挖一挖委托那些事兒,匿名方法,委托的逆變與協變,委托與閉包,C#自執行函數
很多人第一反映可能是"函數指針",個人覺得"函數指針"是委托實例
委托的定義類似interface,是一種方法的"規范"或者說"模版",用來規范方法的"行為",以便將方法作為參數傳遞
public delegate void MyDelegate();
這樣便定義了一個無參無返回值的委托,要求此委托的實例必須是無參無返回值的方法
public class MyClass
{
public static void MyMethod1() { }
public static void MyMethod2() { }
}
MyDelegate myDelegate = new MyDelegate(MyClass.MyMethod1);//定義了委托實例,並添加了相應的操作方法
//MyDelegate myDelegate = MyClass.MyMethod;//<--簡寫就是這樣
myDelegate += MyClass.MyMethod2;//多播委托
上面的代碼展示了委托的基本用法,多播委托也可以用Delegate.Combin()方法來實現
多播委托可以美化成下面的代碼
MyDelegate myDelegate = null; myDelegate += MyClass.MyMethod1; myDelegate += MyClass.MyMethod2;
是不是漂亮多了!
在C#3以後常用委托都可以用Action跟Func來替代了(C#3還是2忘記了- -)
委托存在的意義:方法傳遞
真實案例:
在controller的自定義基類中有一個protected void CreateCookie(string name, string value) 方法
在獲取到微信openid後,進行一些數據庫處理,同時保存此openid的登錄信息到cookies
public static void SetOpenId(string openId, Action<string, string> setCookie)
WeixinTool.SetOpenId(openid, CreateCookie);
這樣便將CreateCookie傳遞給了SetOpenId方法
不需要定義方法名,直接書寫方法體賦值給委托
在lambda表達式出來後用的不多了, 實際上lambda表達式就是匿名方法
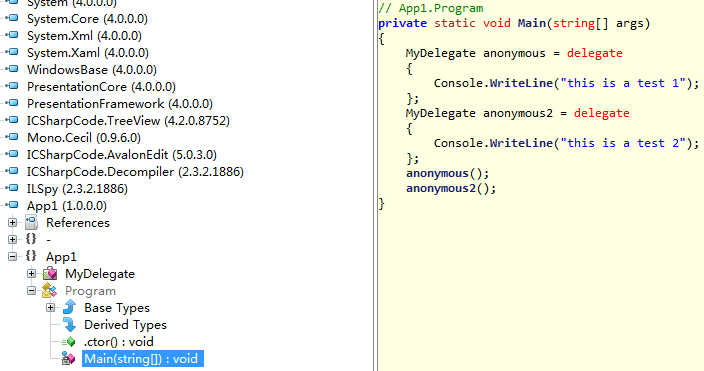
MyDelegate anonymous1 = delegate() { Console.WriteLine("this is a test 1"); };//匿名方法
MyDelegate anonymous2 = () => { Console.WriteLine("this is a test 2"); };//lambda表達式
anonymous1();
anonymous2();
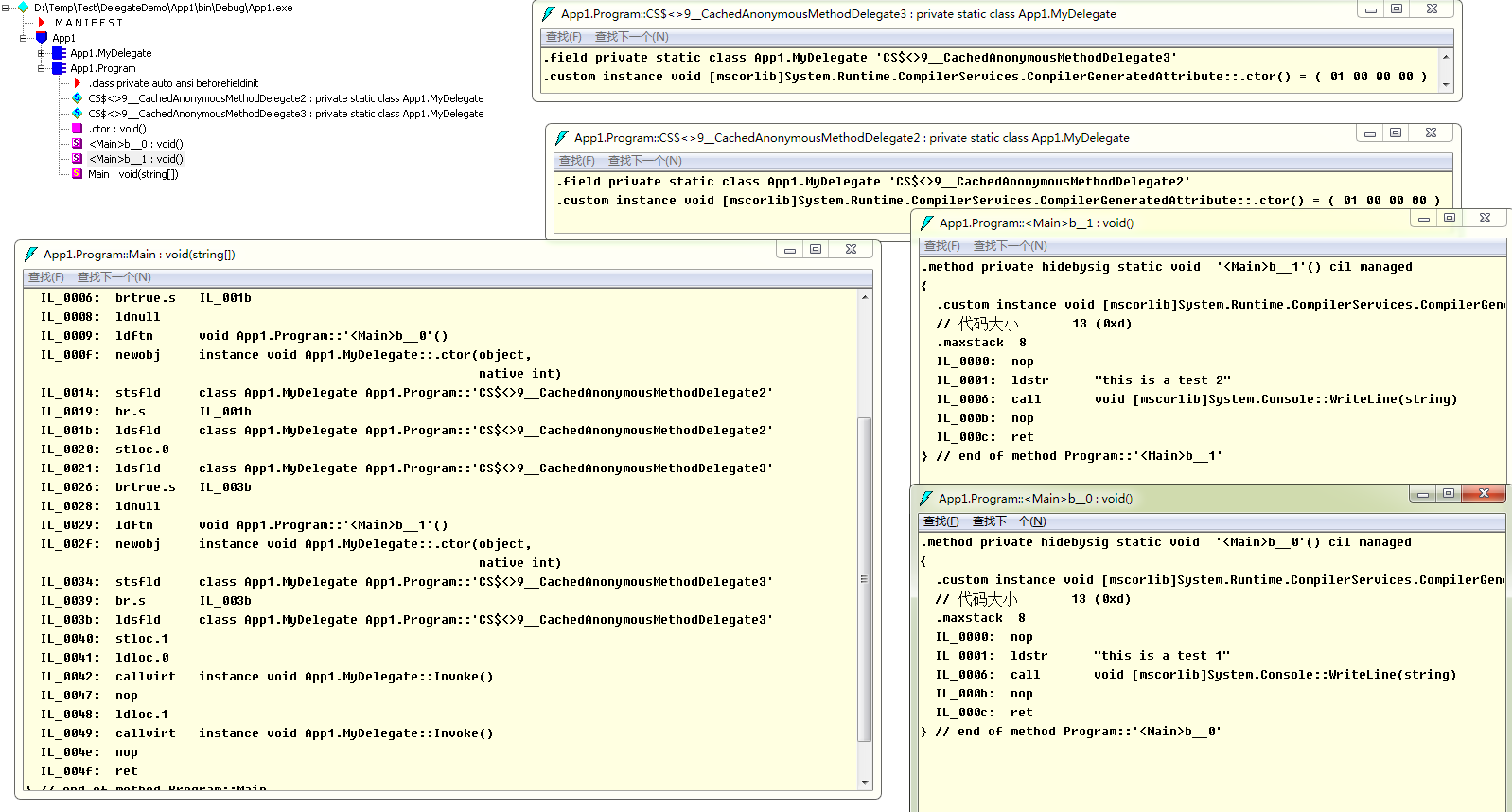
上面的代碼編譯後使用IlSpy查看直接就是倆匿名委托
使用ildasm查看il也是一致的
大家應該都寫過winform啦,點擊按鈕觸發click事件,相關事件處理程序影響該事件
很同學都知道有事件,但並不能准確描述事件是什麼 (前文的多播委托的優化版是不是看著像事件)
public event MyDelegate ChangeSomething;
首先事件是"屬性",是類的一個"屬性",所以只能定義在一個類裡面(或者結構體裡面)
但是event關鍵字讓你不能直接對這個屬性賦值,所以只能用"+="或者"-="來操作這個"屬性"
