在操作系統中,利用進程可以對正在運行的應用程序進行隔離,每個應用程序被加載到單獨的進程中,並為其分配虛擬內存,進程無法直接 訪問物理內存,只能通過操作系統將虛擬內存映射到物理內存中,並保證進程之間的物理內存不會重疊,但是進程最大的缺點就是效率問題, 尤其是進程的切換開銷很大,而進程間不能共享內存,所以不可能從一個進程通過傳遞指針給另一個進程。
在.NET中出現了一個新的概 念:AppDomain——應用程序域,所有.NET應用程序都需要運行在托管環境中,操作系統能提供的只有進程,因此.NET程序需要通過 AppDomain這個媒介來運行在進程中,同時使用該incheng提供的內存空間,只要是.NET的應用都會運行在某個AppDomain中。
當我們 運行一個.NET應用程序或者運行庫宿主時,OS會首先建立一個進程,然後會在進程中加載CLR(這個加載一般是通過調用_CorExeMain或者 _CorBindToRuntimeEx方法來實現),在加載CLR時會創建一個默認的AppDomain,它是CLR的運行單元,程序的Main方法就是在這裡執行,這個默 認的AppDomain是唯一且不能被卸載的,當該進程消滅時,默認AppDomain才會隨之消失。
一個進程中可以有多個AppDomain,且它們直 接是相互隔離的,我們的Assembly是不能單獨執行的,它必須被加載到某個AppDomain中,要想卸載一個Assembly就只能卸載其AppDomain。
最近在我所參加的一個項目中要實現這樣一個模塊:定制一個作業管理器,它可以定時的以不同頻率執行某些.Net應用程序或者存儲過 程,這裡的頻率可以是僅一次、每天、每周還是每月進行執行計劃的實施,對於調用存儲過程沒什麼好說的,但是調用.Net應用程序的時候就 需要考慮如下問題:
一旦Assembly被作業管理器的服務器調用,(比如某個執行計劃正好要被執行了),在調用之前會將程序集加載到 默認AppDomain,然後執行,這就有個問題,如果我需要做替換或者刪除Assembly等這些操作的時候,由於Assembly已經被默認AppDomain加載 ,那麼對它的更改肯定是不允許的,它會彈出這樣的錯誤:
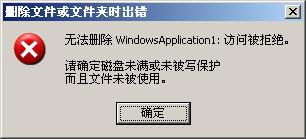
除非你關掉作業管理服務器,然後再操作,顯然這樣做是 很不合理的。
並且默認AppDomain是不能被卸載的,那麼我們該怎麼辦呢,我想到的方法是動態的加載Assembly,新建一個AppDomain, 讓Assembly加載到這個新AppDomain中然後執行,當執行完後卸載這個新的AppDomain即可,方法如下:
1、創建程序集加載類 AssemblyDynamicLoader,該類用來創建新的AppDomain,並生成用來執行.Net程序的RemoteLoader類:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using Ark.Log;
/// <summary>
/// The local loader.
/// </summary>
public class AssemblyDynamicLoader
{
/// <summary>
/// The log util.
/// </summary>
private static ILog log = LogManager.GetLogger (typeof(AssemblyDynamicLoader));
/// <summary>
/// The new appdomain.
/// </summary>
private AppDomain appDomain;
/// <summary>
/// The remote loader.
/// </summary>
private RemoteLoader remoteLoader;
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="LocalLoader"/> class.
/// </summary>
public AssemblyDynamicLoader()
{
AppDomainSetup setup = new AppDomainSetup();
setup.ApplicationName = "ApplicationLoader";
setup.ApplicationBase = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory;
setup.PrivateBinPath = Path.Combine (AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "private");
setup.CachePath = setup.ApplicationBase;
setup.ShadowCopyFiles = "true";
setup.ShadowCopyDirectories = setup.ApplicationBase;
this.appDomain = AppDomain.CreateDomain("ApplicationLoaderDomain", null, setup);
String name = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().FullName;
this.remoteLoader = (RemoteLoader) this.appDomain.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(name, typeof(RemoteLoader).FullName);
}
/// <summary>
/// Invokes the method.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fullName">The full name.</param>
/// <param name="className">Name of the class.</param>
/// <param name="argsInput">The args input.</param>
/// <param name="programName">Name of the program.</param>
/// <returns>The output of excuting.</returns>
public String InvokeMethod(String fullName, String className, String argsInput, String programName)
{
this.remoteLoader.InvokeMethod (fullName, className, argsInput, programName);
return this.remoteLoader.Output;
}
/// <summary>
/// Unloads this instance.
