承接上一篇,這一篇講如何把表達式轉換成記號對象,這裡就涉及到了編譯原理中的詞法分析。關於編譯原理我不想多講,畢竟我自己也不 怎麼熟悉,現在只知道其中有個有限自動機的概念。不管什麼概念,用代碼實現才是最終目標。
因為不清楚字符串中到底包含什麼字符,只能一個個字符進行處理,采用循環一次次向後取一個字符進行判斷。這裡建立一個TokenFactory 記號“工廠”類,由這個類負責對表達式進行分析並“生產”出TokenRecord對象。其中包括兩個方法, LexicalAnalysis和ProduceToken。LexicalAnalysis用於詞法分析,分析到符合規則的記號對象後調用ProduceToken方法,“生產 ”出對應的TokenRecord對象。這裡偷了一點懶,把所有方法全部寫成了static,這樣就不用實例化多個子類了。
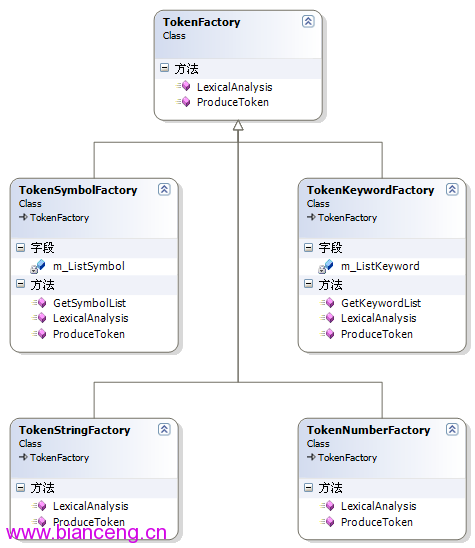
從這個類衍生出多個子類:
TokenKeywordFactory:用於處理關鍵字
TokenSymbolFactory:用於處理運算符
TokenStringFactory:用於處理字符串
TokenNumberFactory:用於處理數字
類圖如下:
分析表達式的入口只有一個,就是TokenFactory中的LexicalAnalysis。TokenFactory類的代碼如下:
internal class TokenFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// 產生記號對象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenWord">記號對應的字符串</param>
/// <param name="Index">記號開始的列序號</param>
/// <returns>記號對象</returns>
protected static TokenRecord ProduceToken(string TokenWord, int Index)
{
throw new Exception("必須在子類中實現方法");
}
/// <summary>
/// 詞法分析
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenList">記號對象列表</param>
/// <param name="Code">表達式</param>
/// <param name="Index">列序號</param>
public static void LexicalAnalysis(List<TokenRecord> TokenList, string Code, ref int Index)
{
char chrTemp;//臨時字符
for (int intIndex = 0; intIndex < Code.Length; intIndex++)
{
chrTemp = Code[intIndex];//獲取當前字符
//關鍵字分析
if (char.IsLetter(chrTemp))//如果當前字符為字母,進行關鍵字處理
{
TokenKeywordFactory.LexicalAnalysis(TokenList, Code, ref intIndex);
}
else if (chrTemp.Equals('\'') || chrTemp.Equals('"'))//如果是字符串分隔符,進行字符串處理
{
TokenStringFactory.LexicalAnalysis(TokenList, Code, ref intIndex);
}
else if (char.IsDigit(chrTemp))//數值處理
{
TokenNumberFactory.LexicalAnalysis(TokenList, Code, ref intIndex);
}
else if (TokenSymbolFactory.GetSymbolDictionary().ContainsKey(chrTemp.ToString()))//運算符處理
{
//有些運算符為雙字符,但這裡所有的雙字符運算符的前一個字符都有對應的單字符運算符,可以 只考慮一個字符
TokenSymbolFactory.LexicalAnalysis(TokenList, Code, ref intIndex);
}
else if (chrTemp.Equals(' '))
{
//如果是空格,則忽略不處理
}
else//錯誤處理
{
//拋出錯誤
throw new SyntaxException(intIndex, 1, "包含不合法字符:" + chrTemp.ToString());
}
}//for
}//LexicalAnalysis
/// <summary>
/// 獲取操作記號字典
/// </summary>
/// <param name="OperateTokenType">操作記號類型</param>
/// <returns>操作記號字典</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo; Date:2008-5-19; Remark:基於本地文件TokenRecord.xml;</remarks>
internal static SortedDictionary<string, string> GetOperateTokenDictionary(OperateTokenTypeEnum OperateTokenType)
{
SortedDictionary<string, string> myDictionary = new SortedDictionary<string, string>();
if (myDictionary.Count == 0)
{
XmlDocument myDoc = new XmlDocument();
myDoc.Load("./TokenRecord.xml");
XmlNodeList KeywordList = myDoc.SelectNodes(string.Format("TokenRecord/{0}/Token",
Enum.GetName(typeof(OperateTokenTypeEnum),OperateTokenType)));
foreach (XmlNode Node in KeywordList)
{
myDictionary.Add(Node.Attributes["Word"].Value, Node.Attributes ["Class"].Value);
}
}
return myDictionary;
