一說到Cookie我想大家都應該知道它是一個保存在客戶端,當浏覽器請求一個url時,浏覽器會攜帶相關的Cookie達到服務器端,所以服務器是可以操作Cookie的,在Response時,會把Cookie信息輸出到客服端。下面我們來看一個demo吧,代碼如下:
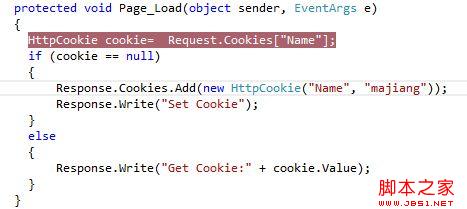
第一次請求結果如下:
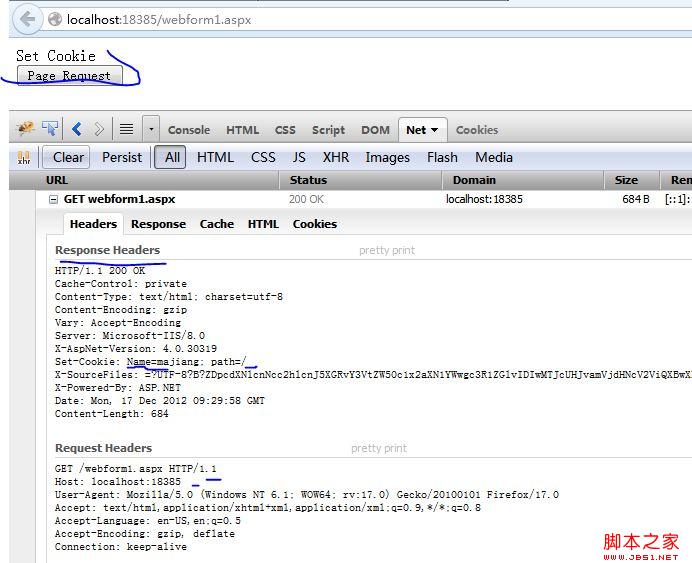
第二次請求結果如下:
到這裡我們可以看到第二次請求傳入的Cookie正好是第一次請求返回的Cookie信息,這裡的cookie信息的維護主要是我們客戶端的浏覽器,但是在Asp.net程序開發時,Cookie往往是在服務端程序裡面寫入,就如我的事例代碼;很少有用客服端js實現的。現在我們就來看看asp.net服務端是如何實現讀寫Cookie的。
首先我們來看看HttpRequest的Cookie是如何定義的:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public HttpCookieCollection Cookies {
get {
EnsureCookies();
if (_flags[needToValidateCookies]) {
_flags.Clear(needToValidateCookies);
ValidateCookieCollection(_cookies);
}
return _cookies;
}
}
這裡的Cookie獲取主要是調用一個EnsureCookies方法,EnsureCookies放主要是調用
復制代碼 代碼如下:
// Populates the Cookies property but does not hook up validation.
internal HttpCookieCollection EnsureCookies() {
if (_cookies == null) {
_cookies = new HttpCookieCollection(null, false);
if (_wr != null)
FillInCookiesCollection(_cookies, true /*includeResponse*/);
if (HasTransitionedToWebSocketRequest) // cookies can't be modified after the WebSocket handshake is complete
_cookies.MakeReadOnly();
}
return _cookies;
}
public sealed class HttpCookieCollection : NameObjectCollectionBase
{
internal HttpCookieCollection(HttpResponse response, bool readOnly) : base(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase)
{
this._response = response;
base.IsReadOnly = readOnly;
}
}
其中這裡的FillInCookiesCollection方法實現也比較復雜:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal void FillInCookiesCollection(HttpCookieCollection cookieCollection, bool includeResponse) {
if (_wr == null)
return;
String s = _wr.GetKnownRequestHeader(HttpWorkerRequest.HeaderCookie);
// Parse the cookie server variable.
// Format: c1=k1=v1&k2=v2; c2=...
int l = (s != null) ? s.Length : 0;
int i = 0;
int j;
char ch;
HttpCookie lastCookie = null;
while (i < l) {
// find next ';' (don't look to ',' as per 91884)
j = i;
while (j < l) {
ch = s[j];
if (ch == ';')
break;
j++;
}
// create cookie form string
String cookieString = s.Substring(i, j-i).Trim();
i = j+1; // next cookie start
if (cookieString.Length == 0)
continue;
HttpCookie cookie = CreateCookieFromString(cookieString);
// some cookies starting with '$' are really attributes of the last cookie
if (lastCookie != null) {
String name = cookie.Name;
// add known attribute to the last cookie (if any)
if (name != null && name.Length > 0 && name[0] == '$') {
if (StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "$Path"))
lastCookie.Path = cookie.Value;
else if (StringUtil.EqualsIgnoreCase(name, "$Domain"))
lastCookie.Domain = cookie.Value;
continue;
}
}
// regular cookie
cookieCollection.AddCookie(cookie, true);
lastCookie = cookie;
// goto next cookie
}
// Append response cookies
if (includeResponse) {
// If we have a reference to the response cookies collection, use it directly
// rather than going through the Response object (which might not be available, e.g.
