信許多人都使用過.NET提供的加密算法,而且在使用的過程我們必須了解每種加密算法的特點(對稱或非對稱,密鑰長度和初始化向量等等)。我也看到過很多人寫過.NET中加密算法總結,但我發現個別存在一些問題,很多人喜歡羅列每種加密算法的具體實現,假設我們要求實現AES和Triple DES加密算法,的確可以很多地分別給出它們的具體實現。
那我們真的有必要給出每個加密算法的具體實現嗎?而且這樣的設計不符合OOP設計思想,最重要的是我們要維護多個加密算法啊!OK接下來讓我們實行一個可擴展和好維護的加密算法Helper。
1.1.2 正文
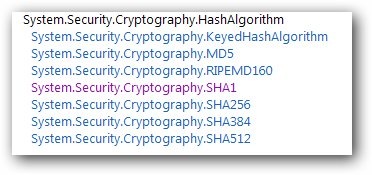
圖1 Hash加密算法繼承層次
從上面的繼承層次我們可以知道.NET中提供七種Hash加密算法,它們都繼承於抽象類HashAlgorithm,而且我們經常使用MD5,SHA1和SHA256等加密算法。下面我們將給出MD5和SHA1的實現。
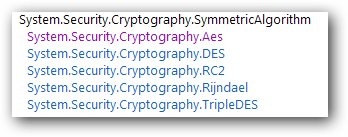
圖2 對稱加密算法繼承層次
從上面的繼承層次我們可以知道.NET中提供五種對稱加密算法,它們都繼承於抽象類SymmetricAlgorithm,下面我們將給出它們的通用實現。
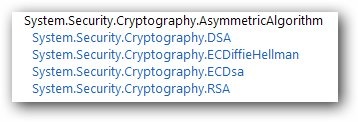
圖3 非對稱加密算法繼承層次
從上面的繼承層次我們可以知道.NET中提供四種非對稱加密算法,它們都繼承於抽象類AsymmetricAlgorithm,下面我們將給出RSA實現。
除了以上加密算法,.NET還提供了很多其他類型的加密,這裡我們主要介紹一些常用的加密算法,如果大家需要了解的話可以查閱MSDN。OK接下來讓我們給出Hash加密算法的實現吧。
Hash加密算法
在給出具體的算法實現之前,首先讓我們回憶一下什麼是Hash加密算法?
Hash加密是通過使用hash函數對要加密的信息進行加密,然後生成相應的哈希值,那麼我們可以定義一個hash()函數,要加密的信息m和加密後的哈希值h。
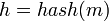
我們對信息m1和m2進行hash加密,就可以獲取相應哈希值hash(m1)和hash(m2)。
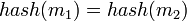
如果信息m1=m2那麼,那麼將得到同一的哈希地址,但是信息m1!=m2也可能得到同一哈希地址,那麼就發生了哈希沖突(collision),在一般的情況下,哈希沖突只能盡可能地減少,而不能完全避免。當發生哈希沖突時,我們要使用沖突解決方法,而主要的沖突解決方法:開放地址法、再哈希法、鏈地址法和建立一個公共溢出區。
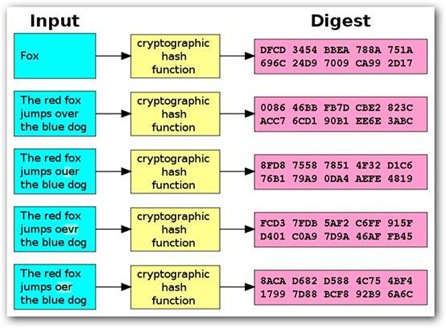
圖4 Hash加密過程(圖片來源wiki)
現在讓我們來實現通用的hash加密方法。
/// <summary>
/// Encrypts the specified hash algorithm.
