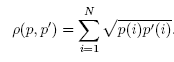圖像處理之相似圖片識別(直方圖應用篇),圖像處理直方圖
算法概述:
首先對源圖像與要篩選的圖像進行直方圖數據采集,對采集的各自圖像直方圖進行歸一化再
使用巴氏系數算法對直方圖數據進行計算,最終得出圖像相似度值,其值范圍在[0, 1]之間
0表示極其不同,1表示極其相似(相同)。
算法步驟詳解:
大致可以分為兩步,根據源圖像與候選圖像的像素數據,生成各自直方圖數據。第二步:使
用第一步輸出的直方圖結果,運用巴氏系數(Bhattacharyya coefficient)算法,計算出相似程
度值。
第一步:直方圖計算
直方圖分為灰度直方圖與RGB直方圖,對於灰度圖像直方圖計算十分簡單,只要初始化一
個大小為256的直方圖數組H,然後根據像素值完成頻率分布統計,假設像素值為124,則
H[124] += 1, 而對於彩色RGB像素來說直方圖表達有兩種方式,一種是單一直方圖,另外一
種是三維直方圖,三維直方圖比較簡單明了,分別對應RGB三種顏色,定義三個直方圖HR,
HG, HB, 假設某一個像素點P的RGB值為(4, 231,129), 則對於的直方圖計算為HR[4] += 1,
HG[231] += 1, HB[129] += 1, 如此對每個像素點完成統計以後,RGB彩色直方圖數據就生成了。
而RGB像素的單一直方圖SH表示稍微復雜點,每個顏色的值范圍為0 ~ 255之間的,假設
可以分為一定范圍等份,當8等份時,每個等份的值范圍為32, 16等份時,每個等份值范
圍為16,當4等份時候,每個等份值的范圍為64,假設RGB值為(14, 68, 221), 16等份之
後,它對應直方圖索引值(index)分別為: (0, 4, 13), 根據計算索引值公式:index = R + G*16 + B*16*16
對應的直方圖index = 0 + 4*16 + 13 * 16 * 16, SH[3392] += 1
如此遍歷所有RGB像素值,完成直方圖數據計算。
第二步:巴氏系數計算,計算公式如下:
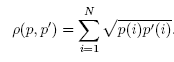
其中P, P’分別代表源與候選的圖像直方圖數據,對每個相同i的數據點乘積開平方以後相加
得出的結果即為圖像相似度值(巴氏系數因子值),范圍為0到1之間。
程序效果:

相似度超過99%以上,極其相似
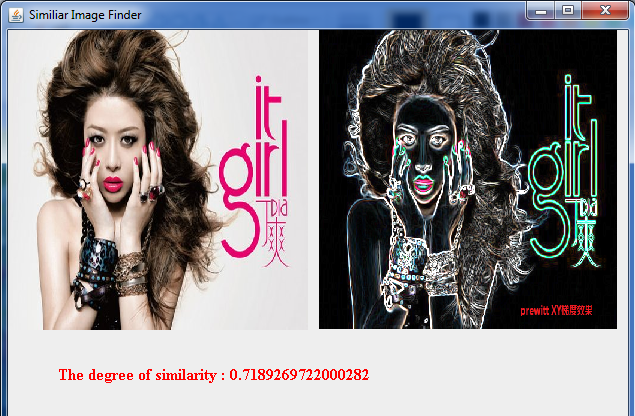
相似度為:72%, 一般相似
程序直方圖計算源代碼如下:
[java] view plaincopy
- public void setGreenBinCount(int greenBinCount) {
- this.greenBins = greenBinCount;
- }
-
- public void setBlueBinCount(int blueBinCount) {
- this.blueBins = blueBinCount;
- }
-
- public float[] filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
- int width = src.getWidth();
- int height = src.getHeight();
-
- int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];
- float[] histogramData = new float[redBins * greenBins * blueBins];
- getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );
- int index = 0;
- int redIdx = 0, greenIdx = 0, blueIdx = 0;
- int singleIndex = 0;
- float total = 0;
- for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {
- int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
- for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {
- index = row * width + col;
- ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;
- tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
- tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
- tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
- redIdx = (int)getBinIndex(redBins, tr, 255);
- greenIdx = (int)getBinIndex(greenBins, tg, 255);
- blueIdx = (int)getBinIndex(blueBins, tb, 255);
- singleIndex = redIdx + greenIdx * redBins + blueIdx * redBins * greenBins;
- histogramData[singleIndex] += 1;
- total += 1;
- }
- }
-
- // start to normalize the histogram data
- for (int i = 0; i < histogramData.length; i++)
- {
- histogramData[i] = histogramData[i] / total;
- }
-
- return histogramData;
- }
計算巴氏系數的代碼如下:
[java] view plaincopy
- /**
- * Bhattacharyya Coefficient
- * http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~kosta/CompVis_Notes/bhattacharyya.pdf
- *
- * @return
- */
- public double modelMatch() {
- HistogramFilter hfilter = new HistogramFilter();
- float[] sourceData = hfilter.filter(sourceImage, null);
- float[] candidateData = hfilter.filter(candidateImage, null);
- double[] mixedData = new double[sourceData.length];
- for(int i=0; i<sourceData.length; i++ ) {
- mixedData[i] = Math.sqrt(sourceData[i] * candidateData[i]);
- }
-
- // The values of Bhattacharyya Coefficient ranges from 0 to 1,
- double similarity = 0;
- for(int i=0; i<mixedData.length; i++ ) {
- similarity += mixedData[i];
- }
-
- // The degree of similarity
- return similarity;
- }
在matlab中進行圖像處理,直方圖處理與區域直方圖處理有什不同他們在人臉識別中誰更有優點?
一般都是用區域直方圖處理吧。
直方圖處理是一般用於圖像增強,從整體上對圖像進行修改。
區域直方圖著重在某一個區域上對圖像進行修改,識別能力更強吧。
matlab 圖像處理中,直方圖均衡處理與直方圖歸一化各有什作用?
1、直方圖均衡化處理的“中心思想”是把原始圖像的灰度直方圖從比較集中的某個灰度區間變成在全部灰度范圍內的均勻分布。直方圖均衡化就是對圖像進行非線性拉伸,重新分配圖像像素值,使一定灰度范圍內的像素數量大致相同。直方圖均衡化就是把給定圖像的直方圖分布改變成“均勻”分布直方圖分布。 2、歸一化是一種無量綱處理手段,使物理系統數值的絕對值變成某種相對值關系。簡化計算,縮小量值的有效辦法。直方圖歸一化類比這個吧!