// if we have already transitioned to a WebSockets request).
HttpCookieCollection storedResponseCookies = _storedResponseCookies;
if (storedResponseCookies == null && !HasTransitionedToWebSocketRequest && Response != null) {
storedResponseCookies = Response.GetCookiesNoCreate();
}
if (storedResponseCookies != null && storedResponseCookies.Count > 0) {
HttpCookie[] responseCookieArray = new HttpCookie[storedResponseCookies.Count];
storedResponseCookies.CopyTo(responseCookieArray, 0);
for (int iCookie = 0; iCookie < responseCookieArray.Length; iCookie++)
cookieCollection.AddCookie(responseCookieArray[iCookie], append: true);
}
// release any stored reference to the response cookie collection
_storedResponseCookies = null;
}
}
說簡單一點它主要調用HttpWorkerRequest的GetKnownRequestHeader方法獲取浏覽器傳進來的Cookie字符串信息,然後再把這些信息根據;來分隔成多個HttpCookie實例。把這些HttpCookie實例添加到傳進來的HttpCookieCollection參數。
這裡HttpWorkerRequest繼承結果如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal class ISAPIWorkerRequestInProcForIIS7 : ISAPIWorkerRequestInProcForIIS6
internal class ISAPIWorkerRequestInProcForIIS6 : ISAPIWorkerRequestInProc
internal class ISAPIWorkerRequestInProc : ISAPIWorkerRequest
internal abstract class ISAPIWorkerRequest : HttpWorkerRequest
其中 GetKnownRequestHeader方法的實現主要是在ISAPIWorkerRequest中,其GetKnownRequestHeader主要是調用了它的ReadRequestHeaders私有方法,在ReadRequestHeaders方法中主要是調用它的this.GetServerVariable("ALL_RAW")方法,所以我們可以認為this.GetServerVariable("ALL_RAW")這個方法是獲取客戶端傳來的Cookie參數,而GetServerVariable方法的實現主要是在ISAPIWorkerRequestInProc 類,具體實現非常復雜。
這裡的GetKnownRequestHeader方法實現非常復雜我們也就不去深研它了,我們只要知道調用這個方法就會返回Cookie的所有字符串信息。在這個方法裡面還調用了一個CreateCookieFromString方法,根據字符串來創建我們的HttpCookie實例。CreateCookieFromString方法實現如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal static HttpCookie CreateCookieFromString(String s) {
HttpCookie c = new HttpCookie();
int l = (s != null) ? s.Length : 0;
int i = 0;
int ai, ei;
bool firstValue = true;
int numValues = 1;
// Format: cookiename[=key1=val2&key2=val2&...]
while (i < l) {
// find next &
ai = s.IndexOf('&', i);
if (ai < 0)
ai = l;
// first value might contain cookie name before =
if (firstValue) {
ei = s.IndexOf('=', i);
if (ei >= 0 && ei < ai) {
c.Name = s.Substring(i, ei-i);
i = ei+1;
}
else if (ai == l) {
// the whole cookie is just a name
c.Name = s;
break;
}
firstValue = false;
}
// find '='
ei = s.IndexOf('=', i);
if (ei < 0 && ai == l && numValues == 0) {
// simple cookie with simple value
c.Value = s.Substring(i, l-i);
}
else if (ei >= 0 && ei < ai) {
// key=value
c.Values.Add(s.Substring(i, ei-i), s.Substring(ei+1, ai-ei-1));
numValues++;
}
else {
// value without key
c.Values.Add(null, s.Substring(i, ai-i));
numValues++;
}
i = ai+1;
}
return c;
}
我們平時很少用到HttpCookie的Values屬性,所以這個屬性大家還是需要注意一下,這個方法就是把一個cookie的字符串轉化為相應的HttpCookie實例。
現在我們回到HttpRequest的Cookies屬性中來,這裡有一個關於Cookie的簡單驗證
復制代碼 代碼如下:
private void ValidateCookieCollection(HttpCookieCollection cc) {
if (_enableGranularValidation) {
// Granular request validation is enabled - validate collection entries only as they're accessed.