/// 1. Generates a cryptographic Hash Key for the provided text data.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hashAlgorithm">The hash algorithm.</param>
/// <param name="dataToHash">The data to hash.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string Encrypt(HashAlgorithm hashAlgorithm, string dataToHash)
{
var tabStringHex = new string[16];
var UTF8 = new System.Text.UTF8Encoding();
byte[] data = UTF8.GetBytes(dataToHash);
byte[] result = hashAlgorithm.ComputeHash(data);
var hexResult = new StringBuilder(result.Length);
for (int i = 0; i < result.Length; i++)
{
//// Convert to hexadecimal
hexResult.Append(result[i].ToString("X2"));
}
return hexResult.ToString();
}
上面的加密方法包含一個HashAlgorithm類型的參數,我們可以傳遞繼承於抽象類HashAlgorithm的具體hash算法(MD5,SHA1和SHA256等),通過繼承多態性我們使得加密方法更加靈活、簡單,最重要的是現在我們只需維護一個通用的加密方法就OK了。
接著我們要添加判斷加密後哈希值是否相等的方法,判斷哈希值是否相等的方法IsHashMatch()方法。
/// <summary>
/// Determines whether [is hash match] [the specified hash algorithm].
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hashAlgorithm">The hash algorithm.</param>
/// <param name="hashedText">The hashed text.</param>
/// <param name="unhashedText">The unhashed text.</param>
/// <returns>
/// <c>true</c> if [is hash match] [the specified hash algorithm];
/// otherwise, <c>false</c>.
/// </returns>
public static bool IsHashMatch(HashAlgorithm hashAlgorithm,
string hashedText, string unhashedText)
{
string hashedTextToCompare = Encrypt(
hashAlgorithm, unhashedText);
return (String.Compare(hashedText,
hashedTextToCompare, false) == 0);
}
對稱加密算法
現在我們完成了通用的Hash加密方法了,接下來我們繼續介紹對稱和非對稱算法。
在實現對稱加密算法之前,先讓我們了解一下對稱加密的過程,假設我們有一組數據要加密那麼我們可以使用一個或一組密鑰對數據進行加密解密,但存在一個問題對稱加密算法的密鑰長度不盡相同,如DES的密鑰長度為64 bit,而AES的長度可以為128bit、192bit或256 bit,難道要我們hard code每種算法的密鑰長度嗎?能不能動態地產生對應算法的密鑰呢?
其實.NET已經提供我們根據不同的對稱算法生成對應密鑰的方法了,並且把這些方法都封裝在PasswordDeriveBytes和Rfc2898DeriveBytes類中。
首先讓我們看一下PasswordDeriveBytes類包含兩個方法CryptDeriveKey和GetBytes用來產生對應算法的密鑰,現在讓我們看一下它們如何產生密鑰。
CryptDeriveKey:
// The sample function.
public void Encrypt()
{
// The size of the IV property must be the same as the BlockSize property.
// Due to the RC2 block size is 64 bytes, so iv size also is 64 bytes.
var iv = new byte[] { 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
var pdb = new PasswordDeriveBytes("pwd", null);
// Set the encrypted algorithm and export key algorithm.
// Then get the key base on encrypt algorithm.
byte[] key = pdb.CryptDeriveKey("RC2", "SHA1", 128, iv);
Console.WriteLine(key.Length * 8);
Console.WriteLine(new RC2CryptoServiceProvider().BlockSize);
// Creates an RC2 object to encrypt with the derived key
var rc2 = new RC2CryptoServiceProvider
{
Key = key,
IV = new byte[] { 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28 }
};
// now encrypt with it
byte[] plaintext = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("NeedToEncryptData");
using (var ms = new MemoryStream())
{
var cs = new CryptoStream(
ms, rc2.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cs.Write(plaintext, 0, plaintext.Length);
cs.Close();
byte[] encrypted = ms.ToArray();
}
}
示意例子一:我們使用SHA1哈希算法為RC2加密算法生成128bit的密鑰,這樣我們就可以根據不同對稱加密算法獲取相應長度的密鑰了,注意我們並沒用動態地生成初始化向量iv,這是為了簡單起見實際中不應該這樣獲取初始化向量。
接下來讓我們看一下通過PBKDF1和PBKDF2s算法生成密鑰的實現。
PBKDF1
GetBytes:PasswordDeriveBytes的GetBytes()方法實現了PBKDF1(Password Based Key Derivation Function)。
PBKDF1算法過程:
1.拼接密鑰和鹽:R0 = Pwd + Salt
2.哈希加密過程:R1 = Hash(R2-1)
……..