}//GetOperateTokenDictionary
}//classTokenFactory
在LexicalAnalysis方法中,只需要判斷當前字符是否符合一定的起始規則,如果符合起始規則,就交給對應的工廠類去處理。
下面用例子來講吧,比如123.3*2-(24+34),分析成記號對象如下:
記號對象
對應表達式
TokenValue
123.3
TokenMultiply
*
TokenValue
2
TokenMinus
-
TokenLeftBracket
(
TokenValue
24
TokenPlus
+
TokenValue
34
TokenRightBracket
)
這裡的處理過程是
1.取字符“1”,轉到TokenNumberFactory,把分析取到的字符串“123.3”轉換為TokenNumber並存到TokenList中
2.取字符“*”,轉到TokenSymbolFactory,把“*”轉換成TokenMultiply並存到TokenList中
3.取字符“2”,轉到TokenNumberFactory,把分析取到的字符串“2”轉換為TokenNumber並存到TokenList中
4.取字符“- ”,轉到TokenSymbolFactory,把“-”轉換成TokenMinus並存到TokenList中
5.取字符“( ”,轉到TokenSymbolFactory,把“(”轉換成TokenLeftBracket並存到TokenList中
6.取字符“2”,轉到TokenNumberFactory,把分析取到的字符串“24”轉換為TokenNumber並存到TokenList中
7.取字符“+”,轉到TokenSymbolFactory,把“+”轉換成TokenPlus並存到TokenList中
8.取字符“3”,轉到TokenNumberFactory,把分析取到的字符串“34”轉換為TokenNumber並存到TokenList中
9.取字符“) ”,轉到TokenSymbolFactory,把“)”轉換成TokenRightBracket並存到TokenList中
至於各個工廠類中怎麼分析提取出對應的字符串,則有各自不同的規則。如果符合規則就繼續向後分析,否則代表分析結束,然後從源字符 串中截取開始分析的序號到結束分析的序號之間的字符串即可。這裡的Index參數相當於C++中的指針,指示當前分析到哪一個字符。因為各個 “工廠”類需要在分析完一個記號後將指針後移,這裡就將Index設置為ref類型。
另一個方法GetOperateTokenDictionary是用來獲取記號字典的,字典的Key是運算符和關鍵字,Value是對應的類名稱。在分析中遇到運算 符和關鍵字的時候,通過查詢字典就可以獲取對應的類名稱,然後通過反射生成類的實例,這樣就可以靈活將操作符和類對應起來。字典的來 源是本地的一個XML文件,當新增一個操作符的時候,到XML文件裡注冊一下,程序就可以識別出新操作符了,“工廠”類不需要做 任何修改。如果需要修改操作符,可以直接在XML文件裡面修改,程序也能識別,比如把mid改成substring,程序照樣可以運行。這就是 “依賴注入”的實際應用。
這裡需要使用的XML如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<TokenRecord>
<TokenKeyword>
<!--以下字符串處理函數記號對象-->
<Token Word="mid" Class="TokenMid" Example="mid('abcdefg',2,3) = 'bcd'" />
<Token Word="left" Class="TokenLeft" Example="left('abcdefg',5) = 'abcde'" />
<Token Word="right" Class="TokenRight" Example="right('abcdefg',5) = 'cdefg'" />
<Token Word="string" Class="TokenToString" Example="string(53.6) = '53.6'" />
<!--以下為數學運算記號對象-->
<Token Word="round" Class="TokenRound" Example="round(0.12345,3) = 0.123" />
<Token Word="abs" Class="TokenAbs" Example="abs(-5) = 5" />
<Token Word="max" Class="TokenMax" Example="max(3,5) = 5" />
<Token Word="min" Class="TokenMin" Example="min(3,5) = 3" />
<!--如果希望取余采用VB的Mod函數,形如Mod(5.4,2) = 1.4,將TokenMod修改為繼承自TokenMethod即可,此時用%必須形如% (5.4,2)-->
<!--<Token Word="mod" Class="TokenMod" Example="5.4 mod 2 = 1.4,mod後必須帶空格" />-->
<Token Word="pow" Class="TokenPow" Example="pow(2,3) = 8" />
<!--以下為三角函數記號對象,均采用角度計算而非弧度-->
<Token Word="sin" Class="TokenSin" Example="sin(30) = 0.5" />
<Token Word="asin" Class="TokenAsin" Example="asin(0.5) = 30" />
<Token Word="cos" Class="TokenCos" Example="cos(60) = 0.5" />
<Token Word="acos" Class="TokenAcos" Example="acos(0.5) = 60" />
<Token Word="tan" Class="TokenTan" Example="tan(45) = 1" />
<Token Word="atan" Class="TokenAtan" Example="atan(1) = 45" />
<Token Word="atan2" Class="TokenAtan2" Example="atan2(30,30) = 45" />
<!--以下為邏輯運算記號對象,可以同時表示為關鍵字和運算符,因為它們的格式一致,都為true operate false-->
<Token Word="and" Class="TokenAnd" Example="true and false = false" />