事件存在的目的是為了實現"發布/訂閱模式",也就是大家常說的pub/sub
為啥不能讓你直接給這個屬性賦值呢,因為"訂閱者"並不知道有多少人訂閱了這個事件,如果大家都用"="來操作,後面的"訂閱者"就會覆蓋前面的"訂閱者",容易造成bug,故而event關鍵字封裝了委托,關閉了直接賦值通道
用過泛型的很多同學都知道,泛型有逆變跟協變,其實委托也有逆變跟協變(接口,數組也有此特性)
那麼啥是逆變與協變呢
簡單來說
基類變子類 -> 逆了天了,這都可以,所以叫逆變
逆變實際是編譯器根據執行上下文推斷類型是可以轉換,才編譯通過的
看似逆天實際也屬於"is-a"關系正常轉換
子類變基類->CLR協助變形,所以叫協變
大家在編程中常用到,"is-a"關系,所以可以正常轉換
對於委托,逆變與協變可以是返回值變化,也可以是參數變化,亦可以是二者同時變化
來來來,我們來看一些具體的栗子:
class Person {}
class Employee : Person {}
delegate Person EmployeeInPersonOut(Employee employee);
class Methods
{
public static Person EmployeeInPersonOut(Employee employee)
{
return new Person();
}
public static Employee EmployeeInEmployeeOut(Employee employee)
{
return new Employee();
}
public static Person PersonInPersonOout(Person person)
{
return new Person();
}
public static Employee PersonInEmployeeOut(Person person)
{
return new Employee();
}
}
//常規使用 EmployeeInPersonOut employeeInPersonOut = Methods.EmployeeInPersonOut; Person person = employeeInPersonOut(new Employee());
//協變使用 /* * 返回值Employee跟Person屬於"is-a"關系,所以是常規轉換 */ EmployeeInPersonOut employeeInPersonOut = Methods.EmployeeInEmployeeOut; Person person = employeeInPersonOut(new Employee());
//逆變使用 /* * 對於委托聲明:委托方法的參數Person竟然可以變成Employee! * 實際是編譯器根據上下文推斷,對象可以成功轉換 * 在執行的時候, 委托聲明EmployeeInPersonOut只能輸入Employee * Employee對於Methods.PersonInPersonOout的參數peron是"is-a關系",所以可以正常轉換成方法參數 */ EmployeeInPersonOut employeeInPersonOut = Methods.PersonInPersonOout; Person person = employeeInPersonOut(new Employee());
//這段就不解釋了,仔細看前兩段就能明白其中原理 EmployeeInPersonOut employeeInPersonOut = Methods.PersonInEmployeeOut; Person person = employeeInPersonOut(new Employee());