3.哈希加密過程:Rn = Hash(Rn - 1)
4.n是迭代的次數(參考PBKDF1規范請點這裡)
現在我們對PBKDF1算法的原理有了初步的了解,接下來我們將通過GetBytes()調用該算法生成密鑰。
/// <summary>
/// Uses the PBKDF1 to genernate key,
/// then use it to encrypt plain text.
/// </summary>
public void PBKDF1()
{
byte[] salt = new byte[] { 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
// Creates an RC2 object to encrypt with the derived key
var pdb = new PasswordDeriveBytes("pwd", salt)
{IterationCount = 23, HashName = "SHA1"};
// Gets the key and iv.
byte[] key = pdb.GetBytes(16);
byte[] iv = pdb.GetBytes(8);
var rc2 = new RC2CryptoServiceProvider { Key = key, IV = iv };
byte[] plaintext = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("NeedToEncryptData");
using (var ms = new MemoryStream())
{
// Encrypts data.
var cs = new CryptoStream(
ms, rc2.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cs.Write(plaintext, 0, plaintext.Length);
cs.Close();
byte[] encrypted = ms.ToArray();
}
}
示意例子二:我們使用PBKDF1算法為RC2加密算法生成128 bit的密鑰和64 bit的初始化向量,要注意的是PasswordDeriveBytes的GetBytes()方法已經過時了,而它的替代項就是接下來要介紹的Rfc2898DeriveBytes的GetBytes()方法。
PBKDF2
GetBytes:由於Rfc2898DeriveBytes的GetBytes()方法實現了PBKDF2算法,而且它也替代了PBKDF1過時的GetBytes()方法,所以我們推薦使用Rfc2898DeriveBytes的GetBytes()方法。
/// <summary>
/// Uses the PBKDF2 to genernate key,
/// then use it to encrypt plain text.
/// </summary>
public void PBKDF2()
{
byte[] salt = new byte[] { 23, 21, 32, 33, 46, 59, 60, 74 };
var rfc = new Rfc2898DeriveBytes("pwd", salt, 23);
// generate key and iv.
byte[] key = rfc.GetBytes(16);
byte[] iv = rfc.GetBytes(8);
// Creates an RC2 object to encrypt with the derived key
var rc2 = new RC2CryptoServiceProvider { Key = key, IV = iv };
// Encrypts the data.
byte[] plaintext = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("NeedToEncryptData");
using (var ms = new MemoryStream())
{
var cs = new CryptoStream(
ms, rc2.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cs.Write(plaintext, 0, plaintext.Length);
cs.Close();
byte[] encrypted = ms.ToArray();
}
}
示意例子三:我們發現PBKDF2()方法和之前的PBKDF1()方法沒有什麼區別,就是無需指定加密密鑰的哈希算法(參考PBKDF2規范請點這裡)。
前面通過三種方法來動態的生成加密密鑰,而且我們將使用Rfc2898DeriveBytes的GetBytes()方法來獲取密鑰,那麼接下來讓我們使用該方法實現通用的對稱加密算法吧!
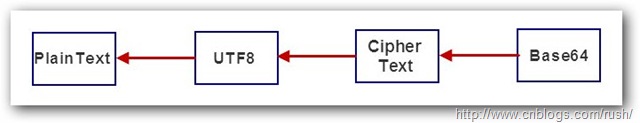
圖5 對稱算法加密過程
首先我們對加密的平文進行編碼,這裡默認使用UTF8對平文進行編碼,也可以使用其他編碼方式,接著使用相應加密算法對編碼後的平文進行加密,最後把加密後的Byte數組轉換為Base64格式字符串返回。
/// <summary>
/// Encrypts with specified symmetric algorithm.
