排序思想:
先取一個小於n的整數d1作為第一個增量,把文件的全部記錄分組。所有距離為d1的倍數的記錄放在同一個組中。先在各組內進行直接插入排序;然後,取第二個增量d2<d1重復上述的分組和排序,直至所取的增量 dt=1(dt<dt-1…<d2<d1),即所有記錄放在同一組中進行直接插入排序為止。
復雜度:O(n3/2)。
穩定性:不穩定。
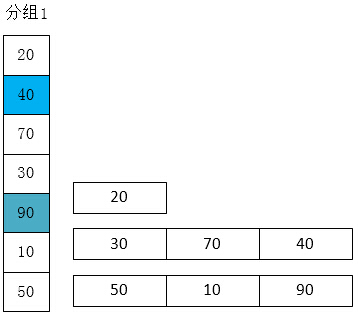
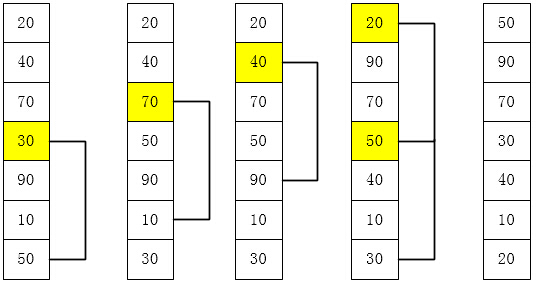
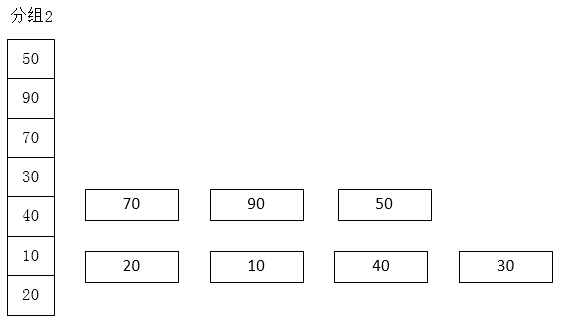
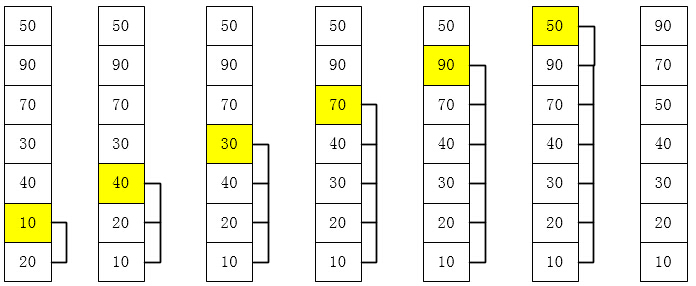
代碼實例:
int[] list = { 50, 10, 90, 30, 70, 40, 20 };
int len = list.Length;
int temp, j;
while (len > 1)
{
len = len / 2;
for (int i = len; i < list.Length; i++)
{
if (list[i] < list[i - len])
{
temp = list[i];