<Token Word="or" Class="TokenOr" Example="true or false = true" />
<Token Word="not" Class="TokenNot" Example="not true = false" />
<Token Word="xor" Class="TokenXor" Example="true xor false = true" />
<!--以下為常量記號對象-->
<Token Word="pi" Class="TokenValue" Example="pi*1 = 3.1415926" />
<Token Word="e" Class="TokenValue" Example="e*1 = 2.71828" />
<Token Word="true" Class="TokenValue" Example="true and false = false" />
<Token Word="false" Class="TokenValue" Example="true and false = false" />
<!--以下為其他記號對象-->
<Token Word="if" Class="TokenIf" Example="if(3>5,12,24) = 24" />
</TokenKeyword>
<TokenSymbol>
<!--以下為分隔符-->
<Token Word="(" Class="TokenLeftBracket" Example="2*(5-3) = 4" />
<Token Word=")" Class="TokenRightBracket" Example="2*(5-3) = 4" />
<Token Word="," Class="TokenComma" Example="left('abcdefg',5) = 'abcde'" />
<!--以下為數學運算符-->
<Token Word="+" Class="TokenPlus" Example="2+3 = 5 或 'abc' + 'def' = 'abcdef'" />
<Token Word="-" Class="TokenMinus" Example="5-3 = 2" />
<Token Word="*" Class="TokenMultiply" Example="3*4 = 12" />
<Token Word="/" Class="TokenDivide" Example="8/2 = 4" />
<Token Word="%" Class="TokenMod" Example="5.4%2 = 1.4" />
<!--如果希望求冪采用VB的^算法,形如2^3 = 8,將TokenPow修改為繼承自TokenArithmetic即可,此時用pow則必須輸入2 pow 3, pow後必須帶空格-->
<!--<Token Word="^" Class="TokenPow" Example="^(2,3) = 8" />-->
<!--以下為比較運算符-->
<Token Word="=" Class="TokenEqual" Example="if(3=5,12,24) = 24" />
<Token Word="==" Class="TokenEqual" Example="if(3==5,12,24) = 24" />
<Token Word="<>" Class="TokenNotEqual" Example="if(3<>5,12,24) = 12" />
<Token Word="!=" Class="TokenNotEqual" Example="if(3!=5,12,24) = 12" />
<Token Word=">" Class="TokenGreatThan" Example="if(3>5,12,24) = 24" />
<Token Word=">=" Class="TokenGreatOrEqual" Example="if(3>=5,12,24) = 24" />
<Token Word="<" Class="TokenLessThan" Example="if(3<5,12,24) = 12" />
<Token Word="<=" Class="TokenLessOrEqual" Example="if(3<=5,12,24) = 12" />
<!--以下為邏輯運算符,未定義短路操作,可自行實現-->
<Token Word="!" Class="TokenNot" Example="!true = false" />
<Token Word="&" Class="TokenAnd" Example="true & false = false" />
<Token Word="&&" Class="TokenAnd" Example="true && false = false" />
<Token Word="|" Class="TokenOr" Example="true | false = true" />
<Token Word="||" Class="TokenOr" Example="true || false = true" />
</TokenSymbol>
</TokenRecord>
接下來介紹各個工廠類。首先是關鍵字工廠TokenKeywordFactory。當TokenFactory分析到英文字母的時候,把任務轉交給 TokenKeywordFactory。該類從分析得到的第一個英文字母開始向後分析,如果後面還是英文字母或者數字,則繼續向後分析,否則結束分析。 在這裡關鍵字允許包含數字,但第一個字符必須是英文字母。分析結束後,截取分析得到的字符串,然後到交給ProduceToken方法產生一個 TokenRecord類的實例。
在ProduceToken方法中,首先判斷傳入的字符串是否存在於關鍵字字典中,如果不存在則報錯,如果存在則用反射產生一個對應類的實例。 其中有些關鍵字是常量,所以進行了特殊處理,需要設置記號對象的值和類型。
以上工作完成後,調整分析指針的位置,回到TokenFactory類,執行後續分析。TokenKeywordFactory的代碼如下:
/// <summary>
/// 關鍵字工廠
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
internal class TokenKeywordFactory : TokenFactory
{
private static SortedDictionary<string, string> m_DictionaryKeyword = new SortedDictionary<string, string>();