/// Can be Aes, DES, RC2, Rijndael and TripleDES.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="algorithm">The symmertric algorithm (Aes, DES, RC2, Rijndael and TripleDES).</param>
/// <param name="plainText">The plain text need to be encrypted.</param>
/// <param name="key">The secret key to encrypt plain text.</param>
/// <param name="iv">The iv should be 16 bytes.</param>
/// <param name="salt">Salt to encrypt with.</param>
/// <param name="pwdIterations">The number of iterations for plain text.</param>
/// <param name="keySize">Size of the key.</param>
/// <param name="cipherMode">The cipher mode.</param>
/// <param name="paddingMode">The padding mode.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static byte[] Encrypt(SymmetricAlgorithm algorithm, byte[] plainText, string key, string iv,
string salt, int pwdIterations, int keySize, CipherMode cipherMode, PaddingMode paddingMode)
{
if (null == plainText)
throw new ArgumentNullException("plainText");
if (null == algorithm)
throw new ArgumentNullException("algorithm");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(iv))
throw new ArgumentNullException("iv");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(salt))
throw new ArgumentNullException("salt");
// Note the salt should be equal or greater that 64bit (8 byte).
var rfc = new Rfc2898DeriveBytes(key, salt.ToByteArray(), pwdIterations);
using (SymmetricAlgorithm symmAlgo = algorithm)
{
symmAlgo.Mode = cipherMode;
//symmAlgo.Padding = paddingMode;
byte[] cipherTextBytes = null;
using (var encryptor = symmAlgo.CreateEncryptor(
rfc.GetBytes(keySize / 8), iv.ToByteArray()))
{
using (var ms = new MemoryStream())
{
using (var cs = new CryptoStream(
ms, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write))
{
cs.Write(plainText, 0, plainText.Length);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
cipherTextBytes = ms.ToArray();
ms.Close();
cs.Close();
}
}
symmAlgo.Clear();
return cipherTextBytes;
}
}
}
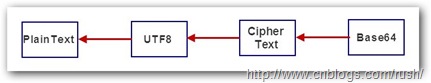
圖5 對稱算法解密過程
通過上圖的解密過程,我們發現解密過程恰恰是加密的反向,首先把Base64格式的密文轉換為Byte數組,接著使用對應的解密算法解密密文,最後對解密後的數據進行編碼返回平文(默認使用UTF8)。
/// <summary>
/// Decrypts the specified algorithm.
/// Can be Aes, DES, RC2, Rijndael and TripleDES.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="algorithm">The symmertric algorithm (Aes, DES, RC2, Rijndael and TripleDES).</param>
/// <param name="cipherText">The cipher text.</param>
/// <param name="key">The secret key to decrypt plain text.</param>
/// <param name="iv">The iv should be 16 bytes.</param>
/// <param name="salt">Salt to decrypt with.</param>
/// <param name="pwdIterations">The number of iterations for plain text.</param>
/// <param name="keySize">Size of the key.</param>
/// <param name="cipherMode">The cipher mode.</param>
/// <param name="paddingMode">The padding mode.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static byte[] Decrypt(SymmetricAlgorithm algorithm, byte[] cipherText,
string key, string iv, string salt, int pwdIterations, int keySize,
CipherMode cipherMode, PaddingMode paddingMode)
{
if (null == cipherText)
throw new ArgumentNullException("cipherText");
if (null == algorithm)
throw new ArgumentNullException("algorithm");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(iv))
throw new ArgumentNullException("iv");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(salt))
throw new ArgumentNullException("salt");
// Note the salt should be equal or greater that 64bit (8 byte).