for (j = i - len; j >= 0 && temp < list[j]; j = j - len)
{
list[j + len] = list[j];
}
list[j + len] = temp;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("希爾排序的結果:{0}",string.Join(",", list));
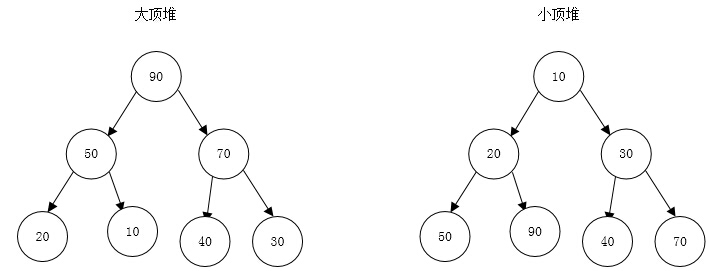
排序思想:指利用堆積樹(堆)這種數據結構所設計的一種排序算法,它是選擇排序的一種。
堆是具有下列性質的完全二叉樹:每個結點的值都大於或等於其左右孩子結點的值,稱為大頂堆;或者每個結點的值都小於或等於其左右孩子結點的值,稱為小頂堆。
復雜度:O(nlogn)。
穩定性:不穩定。
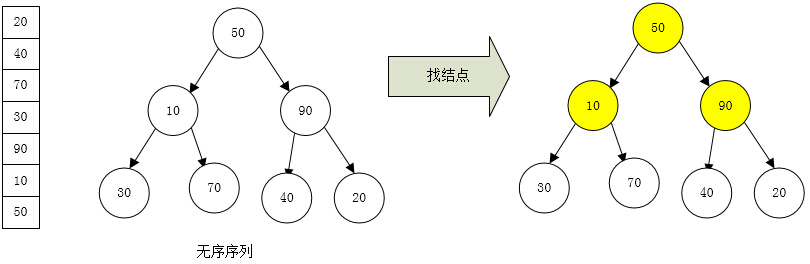
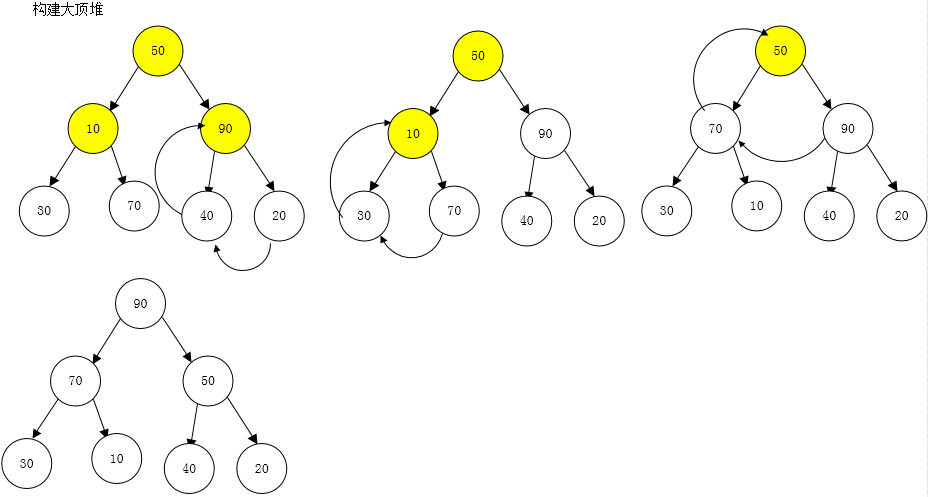
堆排序只用做以下二點:
1:從無序序列中構建起大頂堆。
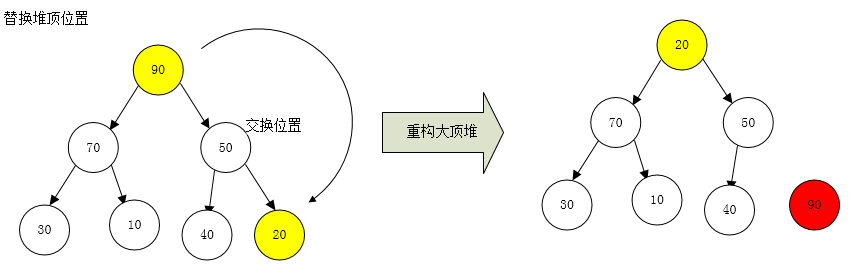
2:交換大頂堆中頂節點和後結點(n)位置,重新調整剩余元素,構建一個新的大頂堆。依次循環....
