GPS測量儀測量的產地面積,然後提交到系統中,系統需要校驗這塊產地和其他產地是否有重疊,重疊超過10%就要提出警告這塊產地已經被XXX登記入庫了。GPS測量儀測量出來的數據是連續的經緯度坐標數據。現在的問題就轉換成求一個一系列點圍成的區域和其他區域是否存在交集。拿到這個需求我想應該很簡單,網上應該有現成的代碼吧。
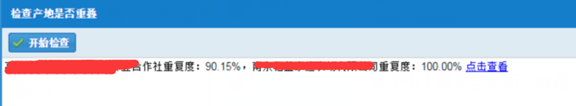
一開始想(XMin,YMin)應該是多邊形的左下角,(XMax,YMin)應該是右下角,對應的找到4個頂點轉換成矩形應該會好做一點吧。但是GPS測量出來的數據可不是都是垂直坐標軸的矩形,有的是斜著的,這樣就找不到XMin和YMin了,而且如果是不規則的多邊形怎麼辦,硬要轉成矩形的話那樣誤差很大啊。
根據網上搜索到的資料顯示,這個問題屬於計算幾何這門學科解決的問題。然後涉及了很多向量啊,向量的叉積啊,還有各種幾何知識,如何在2-3天之內補習這些知識然後寫出代碼來,看起來是個很艱苦的過程。
以上步驟最復雜的應該是求凹包和求交集了,原諒我學到凸包多邊形就已經放棄了。
為何叫奇葩的解法, 其實是為了賺一波眼球而已,我最後選擇的解法是通過gdi32.dll提供的windowsAPI來完成的,下面介紹下用到的幾個API函數
根據點集創建一個多邊形
IntPtr CreatePolygonRgn(Point[] lpPoint, int nCount, int nPolyFillMode);
合並兩個多邊形,可以是OR/AND/XOR,這裡用到的是AND
int CombineRgn(IntPtr dest, IntPtr src1, IntPtr src2, int flags);
獲取一個多邊形的詳細數據,拆解為若干個矩形
int GetRegionData(HandleRef hRgn, int size, IntPtr lpRgnData);
所以最後我們的步驟就是
整個過程看起來很簡單,這裡我上一些代碼,把其中比較難的部分解釋一下。
先引用dll
[DllImport("gdi32")]
private static extern IntPtr CreatePolygonRgn(Point[] lpPoint, int nCount, int nPolyFillMode);
代碼中Point是System.Drawing空間下的
X和Y*1000000是因為GPS信息是118.12334232這樣的數據,如果直接取int的話就都變成118了,精度不夠。
代碼中IntPtr是句柄,windowsAPI編程中都是提供句柄,類似內存指針的玩意。
Point[] poin = new Point[gpsList.Count()];
for (int i = 0; i < gpsList.Count(); i++)
{
string[] xy = gpsList[i].Split(',');
double x = ConvertHelp.obj2Double(xy[0], 0);
double y = ConvertHelp.obj2Double(xy[1], 0);
poin[i].X = (int)(x * 1000000);
poin[i].Y = (int)(y * 1000000);
}
IntPtr orginRgn = IntPtr.Zero;
orginRgn = CreatePolygonRgn(poin, poin.Count(), 1);
先引用dll
/// <summary>
/*
* CombineRgn(
p1: HRGN; {合成後的區域}
p2, p3: HRGN; {兩個原始區域}
p4: Integer {合並選項; 見下表}
): Integer; {有四種可能的返回值}
//合並選項:
RGN_AND = 1;
RGN_OR = 2;
RGN_XOR = 3;
RGN_DIFF = 4;
RGN_COPY = 5; {復制第一個區域}
//返回值:
ERROR = 0; {錯誤}
NULLREGION = 1; {空區域}
SIMPLEREGION = 2; {單矩形區域}
COMPLEXREGION = 3; {多矩形區域}
*/
/// </summary>
/// <param name="dest"></param>
/// <param name="src1"></param>
/// <param name="src2"></param>
/// <param name="flags"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[DllImport("gdi32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int CombineRgn(IntPtr dest, IntPtr src1, IntPtr src2, int flags);
使用起來就很簡單,提供3個參數,第一個參數是合並後返回的句柄,第2個參數是多邊形1號,第3個參數是多邊形2號,最後一個flag參數是合並選項,1是and,2是or根據情況選用,這裡選用And所以是1
返回結果0表示錯誤也就是沒有交集,1表示空區域即無交集,2和3都表示有交集存在。
int nMix = CombineRgn(nextRgn, orginRgn, nextRgn, 1);
if (nMix != 1 && nMix != 0)
{
//有交集
}
計算交集的面積,其實就是如何根據句柄讀取內存裡的數據,因為網上大多數都是C++的寫法,很少能找到。Net的寫法,所以這個部分占用了我一下午時間,包括走了一些彎路 ,最後通過google才找到了正解。
先引用dll,根據API返回的數據結構建立對應的結構
public struct RGNDATAHEADER
{
public int dwSize;
public int iType;
public int nCount;
public int nRgnSize;
public RECT rcBound;
}
public struct RECT
{
public int Left;
public int Top;
public int Right;
public int Bottom;
}
/// <summary>
/// 獲取數據參考:http://www.pinvoke.net/default.aspx/gdi32/GetRegionData.html
/// 數據結構參考:http://www.cnblogs.com/del/archive/2008/05/20/1203446.html
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hRgn"></param>
/// <param name="size"></param>