/// <summary>
/// 獲取關鍵字字典
/// </summary>
/// <returns>關鍵字字典</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo; Date:2008-5-19;</remarks>
internal static SortedDictionary<string, string> GetKeywordDictionary()
{
if (m_DictionaryKeyword.Count == 0)
{
m_DictionaryKeyword = TokenFactory.GetOperateTokenDictionary (OperateTokenTypeEnum.TokenKeyword);
}
return m_DictionaryKeyword;
}
/// <summary>
/// 詞法分析
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenList">記號對象列表</param>
/// <param name="Code">源表達式</param>
/// <param name="Index">分析序號</param>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
public static new void LexicalAnalysis(List<TokenRecord> TokenList, string Code, ref int Index)
{
int intIndexCurrent = Index;//當前序號
bool blnContinue = true;
//string strTempChar = "";//獲取臨時字符
char chrTemp;
string strTempWord = "";//獲取臨時字符串
while (blnContinue && intIndexCurrent < Code.Length)
{
chrTemp = Code[intIndexCurrent];
//關鍵字支持大小寫字母及數字,但不允許以數字開頭
if (char.IsLetter(chrTemp) || char.IsDigit(chrTemp))
{
intIndexCurrent += 1;//把當前序號後移
}
else
{
blnContinue = false;
}
}
strTempWord = Code.Substring(Index, intIndexCurrent - Index);//獲取臨時詞
TokenRecord Token = ProduceToken(strTempWord, Index);
TokenList.Add(Token);
Index = intIndexCurrent - 1;//設置指針到讀取結束位置
}
/// <summary>
/// 產生記號對象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenWord">分析得到的單詞</param>
/// <param name="Index">當前序號</param>
/// <returns>記號對象</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
protected static new TokenRecord ProduceToken(string TokenWord, int Index)
{
TokenRecord Token;
if (GetKeywordDictionary().ContainsKey(TokenWord.ToLower()))
{
string strFullClassName = "ConExpress.Calculator." + GetKeywordDictionary() [TokenWord.ToLower()];
Type TokenType = Type.GetType(strFullClassName);
Token = (TokenRecord)Activator.CreateInstance(TokenType, new object[] { Index, TokenWord.Length });
//對常數的特殊處理
switch (TokenWord.ToLower())
{
case "pi"://以下為常量記號對象
Token.TokenValueType = typeof(double);
Token.TokenValue = Math.PI;
break;
case "e":
Token.TokenValueType = typeof(double);
Token.TokenValue = Math.E;
break;
case "true":
Token.TokenValueType = typeof(bool);
Token.TokenValue = true;
break;
case "false":
Token.TokenValueType = typeof(bool);
Token.TokenValue = false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
//錯誤字符串,拋出錯誤,語法錯誤
throw new SyntaxException(Index, TokenWord.Length, "未知表達式:" + TokenWord);
}
return Token;
}//ProduceToken
}//class TokenKeywordFactory
TokenSymbolFactory運算符工廠類的分析過程和TokenKeywordFactory基本相似。但是運算符一般只包含一個字符或者兩個字符,就不需要 一直向後分析了,只需要判斷運算符字典中是否存在對應的項即可。另外有些操作符的第一個字符是重復的,比如“>”和 “>=”,這時候就需要判斷“>”之後是否還存在“=”。如果向後再截取一個字符,在字典中也存在 對應項,則按雙字符運算符處理,否則就是單字符運算符。TokenSymbolFactory的代碼如下:
/// <summary>
/// 運算符工廠
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
class TokenSymbolFactory : TokenFactory
{