代碼實例:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] list = { 50, 10, 90, 30, 70, 40, 20 };
for (int i = list.Length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) /* 構建大頂堆[list.Length / 2 - 1:無序數組中結點數]*/
{
HeapAdjust(list, i, list.Length);
}
int temp;
for (int i = list.Length - 1; i > 0; i--) /* 替換大頂堆的位置,然後重新構建大頂堆。*/
{
temp = list[0]; /* 替換大頂堆中最大值list[0]和最小值之前的位置list[i]*/
list[0] = list[i];
list[i] = temp;
HeapAdjust(list, 0, i); /* 重新構建大頂堆*/
}
Console.WriteLine("堆排序的結果:{0}", string.Join(",", list));
}
/// <summary>
/// 構建大頂堆
/// </summary>
/// <param name="list">排序集合</param>
/// <param name="NodeIndex">父結點</param>
/// <param name="len">大頂堆長度</param>
static void HeapAdjust(int[] list, int NodeIndex, int len)
{
int temp = list[NodeIndex]; /*二叉樹節點值*/
for (int i = NodeIndex * 2 + 1; i < len; i = NodeIndex * 2 + 1) /*循環二叉樹節點下左右孩子[NodeIndex*2+1找到結點下的左右孩子]*/
{
if (i + 1 < len && list[i] < list[i + 1]) /*i+1:是否存在左右兩個孩子,list[i]<list[i+1]:默認左孩子大於右孩子*/
{
i++; /*左孩子小於右孩子直接i++ ,list[i]為右孩子值*/
}
if (temp >= list[i]) /*節點大於等於(左/右)孩子直接退出不替換節點值*/
{
break;
}
list[NodeIndex] = list[i]; /*替換節點和(左/右)孩子之間的值,保持結點大於左右孩子*/
NodeIndex = i; /*重新設置結點值,循環查詢*/
}
list[NodeIndex] = temp; /*替換(左/右)孩子和結點之間的值*/
}
排序思想:“歸並”一詞的中文含義就是合並、並入的意思,而在數據結構中的定義是將兩個或兩個以上的有序表組合成一個新的有序表。
歸並排序(Merging Sort)就是利用歸並的思想實現的排序方法。它的原理是假設初始序列含有n個記錄,則可以看成是n個有序的子序列,每個子序列的長度為1,然後兩兩歸並,得到⌈n/2⌉(⌈x⌉表示不小於x的最小整數)個長度為2或1的有序子序列;再兩兩歸並,……,如此重復,直至得到一個長度為n的有序序列為止,這種排序方法稱為2路歸並排序。
復雜度:O(nlogn) 。
穩定性:穩定。
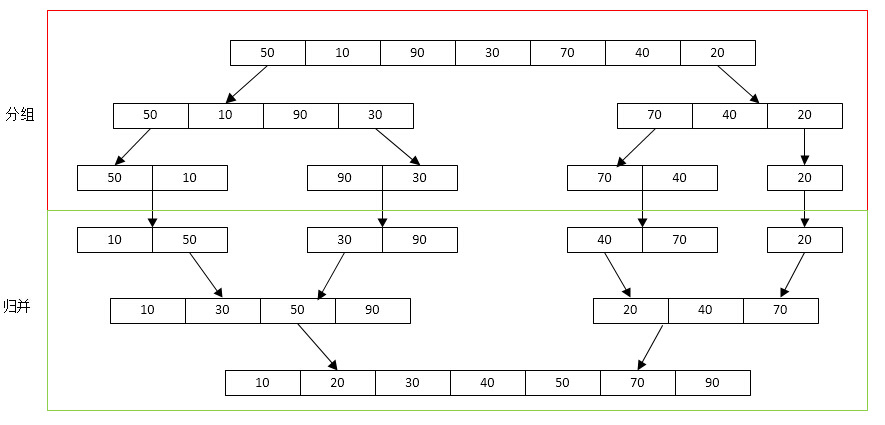
代碼實例:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] list = { 50, 10, 90, 30, 70, 40, 20 };
MeSort(list, 0, list.Length - 1);
Console.WriteLine("歸並排序的結果:{0}", string.Join(",", list));
}
static void MeSort(int[] list, int start, int end)
{
if (start < end)
{
int middle = (start + end) / 2; /*對數組進行分組*/
MeSort(list, start, middle); /*分組左序列*/
MeSort(list, middle + 1, end); /*分組右序列*/
MergeS(list, start, middle, end); /*對左右序列進行合並(歸並)*/
}
}
static void MergeS(int[] list, int first, int middle, int end)
{
int IndexA = first; /*左序列起始位置*/