var rfc = new Rfc2898DeriveBytes(key, salt.ToByteArray(), pwdIterations);
using (SymmetricAlgorithm symmAlgo = algorithm)
{
symmAlgo.Mode = cipherMode;
//symmAlgo.Padding = paddingMode;
byte[] plainTextBytes = new byte[cipherText.Length];
int cnt = -1;
using (var encryptor = symmAlgo.CreateDecryptor(
rfc.GetBytes(keySize / 8), iv.ToByteArray()))
{
using (var ms = new MemoryStream(cipherText))
{
using (var cs = new CryptoStream(
ms, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Read))
{
cnt = cs.Read(plainTextBytes, 0, plainTextBytes.Length);
ms.Close();
cs.Close();
}
}
}
symmAlgo.Clear();
Array.Resize(ref plainTextBytes, cnt);
return plainTextBytes;
}
}
在前面的加密和解密方法,我們通過Rfc2898DeriveBytes獲取密碼、salt 值和迭代次數,然後通過調用GetBytes方法生成密鑰。
現在我們已經完成了通用的對稱加密算法,我們只需一組加密和解密方法就可以隨意的使用任意一種對稱加密算法了,而不是為每個加密和解密算法編寫相應的加密和解密方法。
非對稱加密算法
.NET Framework中提供四種非對稱加密算法(DSA,ECDiffieHellman, ECDsa和RSA),它們都繼承於抽象類AsymmetricAlgorithm,接下來我們將提供RSA算法的實現。
RSA加密算法是一種非對稱和雙鑰加密算法,在公鑰加密標准和電子商業中RSA被廣泛使用。
在雙鑰加密的情況下,密鑰有兩把,一把是公開的公鑰,還有一把是不公開的私鑰。
雙鑰加密的原理如下:
a) 公鑰和私鑰是一一對應的關系,有一把公鑰就必然有一把與之對應的、獨一無二的私鑰,反之亦成立。
b) 所有的(公鑰, 私鑰)對都是不同的。
c) 用公鑰可以解開私鑰加密的信息,反之亦成立。
d) 同時生成公鑰和私鑰應該相對比較容易,但是從公鑰推算出私鑰,應該是很困難或者是不可能的。
現在的數字簽名加密主要是使用RSA算法,什麼是數字簽名大家請點這裡(中文)和這裡(英文)。
現在我們知道RSA算法是使用公鑰和密鑰進行加密和解密,所以我們先定義一個方法來生成公鑰和密鑰。
/// <summary>
/// Generates the RSA public and private key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="algorithm">The algorithm to creates key.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static void GenerateRSAKey(RSACryptoServiceProvider algorithm)
{
// Contains public and private key.
RSAPrivateKey = algorithm.ToXmlString(true);
using (var streamWriter = new StreamWriter("PublicPrivateKey.xml"))
{
streamWriter.Write(RSAPrivateKey);
}
// Only contains public key.
RSAPubicKey = algorithm.ToXmlString(false);
using (var streamWriter = new StreamWriter("PublicOnlyKey.xml"))
{
streamWriter.Write(RSAPubicKey);
}
}
通過RSACryptoServiceProvider的ToXmlString()方法我們生成了一對公鑰和密鑰,當參數為true 表示同時包含 RSA 公鑰和私鑰,反之表示僅包含公鑰。
/// <summary>
/// Encrypts with the specified RSA algorithm.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rsa">A RSA object.</param>
/// <param name="plainText">The plain text to decrypt.</param>
/// <param name="key">The key.</param>
/// <param name="encoding">The encoding.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string Encrypt(RSACryptoServiceProvider rsa,
string plainText, string key, Encoding encoding)
{
if (null == rsa)
throw new ArgumentNullException("rsa");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(plainText))
throw new ArgumentNullException("plainText");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
if (null == encoding)
throw new ArgumentNullException("encoding");
string publicKey;
// Reads public key.
using (var streamReader = new StreamReader("PublicOnlyKey.xml"))
{
publicKey = streamReader.ReadToEnd();
}
rsa.FromXmlString(publicKey);
byte[] cipherBytes = rsa.Encrypt(plainText.ToBytesEncoding(encoding), true);
rsa.Clear();
return cipherBytes.ToBase64String();
}
接著我們定義RSA的加密方法,首先我們從流中讀取密鑰和公鑰,然後傳遞給FromXmlString()方法,最後對平文進行加密。
/// <summary>
/// Decrypts with the specified RSA algorithm.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rsa">a RSA object.</param>
/// <param name="cipherText">The cipher text to encrypt.</param>
/// <param name="key">The key.</param>
/// <param name="encoding">The encoding.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string Decrypt(RSACryptoServiceProvider rsa,
string cipherText, string key, Encoding encoding)
{
string privateKey;
// Reads the private key.