cc.EnableGranularValidation((key, value) => ValidateString(value, key, RequestValidationSource.Cookies));
}
else {
// Granular request validation is disabled - eagerly validate all collection entries.
int c = cc.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {
String key = cc.GetKey(i);
String val = cc.Get(i).Value;
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(val))
ValidateString(val, key, RequestValidationSource.Cookies);
}
}
}
其中HttpCookieCollection的EnableGranularValidation實現如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal void EnableGranularValidation(ValidateStringCallback validationCallback)
{
this._keysAwaitingValidation = new HashSet<string>(this.Keys.Cast<string>(), StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
this._validationCallback = validationCallback;
}
private void EnsureKeyValidated(string key, string value)
{
if ((this._keysAwaitingValidation != null) && this._keysAwaitingValidation.Contains(key))
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
this._validationCallback(key, value);
}
this._keysAwaitingValidation.Remove(key);
}
}
到這裡我們知道默認從浏覽器發送到服務器端的Cookie都是需要經過次驗證的。這裡的ValidateString方法具體實現我們就不說了,不過大家需要知道它是調用了RequestValidator.Current.IsValidRequestString方法來實現驗證的,有關RequestValidator的信息大家可以查看HttpRequest的QueryString屬性 的一點認識 。現在我們獲取Cookie已經基本完成了。那麼我們接下來看看是如何添加Cookie的了。
首先我們來看看HttpResponse的Cookie屬性:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public HttpCookieCollection Cookies
{
get
{
if (this._cookies == null)
{
this._cookies = new HttpCookieCollection(this, false);
}
return this._cookies;
}
}
接下來我們看看HttpCookie的實現如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public sealed class HttpCookie {
private String _name;
private String _path = "/";
private bool _secure;
private bool _httpOnly;
private String _domain;
private bool _expirationSet;
private DateTime _expires;
private String _stringValue;
private HttpValueCollection _multiValue;
private bool _changed;
private bool _added;
internal HttpCookie() {
_changed = true;
}
/*
* Constructor - empty cookie with name
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref='System.Web.HttpCookie'/>
/// class.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public HttpCookie(String name) {
_name = name;
SetDefaultsFromConfig();
_changed = true;
}
/*
* Constructor - cookie with name and value
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref='System.Web.HttpCookie'/>
/// class.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public HttpCookie(String name, String value) {
_name = name;
_stringValue = value;
SetDefaultsFromConfig();
_changed = true;
}
private void SetDefaultsFromConfig() {
HttpCookiesSection config = RuntimeConfig.GetConfig().HttpCookies;
_secure = config.RequireSSL;
_httpOnly = config.HttpOnlyCookies;
if (config.Domain != null && config.Domain.Length > 0)
_domain = config.Domain;
}
/*
* Whether the cookie contents have changed
*/
internal bool Changed {
get { return _changed; }
set { _changed = value; }
}
/*
* Whether the cookie has been added
*/
internal bool Added {
get { return _added; }
set { _added = value; }
}
// DevID 251951 Cookie is getting duplicated by ASP.NET when they are added via a native module
// This flag is used to remember that this cookie came from an IIS Set-Header flag,
// so we don't duplicate it and send it back to IIS
internal bool FromHeader {
get;
set;
}
/*
* Cookie name
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Gets
/// or sets the name of cookie.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public String Name {
get { return _name;}
set {
_name = value;
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* Cookie path
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Gets or sets the URL prefix to transmit with the
/// current cookie.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public String Path {
get { return _path;}
set {
_path = value;
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* 'Secure' flag
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Indicates whether the cookie should be transmitted only over HTTPS.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public bool Secure {
get { return _secure;}
set {
_secure = value;
_changed = true;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Determines whether this cookie is allowed to participate in output caching.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// If a given HttpResponse contains one or more outbound cookies with Shareable = false (the default value),
/// output caching will be suppressed for that response. This prevents cookies that contain potentially
/// sensitive information, e.g. FormsAuth cookies, from being cached in the response and sent to multiple
/// clients. If a developer wants to allow a response containing cookies to be cached, he should configure
/// caching as normal for the response, e.g. via the OutputCache directive, MVC's [OutputCache] attribute,
/// etc., and he should make sure that all outbound cookies are marked Shareable = true.
/// </remarks>
public bool Shareable {
get;
set; // don't need to set _changed flag since Set-Cookie header isn't affected by value of Shareable
}
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Indicates whether the cookie should have HttpOnly attribute
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public bool HttpOnly {
get { return _httpOnly;}
set {
_httpOnly = value;
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* Cookie domain
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Restricts domain cookie is to be used with.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public String Domain {
get { return _domain;}
set {
_domain = value;
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* Cookie expiration
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Expiration time for cookie (in minutes).