協變在winform中的應用
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var button = new Button(){Text = "click me!"};
button.Click += HandleEvent;
button.KeyPress += HandleEvent;
var form = new Form();
form.Controls.Add(button);
Application.Run(form);
}
static void HandleEvent(object sender, EventArgs args)
{
MessageBox.Show(args.GetType().FullName);
}
}
用匿名無參委托忽略事件參數也是可以的
button.Click += delegate {/*do something.*/};
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var action = ClosureMethod();
action();
action();
action();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static Action ClosureMethod()
{
int localCounter = 0;
Action x = delegate
{
localCounter++;
Console.WriteLine(localCounter);
};
return x;
}
}
這段代碼依次輸出1,2,3
這就是閉包
可以參考javascript中的閉包,猜測一下:匿名方法使用了局部變量"localCounter",使得在方法執行完後無法釋放變量,從而形成了一個"范圍內的全局變量"
下面我們來驗證一下這個猜測
祭出神器:IL DASM
為了看著簡單點,我把代碼稍微做了點修改
static Action ClosureMethod()
{
string local = "零";
Action x = delegate
{
local += "壹";
Console.WriteLine(local);
};
return x;
}
漢字在il中更容易找到位置
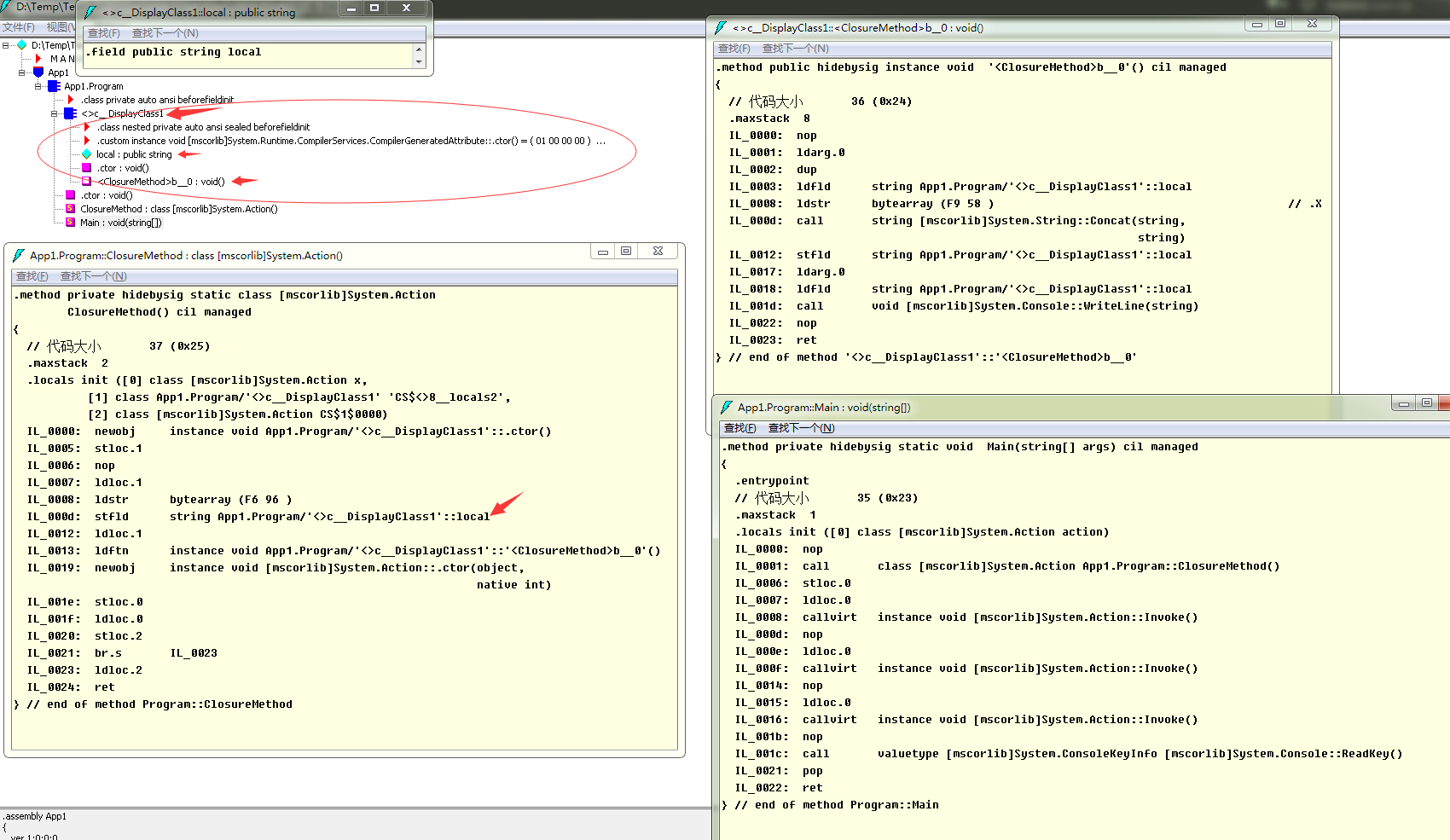
從il中可以看出
C#閉包並不是與js一樣是由於垃圾回收機制的原因
由於匿名方法捕獲了一個"外部方法"的局部變量"local"
使得編譯器生成了一個"內部類"(<>c_DisplayClass1)
而"外部方法"直接使用了這個"內部類"的實例中的變量(il中的<>c_DisplayClass1::local)
委托"Aciton x"也使用了該實例
這樣變完成了"閉包", 所以C#中的閉包完全是編譯器的功勞
static IList<string> StringFilter(List<string> list, int length)
{
return list.FindAll(delegate(string str)
{
return str.Length > length;
});
}
當然也可以使用lambda表達式
static IList<string> StringFilter(List<string> list, int length)
{
return list.FindAll(str => str.Length > length);
}
前面說過lambda表達式實際就是匿名方法
上面的代碼都捕獲了外部變量length