int IndexB = middle + 1; /*右序列起始位置*/
int[] tempList = new int[end - first + 1]; /*左右序列合並後的臨時數組*/
int tempIndex = 0;
while (IndexA <= middle && IndexB <= end) /*循環左右序列中的數據*/
{
if (list[IndexA] >= list[IndexB]) /*對比左右序列中數據大小*/
{
tempList[tempIndex++] = list[IndexB++]; /*右元素大於左元素,把右元素存放到臨時數組tempList中,並把臨時數組tempIndex++,然後在取右序列中下一元素*/
}
else
{
tempList[tempIndex++] = list[IndexA++]; /*左元素大於右元素,把左元素存放到臨時數組tempList中,並把臨時數組tempIndex++,然後在取在序列中下一元素*/
}
}
while (IndexA <= middle) /*有一側子表遍歷完後,跳出循環,將另外一側子表剩下的數一次放入暫存數組中*/
{
tempList[tempIndex++] = list[IndexA++];
}
while (IndexB <= end)
{
tempList[tempIndex++] = list[IndexB++];
}
tempIndex = 0; /*設置臨時數組從第1位開始替換*/
for (int i = first; i <= end; i++) /*臨時數組替換List數組中數據*/
{
list[i] = tempList[tempIndex++];
}
}
排序思想:通過一趟排序將要排序的數據分割成獨立的兩部分,其中一部分的所有數據都比另外一部分的所有數據都要小,然後再按此方法對這兩部分數據分別進行快速排序,整個排序過程可以遞歸進行,以此達到整個數據變成有序序列。
復雜度:O(nlogn) 。
穩定性:不穩定。
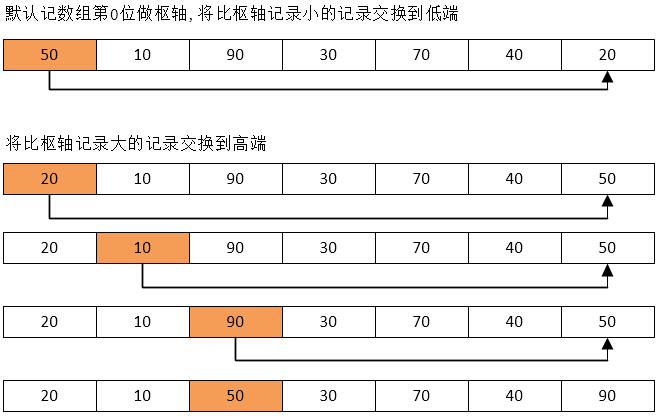
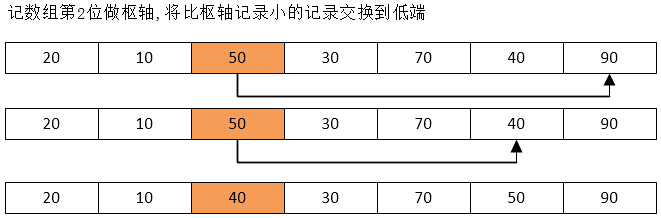
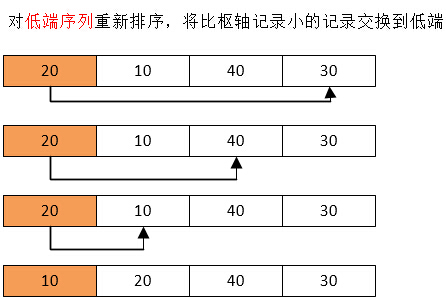

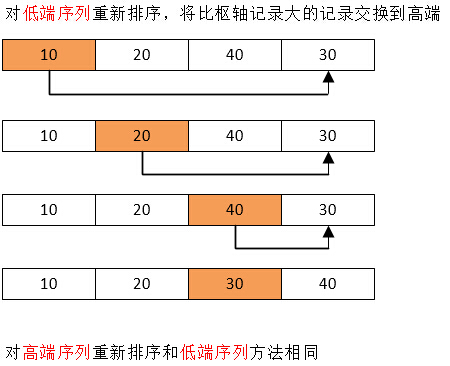
代碼實例:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] list = { 50, 10, 90, 30, 70, 40, 20 };
QuickSort(list, 0, list.Length - 1);
Console.WriteLine("快速排序的結果:{0}", string.Join(",", list));
}
private static void QuickSort(int[] list, int start, int end)
{
int pivot;
if (start < end)
{
pivot = Partition(list, start, end); /* 對序列一分為二數出中間值 */
QuickSort(list, start, pivot - 1); /* 對低端序列進行排序 */
QuickSort(list, pivot + 1, end); /* 對高端序列進行排序 */
}
}
private static int Partition(int[] list, int first, int end)
{
int pivotkey = list[first]; /* 默認取序列中第0位為樞軸 */
while (first < end)
{
while (first < end && list[end] >= pivotkey) /*比樞軸小的記錄交換到低端*/
{
end--;
}
swap(list, first, end);
while (first < end && list[first] <= pivotkey) /*比樞軸大的記錄交換到高端*/
{
first++;
}
swap(list, first, end);
}
return first; /*返回樞軸值*/
}
/// <summary>
/// 替換數組A於B之間的位置
/// </summary>
private static void swap(int[] list, int A, int B)
{
int temp = list[A];
list[A] = list[B];
list[B] = temp;
}
常見排序方法基本就這些。已分享完畢.....
排序性能和速度快速排序優於其他常見排序方法。