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public DateTime Expires {
get {
return(_expirationSet ? _expires : DateTime.MinValue);
}
set {
_expires = value;
_expirationSet = true;
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* Cookie value as string
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Gets
/// or
/// sets an individual cookie value.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public String Value {
get {
if (_multiValue != null)
return _multiValue.ToString(false);
else
return _stringValue;
}
set {
if (_multiValue != null) {
// reset multivalue collection to contain
// single keyless value
_multiValue.Reset();
_multiValue.Add(null, value);
}
else {
// remember as string
_stringValue = value;
}
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* Checks is cookie has sub-keys
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>Gets a
/// value indicating whether the cookie has sub-keys.</para>
/// </devdoc>
public bool HasKeys {
get { return Values.HasKeys();}
}
private bool SupportsHttpOnly(HttpContext context) {
if (context != null && context.Request != null) {
HttpBrowserCapabilities browser = context.Request.Browser;
return (browser != null && (browser.Type != "IE5" || browser.Platform != "MacPPC"));
}
return false;
}
/*
* Cookie values as multivalue collection
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>Gets individual key:value pairs within a single cookie object.</para>
/// </devdoc>
public NameValueCollection Values {
get {
if (_multiValue == null) {
// create collection on demand
_multiValue = new HttpValueCollection();
// convert existing string value into multivalue
if (_stringValue != null) {
if (_stringValue.IndexOf('&') >= 0 || _stringValue.IndexOf('=') >= 0)
_multiValue.FillFromString(_stringValue);
else
_multiValue.Add(null, _stringValue);
_stringValue = null;
}
}
_changed = true;
return _multiValue;
}
}
/*
* Default indexed property -- lookup the multivalue collection
*/
/// <devdoc>
/// <para>
/// Shortcut for HttpCookie$Values[key]. Required for ASP compatibility.
/// </para>
/// </devdoc>
public String this[String key]
{
get {
return Values[key];
}
set {
Values[key] = value;
_changed = true;
}
}
/*
* Construct set-cookie header
*/
internal HttpResponseHeader GetSetCookieHeader(HttpContext context) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
// cookiename=
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(_name)) {
s.Append(_name);
s.Append('=');
}
// key=value&...
if (_multiValue != null)
s.Append(_multiValue.ToString(false));
else if (_stringValue != null)
s.Append(_stringValue);
// domain
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(_domain)) {
s.Append("; domain=");
s.Append(_domain);
}
// expiration
if (_expirationSet && _expires != DateTime.MinValue) {
s.Append("; expires=");
s.Append(HttpUtility.FormatHttpCookieDateTime(_expires));
}
// path
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(_path)) {
s.Append("; path=");
s.Append(_path);
}
// secure
if (_secure)
s.Append("; secure");
// httponly, Note: IE5 on the Mac doesn't support this
if (_httpOnly && SupportsHttpOnly(context)) {
s.Append("; HttpOnly");
}
// return as HttpResponseHeader
return new HttpResponseHeader(HttpWorkerRequest.HeaderSetCookie, s.ToString());
}
}
現在我們回到HttpCookieCollection的Add方法看看,
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public void Add(HttpCookie cookie) {
if (_response != null)
_response.BeforeCookieCollectionChange();
AddCookie(cookie, true);
if (_response != null)
_response.OnCookieAdd(cookie);
}
public sealed class HttpResponse
{
internal void BeforeCookieCollectionChange()
{
if (this._headersWritten)
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Cannot_modify_cookies_after_headers_sent"));
}
}
internal void OnCookieAdd(HttpCookie cookie)
{
this.Request.AddResponseCookie(cookie);
}
}
public sealed class HttpRequest
{
internal void AddResponseCookie(HttpCookie cookie)
{
if (this._cookies != null)
{
this._cookies.AddCookie(cookie, true);
}
if (this._params != null)
{
this._params.MakeReadWrite();
