某些仿真模擬項目中時常會遇到大量的計算的問題,做一個幾千次的仿真會耗費數個小時,用戶多次的提出要求提高計算的效率,我們也多次修改計算的邏輯,讓計算路徑變得更短,但是依舊達不到非常明顯的效果。
計算時我觀察了一下CPU的使用情況曲線,發現CPU占用並不是很多,而且即便是占用CPU很高的計算邏輯,也只是占用了一個CPU的內核,那如何更充分的利用現在主流的多核CPU做運算呢?
.Net4.0中提供了新的命名空間:System.Threading.Tasks,用於提供並行計算的相關類,這裡我主要介紹一個簡單的類:Parallel,用於提供對並行循環和區域的支持。
簡單來說,Parallel可以把一個普通的for或者foreach循環變為並行運算處理,我們看下代碼:
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Test
{
static int N = 1000;
static void TestMethod()
{
// Using a named method.
Parallel.For(0, N, Method2);
// Using an anonymous method.
Parallel.For(0, N, delegate(int i)
{
// Do Work.
});
// Using a lambda expression.
Parallel.For(0, N, i =>
{
// Do Work.
});
}
static void Method2(int i)
{
// Do work.
}
}只要做小小的變動就能讓原有的for或者foreach並行執行的代碼,很神奇吧~
下面我做了一個小小的實驗,一個普通的for和Parallel.For的效率倒地能差多少?
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
namespace ParallelLoopDemo
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnNormalLoop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int time = 0;
int.TryParse(textBox1.Text, out time);
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
for (int i = 0; i <= time; i++)
{
Calc(i);
}
sw.Stop();
label2.Text = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString();
}
private void btnParallelLoop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int time = 0;
int.TryParse(textBox1.Text, out time);
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
Parallel.For(0, time + 1, i =>
{
Calc(i);
});
sw.Stop();
label2.Text = sw.ElapsedMilliseconds.ToString();
}
private void Calc(int time)
{
Math.Pow(time, time + 1);
}
}
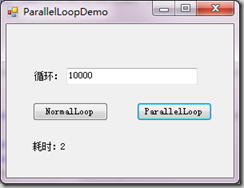
}分別對比下兩者在10000次下的運行效率吧
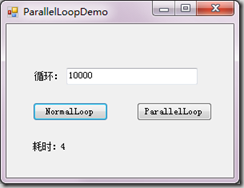
這是常規for循環的CPU占用圖
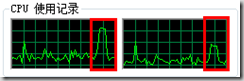
下面是Parallel.For的CPU占用圖
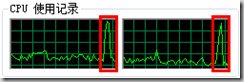
明顯可以看出Parallel.For可以能好的利用多核CPU,假設如果有4核CPU的話,效率應該是4倍,不知道哪位可以幫忙試驗下。
只需要簡單的膽碼修改能換來效率的翻倍提高是一件很劃算的事,但是需要注意的是:Parallel.For采用並行運算,需要考慮運算的前置條件以及需要考慮的問題,比如互鎖,界面刷新等。