/// <param name="lpRgnData"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[DllImport("gdi32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, SetLastError = true, ExactSpelling = true)]
public static extern int GetRegionData(HandleRef hRgn, int size, IntPtr lpRgnData);
下面的代碼只講一下GetRegionData這個API的調用的特殊之處,首先他要調用2次才能正確獲取到數據。
第一次調用如下GetRegionData(hr, 0, IntPtr.Zero),傳遞一個空句柄,此時會返回一個int的值,告訴你需要准備一個多大的內存區域。
然後要申請一個內存區域准備去接值。IntPtr bytes = Marshal.AllocCoTaskMem(dataSize);就是准備一個特定大小的內存區域的句柄。
第二次調用GetRegionData(hr, dataSize, bytes)的時候就能把我們想要的數據填充到bytes這個句柄指向的內存區域了。
接下來的問題就是有了句柄如何取結構化的數據了,C#裡支持指針操作,但是是unsafe的代碼。最關鍵一句話在下面已經加了注釋 了。
const int RDH_RECTANGLES = 1;
/// <summary>
/// 分割多邊形,獲取多邊形內所有的矩形
/// </summary>
/// <param name="hRgn"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public unsafe static RECT[] RectsFromRegion(IntPtr hRgn)
{
RECT[] rects = null;
var hr = new HandleRef(null, hRgn);
// First we call GetRegionData() with a null buffer.
// The return from this call should be the size of buffer
// we need to allocate in order to receive the data.
int dataSize = GetRegionData(hr, 0, IntPtr.Zero);
if (dataSize != 0)
{
IntPtr bytes = IntPtr.Zero;
// Allocate as much space as the GetRegionData call
// said was needed
bytes = Marshal.AllocCoTaskMem(dataSize);
// Now, make the call again to actually get the data
int retValue = GetRegionData(hr, dataSize, bytes);
// From here on out, we have the data in a buffer, and we
// just need to convert it into a form that is more useful
// Since pointers are used, this whole routine is 'unsafe'
// It's a small sacrifice to make in order to get this to work.
// [RBS] Added missing second pointer identifier
RGNDATAHEADER* header = (RGNDATAHEADER*)bytes;
if (header->iType == RDH_RECTANGLES)
{
rects = new RECT[header->nCount];
// The rectangle data follows the header, so we offset the specified
// header size and start reading rectangles.
//獲取偏移
int rectOffset = header->dwSize;
for (int i = 0; i < header->nCount; i++)
{
// simple assignment from the buffer to our array of rectangles
// will give us what we want.
//首先把bytes轉換成指針,得到bytes的地址,然後加上偏移,再轉換為RECT類型的指針。
rects[i] = *((RECT*)((byte*)bytes + rectOffset + (Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(RECT)) * i)));
}
}
}
// Return the rectangles
return rects;
}
因為上面獲取到的數據其實是一個RECT的數組,而RECT裡面包含的是上下左右四個點的坐標信息,那麼很顯然我們得到的是一個矩形的數組,每次分解大概有2000多個矩形,不用管多少了,直接拿來用就是了
/// <summary>
/// 計算多邊形的面積
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rgn"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int CalculateAreas(IntPtr rgn)
{
RECT[] rectData = RectsFromRegion(rgn);
int ret = 0;
foreach (var rect in rectData)
{
int areas = (rect.Bottom - rect.Top) * (rect.Right - rect.Left);
if (areas < 0)
areas = areas * -1;
ret += areas;
//Console.WriteLine("{0},{1},{2},{3},{4}", rect.Top, rect.Left, rect.Right, rect.Bottom, areas);
}
return ret;
}
這次這個需求一開始以為不復雜,網上應該有現成的代碼,實際上搜索後發現涉及的計算幾何的知識對幾何和算法的要求特別高,無奈幾何知識都還給老師了,補習的話短短2-3天應該是來不及了。百度的能力畢竟有限,有的時候google能提供更大的幫助。通過另辟蹊徑借用windowsAPI解決了這個問題,同時了解了C#在指針操作上的知識。