using (var streamReader = new StreamReader("PublicPrivateKey.xml"))
{
privateKey = streamReader.ReadToEnd();
}
rsa.FromXmlString(privateKey);
byte[] plainBytes = rsa.Decrypt(cipherText.FromBase64String(), true);
rsa.Clear();
return plainBytes.FromByteToString(encoding);
}
參照加密方法我們很快的實現RSA的解密方法,同樣我們從流中讀取密鑰,然後傳遞給FromXmlString()方法,最後對密文進行解密,注意調用的是RSA算法的Decrypt()方法,在使用膠水代碼時千萬別忘記修改了。
現在我們終於完成了通用的加密解密方法,接下來肯定是要測試一下這些方法的效果如何,這次我使用單元測試。
[TestMethod]
public void TestStart()
{
try
{
string cipherText;
string plainText;
#region Hash Algo
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateHashAlgoMd5(), @"您們好(Hello everyone).");
Assert.IsTrue(CryptographyUtils.IsHashMatch(
CryptographyUtils.CreateHashAlgoMd5(),
cipherText, @"您們好(Hello everyone)."));
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateHashAlgoSHA1(),
@"您們好(Hello everyone).");
Assert.IsTrue(CryptographyUtils.IsHashMatch(
CryptographyUtils.CreateHashAlgoSHA1(),
cipherText, @"您們好(Hello everyone)."));
#endregion
#region Asymm Algo
CryptographyUtils.GenerateRSAKey(CryptographyUtils.CreateAsymmAlgoRSA());
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateAsymmAlgoRSA(), @"%dk>JK.RusH", @"c579D-E>?$)_");
plainText = CryptographyUtils.Decrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateAsymmAlgoRSA(), cipherText, @"c579D-E>?$)_");
Assert.AreEqual<string>(@"%dk>JK.RusH", plainText);
#endregion
#region Symm Algo
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoAes(),
"JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
"JK_huangJK_huang", 256);
plainText = CryptographyUtils.Decrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoAes(),
cipherText, "JK_huangJK_huang", 256);
Assert.AreEqual<string>("JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
plainText);
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoDES(),
"JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
"JK_huangJK_huang", 64);
plainText = CryptographyUtils.Decrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoDES(),
cipherText, "JK_huangJK_huang", 64);
Assert.AreEqual<string>("JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
plainText);
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoRC2(),
"JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
"JK_huangJK_huang", 128);
plainText = CryptographyUtils.Decrypt(CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoRC2(),
cipherText, "JK_huangJK_huang", 128);
Assert.AreEqual<string>("JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航", plainText);
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoRijndael(),
"JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
"JK_huangJK_huang", 256);
plainText = CryptographyUtils.Decrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoRijndael(),
cipherText, "JK_huangJK_huang", 256);
Assert.AreEqual<string>("JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航", plainText);
cipherText = CryptographyUtils.Encrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoTripleDes(),
"JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航",
"JK_huangJK_huang", 192);
plainText = CryptographyUtils.Decrypt(
CryptographyUtils.CreateSymmAlgoTripleDes(),
cipherText, "JK_huangJK_huang", 192);
Assert.AreEqual<string>("JK_huangJK_huangJK_huang黃鈞航", plainText);
#endregion
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Debug.Assert(false, ex.Message);
}
}
圖6 單元測試結果
1.1.3 總結
本文給出了.NET中的一些加密算法的通用實現(哈希加密,對稱加密和非對稱加密算法),由於加密和解密的方法都是比較固定,而且每中算法有具有其特性,所以這裡我們給出了它們的實現,而且我們可以把上的方法封裝在一個加密Helper類,這樣可以大大提高我們開發效率,而且它充分的利用多態性使得加密算法靈活性和維護性大大提高。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持腳本之家。