上面的設置表示:緩存5分鐘,根據不同的查詢字符串更新緩存。Location使用的是默認值Any,也就是可以在浏覽器、代理服務器、Web服務器三個地方進行緩存,在Response Headers中的體現就是Cache-Control:public, max-age=300。(如果你要用CDN加速,Cache-Control就要用public)。
然後,我們在Firefox浏覽器中訪問這個頁面,並打開Firebug,見下圖:
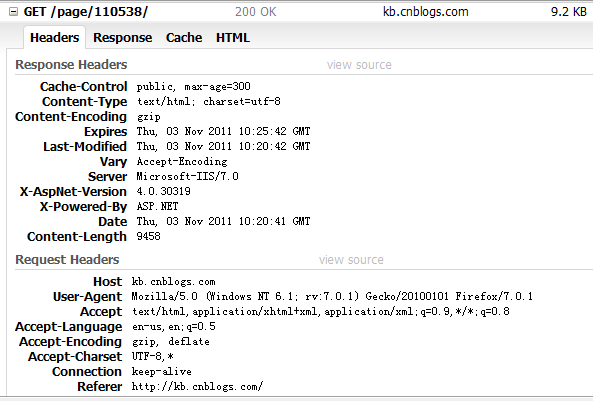
第一次訪問,返回狀態碼為"200 OK",正常。這裡Response Headers中的Vary:Accept-Encoding是因為IIS啟用“動態內容壓縮”產生的,如果不啟用,就不會出現。
這時緩存應該被建立起來了,我們按F5刷新一下浏覽器,看一下結果,見下圖:
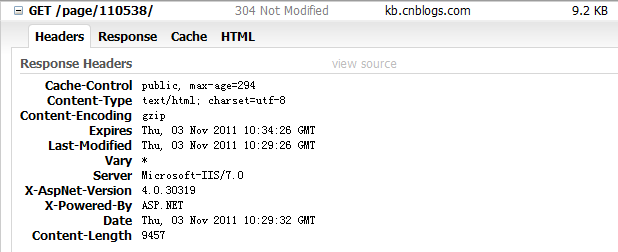
第二次訪問,返回狀態碼為"304 Not Modified",浏覽器緩存生效,這也是我們期望的。
但是,請注意一下上圖中的Vary:*,它會讓浏覽器的緩存失效,我們再按一下F5驗證一下。
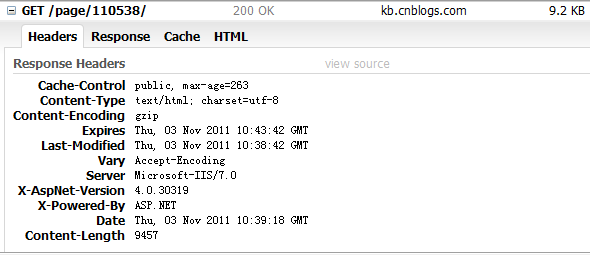
果然,浏覽器緩存失效,返回狀態碼變回了200 OK。緩存時間有5分鐘呢,第三次就失效了,這樣的結果顯然不是我們期望的。
上面的測試是在Web服務器上IIS啟用動態內容壓縮(dynamic content compression)的情況下進行的,如果關閉動態內容壓縮,每次請求返回都是200 OK,Vary都是星號。也就是說浏覽器游覽緩存根本沒起作用。
Bug欣賞完畢,我們進行第二個測試。
將OutputCache的VaryByParam屬性值設置為none:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
<%@ OutputCache Duration="600" VaryByParam="none"%>
測試結果顯示,浏覽器第一次請求之後,接下來在緩存時間內,服務器的響應都是"304 Not Modified",這才是我們想要的效果。
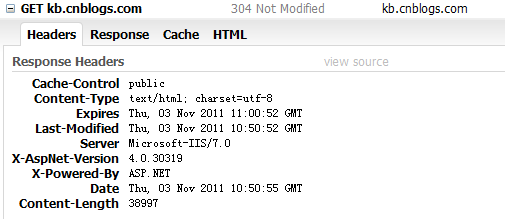
但是,在實際應用中,我們使用VaryByParam="none"很少,用的更多的是為VaryByParam指定對應的值。
所以這個Bug影響很大,增加了服務器負擔,浪費了帶寬。
Bug相關信息
在微軟的官方文檔ASP.NET 4 Breaking Changes中專門提到了這個bug —— "Output Caching Changes to Vary * HTTP Header":
In ASP.NET 1.0, a bug caused cached pages that specified Location="ServerAndClient" as an output–cache setting to emit a Vary:* HTTP header in the response. This had the effect of telling client browsers to never cache the page locally.
In ASP.NET 1.1, the System.Web.HttpCachePolicy.SetOmitVaryStar method was added, which you could call to suppress the Vary:* header. This method was chosen because changing the emitted HTTP header was considered a potentially breaking change at the time. However, developers have been confused by the behavior in ASP.NET, and bug reports suggest that developers are unaware of the existing SetOmitVaryStar behavior.
In ASP.NET 4, the decision was made to fix the root problem. The Vary:* HTTP header is no longer emitted from responses that specify the following directive:
<%@OutputCache Location="ServerAndClient" %>
As a result, SetOmitVaryStar is no longer needed in order to suppress the Vary:* header.
In applications that specify Location="ServerAndClient" in the @ OutputCache directive on a page, you will now see the behavior implied by the name of the Location attribute's value – that is, pages will be cacheable in the browser without requiring that you call the SetOmitVaryStar method.
從上面的文檔中我們可以知道這個Bug的歷史:
在ASP.NET 1.0時,如果在OutputCache中設置Location="ServerAndClient",在ASP.NET在響應時會浏覽器發送Vary:* HTTP header。
在ASP.NET 1.1時,微軟針對這個Bug,提供一個專門的方法System.Web.HttpCachePolicy.SetOmitVaryStar(bool omit),通過SetOmitVaryStar(true)修改HTTP header,去掉Vary:*。
在ASP.NET 4時,微軟鄭重地宣布從根本上解決了這個問題。
而且,文檔中提到這個bug只會出現在Location="ServerAndClient"時。
可是,我用ASP.NET 4的實測試情況是:不僅Location="ServerAndClient"時的Bug沒有解決,而且Location="Any"時也會出現同樣的Bug。
解決方法
解決方法很簡單,只要用ASP.NET 1.1時代提供的System.Web.HttpCachePolicy.SetOmitVaryStar(bool omit)就能解決問題,只需在Page_Load中添加如下代碼:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Response.Cache.SetOmitVaryStar(true);
}
相關文檔
ASP.NET caching tests find a bug with VaryByParam
How to cache asp.net web site for better performance
Microsoft Connect: The ServerAndClient parameter with the OutputCache page directive does not cache on the client, without code
小結
小bug,解決方法也很簡單。但是,如果你不知道這個bug,又會陷入微軟的一個騙局(之前提到一個WCF Client的騙局),不知不覺中浪費了服務器資源與帶寬。
微軟那麼有錢,有那麼多天才程序員,可是Bug也很難避免,可見開發優秀的軟件是多麼具有挑戰性的工作!
補充
ASP.NET MVC 中不存在這個問題。