類似如下字符串
"ID", "NameValue", "CodeValue", "ExchangeTypeValue", 6, "invalid"
"ID2", "NameValue2", "CodeValue2", "ExchangeTypeValue2", 6, "invalid"
.......
有可能是文件中存在的,或者調用其他程序返回的結構化數據,那麼該如何解析?當其他場景中,只是返回順序(屬性順序)變了,類結構還是一樣,又如何應對?當有很多類似場景時,是不是該抽象出一個泛型方法來應對該場景?當然,也不僅僅於上述情況,可能返回的結構是確定,只是形式不一樣,這個過程這裡暫時省略,因為正則表達式完全能夠解析出來。要用以下的方法,必須轉換成IEnumerable<IEnumerable<string>>結構,IEnumerable<IEnumerable<string>>結構中IEnumerable<string>為一個對象所有的值,總體是多個對象的值集合。本文中用反射寫的(關於IL操作的後續文章提供),相關的類圖如下:
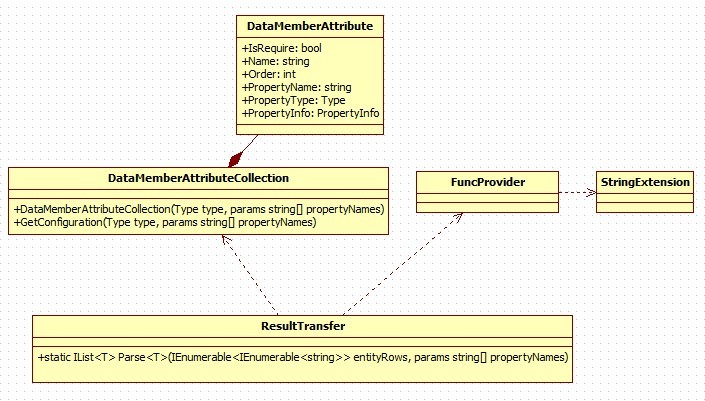
ResultTransfer主要用於對IEnumerable<IEnumerable<string>>結構的解析,另外還可以指定params string[] propertyNames屬性參數列表來確定解析順序(也即是屬性順序),主要方法如下:
第一個參數entityRows為對象列表值集合。
第二個參數propertyNames為可選參數,輸入該參數後,如果propertyNames中存在相關屬性,則按照propertyNames對應的屬性順序進行解析。否則按照提供的T類中屬性的DataMemberAttribute來確定屬性順序進行解析。
實現代碼非常簡潔和簡單,方法具體如下所示:
IList<T> Parse<T>(IEnumerable<IEnumerable<>> entityRows, [] propertyNames) T : (entityRows == || entityRows.Count() == List<T><T> entities = List<T> members = DataMemberAttributeCollection( (members.Count <= List<T>= ( propertyValues (propertyValues == || propertyValues.Count() == <T> T Generate<T>(IEnumerable<> T : = Activator.CreateInstance<T> memberCount = propertyCount = (memberCount == || propertyCount == convertCount = propertyValueIndex = ( propertyValue (propertyValueIndex >=++= members[propertyValueIndex - = (propertyValue == , (propertyValue.GetType() == result = funcProvider.DynamicInvoke(currAttribute.PropertyType, (propertyValue ??
DataMemberAttributeCollection集合類主要用於設置解析屬性的順序,同樣,該類提供二個參數的構造函數用於生成相應的配置信息public DataMemberAttributeCollection(Type type, params string[] propertyNames)。
主要代碼如下:
GetConfiguration(Type type, (type == || type.GetProperties().Length <= (propertyNames == || propertyNames.Length == ._memberAttributes = ._memberAttributes.OrderBy(p => AddDataMemberAttributes(Type type, <PropertyInfo> validPropertyInfos = List<PropertyInfo> ( propertyName (= (tempPropertyInfo == ArgumentException(.Format( (validPropertyInfos.Count() > ( property = (PropertyInfo propertyInfo = AttributeUtility.GetCustomAttribute<DataMemberAttribute> (attr == (! (._memberAttributes.Count(p => p.Order == attr.Order) > ArgumentException(.Format( (====
該類確保指定Type的類中DataMemberAttribute是否設置正確(是否有相同的Order),確保是否輸入了錯誤的propertyName。
對於具體應用的話,用單元測試來得方便與直接。
(1)對於只輸入一個參數的應用如下:
<IList<>> entityRows = List<IList<>> List<>() { , , , , , contracts = ResultTransfer.Parse<ContinousContract>== ].Code, ].Name, ].ExchangeType, ].OrgidID, ].ExchangeTypeValue,
(2)對於只輸入無效參數的應用如下:
<IList<>> entityRows = List<IList<>> List<>() { , , , , , contracts = ResultTransfer.Parse<ContinousContract>== ].Code, ].Name, ].ExchangeType, ].OrgidID, ].ExchangeTypeValue,
輸入無效的IEnumerable<IEnumerable<string>>參數,方法內部會進行隱式的轉換,比如“sss”轉換成0。
(3)對於二個參數時的應用如下:
<IList<>> entityRows = List<IList<>> List<>() { , , , , propertyNames = List<>() { , , , contracts = ResultTransfer.Parse<ContinousContract>== ].Code, ].Name, ].ExchangeType, ].OrgidID, ].ExchangeTypeValue,
一旦輸入二個參數,且propertyNames參數的個數大於0,則以propertyNames對應的屬性順序進行解析。對於輸入錯誤的屬性名,方法內部會拋出異常,當然也可以增加一個參數用於控制是否拋出異常,或者寫入日志文件中等。
對於將固定格式的字符串解析成IEnumerable<IEnumerable<string>>,正則表達式解析的話比較簡單,此文不做講解,略過...