前天關注了老趙的微信公眾號:趙人希。昨天就推送了一個快速問答,下面把我的答題經歷跟大家分享,希望對於菜鳥同胞們有所幫助啟發。
其實這個問題在他的博客裡有專門的篇幅講解,我猜到了,哈哈。但是大牛講問題都是在一個高度上,水平差點的需要費點力氣才能理解,而這個過程就是拉進我們與大牛距離的過程,用心總結下,才能不斷強化自己靠近他們。
在我平時的編碼中,用的最頻繁的就是代碼段[1]:
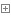
其中Dictionary<鍵,值>的鍵通常就是int或者string類型,那現在我們需要自定義值類型,並把它作為字典的鍵應該怎麼做?
整天定義引用類型,值類型還真寫的少,其實是對值類型的優勢了解的少!代碼段[2]:
1 private struct MyKey
2 {
3 private readonly int _a;
4 private readonly int _b;
5 public MyKey(int a, int b)
6 {
7 _a = a;
8 _b = b;
9 }
10 }
這就OK了,可以根據自己的需求加入一些屬性和方法,對於一些簡單的需求,定義一個struct要更高效節省。
代碼段[2]中的值類型就可以用於字典的鍵,但是,這就夠了嗎?萬事都有不完美,你有沒有考慮到值類型隨之而來的[裝箱]!比如代碼段[3]:
1 public static void Main()
2 {
3 Dictionary<MyKey, string> testDic = new Dictionary<MyKey, string>();
4 MyKey key12 = new MyKey(1, 2);
5 testDic.Add(key12, "1&2");
6 Console.ReadKey();
7 }
插一句:在我們分析問題時,要想明白原理,弄清楚.net框架中是怎麼實現的,就必須抄家伙(.NET Reflector)!這是我們進步的一個重要工具。
Dictionary中Add方法調用的Insert方法的部分實現,如代碼段[4]:
1 int num = this.comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7fffffff;
2 int index = num % this.buckets.Length;
3 int num3 = 0;
4 for (int i = this.buckets[index]; i >= 0; i = this.entries[i].next)
5 {
6 if ((this.entries[i].hashCode == num) && this.comparer.Equals(this.entries[i].key, key))
7 {
8 if (add)
9 {
10 ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_AddingDuplicate);
11 }
12 this.entries[i].value = value;
13 this.version++;
14 return;
15 }
16 num3++;
17 }
注意:其中用到了對象的GetHashCode和Equals方法,我們知道所有類型最終都繼承自System.Object,如果在自定義的類型以及其繼承層次的所有類中沒有重寫GetHashCode和Equals方法(自定義值類型的繼承層次是MyKey=>System.ValueType=>System.Object),那麼就會調用基類Object的相應方法,那必然會導致[裝箱]操作。
而在Dictionary中,代碼段[4]顯示的是通過this.comparer調用的這兩個方法,那this.comparer是什麼呢?繼續挖掘,它是Dictionary類中維護的一個IEqualityComparer<T>類型的對象。代碼段[5]:
1 public Dictionary(int capacity, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer)
2 {
3 if (capacity < 0)
4 {
5 ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentOutOfRangeException(ExceptionArgument.capacity);
6 }
7 if (capacity > 0)
8 {
9 this.Initialize(capacity);
10 }
11 this.comparer = comparer ?? EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default;
12 }
如果在創建Dictionary時沒有在參數中提供比較器,則會使用默認的EqualityComparer<T>.Default對象給this.comparer賦值,它的構造方法是代碼段[6]:

可以看出,根據不同的情況它會使用各式不同的比較器。其中最適合我們的自然就是實現IEquatable<T>接口的分支了:
1 if (typeof(IEquatable<T>).IsAssignableFrom(c))
2 {
3 return (EqualityComparer<T>) RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType) typeof(GenericEqualityComparer<int>), c);
4 }
為了能夠符合這個if的條件,我們的自定義值類型MyKey應當實現IEquatable<MyKey>接口(實現Equals方法),並且重寫GetHashCode方法(Object的GetHashCode方法也會導致裝箱),才能徹底避免裝箱操作。
因此,我的最終實現是代碼段[7]:
1 public struct MyKey : IEquatable<MyKey>
2 {
3 private readonly int _a;
4 private readonly int _b;
5
6 public MyKey(int a, int b)
7 {
8 _a = a;
9 _b = b;
10 }
11 public override int GetHashCode()
12 {
13 return (this._a ^ this._b);
14 }
15
16 public bool Equals(MyKey that)
17 {
18 return (this._a == that._a) && (this._b == that._b);
19 }
20 }
就這樣,一個簡單的問答被我們剖析了個遍,很過瘾吧!
最後,文中如果有不對的地方,歡迎各位大牛指正!這裡先謝過了!
如果你覺得本文對你有幫助,那就點個贊吧,權當鼓勵。