private static SortedDictionary<string, string> m_DictionarySymbol = new SortedDictionary<string, string>();
/// <summary>
/// 獲取運算符字典
/// </summary>
/// <returns>運算符字典</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo; Date:2008-5-19;</remarks>
internal static SortedDictionary<string, string> GetSymbolDictionary()
{
if (m_DictionarySymbol.Count == 0)
{
m_DictionarySymbol = TokenFactory.GetOperateTokenDictionary (OperateTokenTypeEnum.TokenSymbol);
}
return m_DictionarySymbol;
}
/// <summary>
/// 詞法分析
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenList">記號對象列表</param>
/// <param name="Code">源表達式</param>
/// <param name="Index">分析序號</param>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
public new static void LexicalAnalysis(List<TokenRecord> TokenList, string Code, ref int Index)
{
string strTempWord;
if ((Index < Code.Length - 1) && GetSymbolDictionary().ContainsKey(Code.Substring(Index, 2)))//如果是雙字節操作符
{
strTempWord = Code.Substring(Index, 2);
Index += 1;//指針後移一位
}
else
{
strTempWord = Code.Substring(Index, 1);
}
TokenRecord Token = ProduceToken(strTempWord, Index);
TokenList.Add(Token);
}
/// <summary>
/// 產生記號對象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenWord">分析得到的單詞</param>
/// <param name="Index">當前序號</param>
/// <returns>記號對象</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
protected new static TokenRecord ProduceToken(string TokenWord, int Index)
{
TokenRecord Token;
if (GetSymbolDictionary().ContainsKey(TokenWord.ToLower()))
{
string strFullClassName = "ConExpress.Calculator." + GetSymbolDictionary() [TokenWord.ToLower()];
Type TokenType = Type.GetType(strFullClassName);
Token = (TokenRecord)Activator.CreateInstance(TokenType, new object[] { Index, TokenWord.Length });
}
else
{
//錯誤字符串,拋出錯誤,語法錯誤
throw new SyntaxException(Index, TokenWord.Length, "未知表達式:" + TokenWord);
}
return Token;
}//ProduceToken
}//class TokenSymbolFactory
TokenStringFactory字符串工廠類的分析是按照VB語法,只有引號需要轉義,用兩個引號即可,其他特殊字符不需要轉義。而且引號和 JavaScript一樣,可以用大寫或者小寫,只要兩端匹配就可以了。如果在單引號標記的字符串中包含雙引號,則不需要轉義,雙引號標記的字 符串中出現單引號也不需要轉義。字符串的分析是以引號作為界定,向後分析的過程中,如果遇到與起始引號相同的字符,判斷後面是否存在 重復引號,存在則轉義,不存在則結束分析。將兩個引號之間的字符串截取,創建一個TokenValue對象,結束分析。TokenStringFactory代碼 如下:
/// <summary>
/// 字符串工廠
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
class TokenStringFactory : TokenFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// 詞法分析
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenList">記號對象列表</param>
/// <param name="Code">源表達式</param>
/// <param name="Index">分析序號</param>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
public new static void LexicalAnalysis(List<TokenRecord> TokenList, string Code, ref int Index)
{
string strQuotationMark = Code.Substring(Index, 1);//引號,可以是單引號,也可以是雙引號
int intIndexCurrent = Index + 1;//指向後一個字符
string strTempChar = "";//臨時字符
StringBuilder strTempWord = new StringBuilder();//臨時字符串
bool blnContinue = true;
while (blnContinue && intIndexCurrent < Code.Length)//循環直到標志位置False或超出長度
{