就像閉包部分第一段代碼的計數器,在"ClosureMethod"方法執行完畢後,變量"localCounter"的生命周期延長了
在for中使用閉包
坑1:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var actions = LoopClosure();
actions[0]();
actions[0]();
actions[0]();
actions[1]();
actions[2]();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static IList<Action> LoopClosure()
{
var list = new List<Action>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int val = i*10;
list.Add(delegate
{
val++;
Console.WriteLine(val);
});
}
return list;
}
輸出結果是1,2,3,11,21
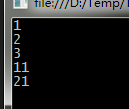
此循環雖然只有生成了一個"內部類",但是每次循環都產生了一個"內部類"的實例,所以會有上述結果
坑2:
var actions = new List<Action>(); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) actions.Add(() => Console.WriteLine(i));//access to modified closure 'i' foreach (var action in actions) action();
輸出結果是3,3,3
因為使用了變化/修改過的閉包變量
但是在foreach中是沒有這個坑的
var actions = Enumerable.Range(0, 3).Select(i => (Action)(() => Console.WriteLine(i))).ToList();
這樣的在foreach中的閉包就能正常輸出0,1,2
//無參自執行
((Action)(delegate
{
Console.WriteLine("I'm a IIFE method.");
}))();
//有參自執行
((Action<int>)(delegate(int i) {
Console.WriteLine("I'm a IIFE method with parameter:{0}", i);
}))(2);
參考資料:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/ee207183.aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/dd233060.aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/dd465122.aspx
http://csharpindepth.com/articles/chapter5/closures.aspx
歡迎以任何形式的轉載本文,轉載請注明出處,尊重他人勞動成果
轉載請注明:文章轉載自:博客園[http://www.cnblogs.com]
本文標題:說說委托那些事兒
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/eyu/p/all_those_delegate_things.html