this._params.Add(cookie.Name, cookie.Value);
this._params.MakeReadOnly();
}
}
}
到這裡我們應該知道每添加或修改一個Cookie都會調用HttpResponse的BeforeCookieCollectionChange和OnCookieAdd方法,BeforeCookieCollectionChange是確認我們的cookie是否可以添加的,以前在項目中就遇到這裡的錯誤信息說什麼“在header發送後不能修改cookie”,看見默認情況下_headersWritten是false,那麼它通常在哪裡被設置為true了,在HttpReaponse的BeginExecuteUrlForEntireResponse、Flush、EndFlush方法中被設置為true,而我們最常接觸到的還是Flush方法。這裡的OnCookieAdd方法確保Cookie實例同時也添加到HttpRequest中。
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal void AddCookie(HttpCookie cookie, bool append) {
ThrowIfMaxHttpCollectionKeysExceeded();
_all = null;
_allKeys = null;
if (append) {
// DevID 251951 Cookie is getting duplicated by ASP.NET when they are added via a native module
// Need to not double add response cookies from native modules
if (!cookie.FromHeader) {
// mark cookie as new
cookie.Added = true;
}
BaseAdd(cookie.Name, cookie);
}
else {
if (BaseGet(cookie.Name) != null) {
// mark the cookie as changed because we are overriding the existing one
cookie.Changed = true;
}
BaseSet(cookie.Name, cookie);
}
}
private void ThrowIfMaxHttpCollectionKeysExceeded() {
if (Count >= AppSettings.MaxHttpCollectionKeys) {
throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.GetString(SR.CollectionCountExceeded_HttpValueCollection, AppSettings.MaxHttpCollectionKeys));
}
}
這裡的AddCookie方法也非常簡單,不過每次添加都會去檢查Cookie的個數是否超過最大值。其實添加Cookie還可以調用HttpResponse的AppendCookie方法,
復制代碼 代碼如下:
public void AppendCookie(HttpCookie cookie)
{
if (this._headersWritten)
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Cannot_append_cookie_after_headers_sent"));
}
this.Cookies.AddCookie(cookie, true);
this.OnCookieAdd(cookie);
}
這裡它的實現和HttpCookieCollection的 public void Add(HttpCookie cookie)方法實現一致。
同樣我們也知道這些Cookie是在HttpResponse的GenerateResponseHeadersForCookies方法中被使用,
其中GenerateResponseHeadersForCookies方法的實現如下:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
internal void GenerateResponseHeadersForCookies()
{
if (_cookies == null || (_cookies.Count == 0 && !_cookies.Changed))
return; // no cookies exist
HttpHeaderCollection headers = Headers as HttpHeaderCollection;
HttpResponseHeader cookieHeader = null;
HttpCookie cookie = null;
bool needToReset = false;
// Go through all cookies, and check whether any have been added
// or changed. If a cookie was added, we can simply generate a new
// set cookie header for it. If the cookie collection has been
// changed (cleared or cookies removed), or an existing cookie was
// changed, we have to regenerate all Set-Cookie headers due to an IIS
// limitation that prevents us from being able to delete specific
// Set-Cookie headers for items that changed.
if (!_cookies.Changed)
{
for(int c = 0; c < _cookies.Count; c++)
{
cookie = _cookies[c];
if (cookie.Added) {
// if a cookie was added, we generate a Set-Cookie header for it
cookieHeader = cookie.GetSetCookieHeader(_context);
headers.SetHeader(cookieHeader.Name, cookieHeader.Value, false);
cookie.Added = false;
cookie.Changed = false;
}
else if (cookie.Changed) {
// if a cookie has changed, we need to clear all cookie
// headers and re-write them all since we cant delete
// specific existing cookies
needToReset = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (_cookies.Changed || needToReset)
{
// delete all set cookie headers
headers.Remove("Set-Cookie");
// write all the cookies again
for(int c = 0; c < _cookies.Count; c++)
{
// generate a Set-Cookie header for each cookie
cookie = _cookies[c];
cookieHeader = cookie.GetSetCookieHeader(_context);
headers.SetHeader(cookieHeader.Name, cookieHeader.Value, false);
cookie.Added = false;
cookie.Changed = false;
}
_cookies.Changed = false;
}
}
這裡我們還是來總結一下吧:在HttpWorkerRequest中我們調用 GetKnownRequestHeader方法來獲取Cookie的字符串形式,然後再將這裡的字符串轉化為HttpCookie集合供 HttpRequest使用,在HttpResponse中的GenerateResponseHeadersForCookies方法中會處理我們的 cookie實例,調用cookie的GetSetCookieHeader方法得到HttpCookie對應的字符串值,然後把該值添加到 HttpHeaderCollection 集合中(或者修改已有的值)。在獲取cookie是這裡有一個驗證需要我們注意的就是 RequestValidator.Current.IsValidRequestString方法。 在添加或修改Cookie是有2個地方的檢查(1)檢查Cookie的個數是否達到我們配置的cookie最大個數,(2)現在是否已經寫入頭信息,如果 頭信息已經寫了則不能操作cookie。