strTempChar = Code.Substring(intIndexCurrent, 1);
if (strTempChar.Equals(strQuotationMark))//如果是字符串分隔符
{
if ((intIndexCurrent < Code.Length - 1)
&& Code.Substring(intIndexCurrent + 1, 1).Equals(strQuotationMark))// 如果後面還是引號,則進行轉義,將兩個引號轉義為一個引號字符
{
strTempWord.Append(strQuotationMark);//添加一個引號字符到臨時字符串中
intIndexCurrent += 2;//向後移兩位
}
else
{
blnContinue = false;//遇到字符串結束引號,退出
}
}
else
{
strTempWord.Append(strTempChar);//添加當前字符到臨時字符串中
intIndexCurrent += 1;//向後移一位
}//if
}//while
TokenRecord Token = ProduceToken(strTempWord.ToString(), Index);
TokenList.Add(Token);
Index = intIndexCurrent;//指針移到當前指針,即字符串結束引號
}//LexicalAnalysis
/// <summary>
/// 產生記號對象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenWord">分析得到的單詞</param>
/// <param name="Index">當前序號</param>
/// <returns>記號對象</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
public new static TokenRecord ProduceToken(string TokenWord, int Index)
{
TokenRecord Token = new TokenValue(Index, TokenWord.Length);
Token.TokenValue = TokenWord;
Token.TokenValueType = typeof(string);
return Token;
}
}//class TokenStringFactory
TokenNumberFactory數值工廠的分析最簡單,主要是判斷下一個字符是否是數字或者小數點。將分析得到的字符串轉換為double類型,然後 賦值給創建的TokenValue對象即可。TokenNumberFactory代碼如下:
/// <summary>
/// 數值工廠
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
class TokenNumberFactory : TokenFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// 詞法分析
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenList">記號對象列表</param>
/// <param name="Code">源表達式</param>
/// <param name="Index">分析序號</param>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
public new static void LexicalAnalysis(List<TokenRecord> TokenList, string Code, ref int Index)
{
int intIndexCurrent = Index;//指向後一個字符
bool blnContinue = true;
char chrTemp;
string strTempWord;
while (blnContinue && intIndexCurrent < Code.Length)
{
chrTemp = Code[intIndexCurrent];
if (char.IsDigit(chrTemp) || chrTemp.Equals('.'))
{
intIndexCurrent += 1;
}
else
{
blnContinue = false;
}
}//while
strTempWord = Code.Substring(Index, intIndexCurrent - Index);//取得臨時字符串
TokenRecord Token = ProduceToken(strTempWord, Index);
TokenList.Add(Token);
Index = intIndexCurrent - 1;//指針移到當前指針的前一位,然後賦值給循環指針
}//LexicalAnalysis
/// <summary>
/// 產生記號對象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="TokenWord">分析得到的單詞</param>
/// <param name="Index">當前序號</param>
/// <returns>記號對象</returns>
/// <remarks>Author:Alex Leo</remarks>
public new static TokenRecord ProduceToken(string TokenWord, int Index)
{
TokenRecord Token = new TokenValue(Index + 1, TokenWord.Length);
Token.TokenValueType = typeof(double);
double dblValue;
if (double.TryParse(TokenWord, out dblValue))
{
Token.TokenValue = dblValue;
}
else
{
throw new SyntaxException(Index, TokenWord.Length, "表達式 " + TokenWord + " 無 法轉換成數值。");
}
return Token;
}//ProduceToken
}//class TokenNumberFactory
通過這些“工廠”類就可以完成把表達式分析成記號對象列表,為程序理解表達式做好了基礎工作。在下一篇中會介紹如何將記 號對象分析成樹視圖,進而通過樹視圖逐級求解。