/// </summary>
public void Unload()
{
try
{
AppDomain.Unload(this.appDomain);
this.appDomain = null;
}
catch (CannotUnloadAppDomainException ex)
{
log.Error("To unload assembly error!", ex);
}
}
}
2、創 建RemoteLoader類,它可以在AppDomain中自由穿越,這就需要繼承System.MarshalByRefObject這個抽象類,這裡RemoteLoader如果不繼承 MarshalByRefObject類則一定會報錯(在不同AppDomain間傳遞對象,該對象必須是可序列化的)。以RemoteLoader類做為代理來調用待執行 的.Net程序。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
/// <summary>
/// The Remote loader.
/// </summary>
public class RemoteLoader : MarshalByRefObject
{
/// <summary>
/// The assembly we need.
/// </summary>
private Assembly assembly = null;
/// <summary>
/// The output.
/// </summary>
private String output = String.Empty;
/// <summary>
/// Gets the output.
/// </summary>
/// <value>The output.</value>
public String Output
{
get
{
return this.output;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Invokes the method.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fullName">The full name.</param>
/// <param name="className">Name of the class.</param>
/// <param name="argsInput">The args input.</param>
/// <param name="programName">Name of the program.</param>
public void InvokeMethod(String fullName, String className, String argsInput, String programName)
{
this.assembly = null;
this.output = String.Empty;
try
{
this.assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom(fullName);
Type pgmType = null;
if (this.assembly != null)
{
pgmType = this.assembly.GetType (className, true, true);
}
else
{
pgmType = Type.GetType(className, true, true);
}
Object[] args = RunJob.GetArgs(argsInput);
BindingFlags defaultBinding = BindingFlags.DeclaredOnly | BindingFlags.Public
| BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.IgnoreCase
| BindingFlags.InvokeMethod | BindingFlags.Static;
CultureInfo cultureInfo = new CultureInfo("es- ES", false);
try
{
MethodInfo methisInfo = RunJob.GetItsMethodInfo(pgmType, defaultBinding, programName);
if (methisInfo == null)
{
this.output = "EMethod does not exist!";
}
if (methisInfo.IsStatic)
{
if (methisInfo.GetParameters().Length == 0)
{
if (methisInfo.ReturnType == typeof(void))
{
pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, null, null, cultureInfo);
this.output = "STo call a method without return value successful.";
}
else
{
this.output = (String)pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, null, null, cultureInfo);
}
}
else
{
if (methisInfo.ReturnType == typeof(void))
{
pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, null, args, cultureInfo);
this.output = "STo call a method without return value successful.";
}
else
{
this.output = (String)pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, null, args, cultureInfo);
}
}
}
else
{
if (methisInfo.GetParameters().Length == 0)
{
object pgmClass = Activator.CreateInstance(pgmType);
if (methisInfo.ReturnType == typeof(void))
{
pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, pgmClass, null, cultureInfo);
this.output = "STo call a method without return value successful.";
}
else
{
this.output = (String)pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, pgmClass, null, cultureInfo); //'ymtpgm' is program's name and the return value of it must be started with 'O'.
}
}
else
{
object pgmClass = Activator.CreateInstance(pgmType);
if (methisInfo.ReturnType == typeof(void))
{
pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, pgmClass, args, cultureInfo);
this.output = "STo call a method without return value successful.";
}
else
{
this.output = (String)pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, pgmClass, args, cultureInfo); //'ymtpgm' is program's name and the return value of it must be started with 'O'.
}
}
}
}
catch
{
this.output = (String)pgmType.InvokeMember(programName, defaultBinding, null, null, null, cultureInfo);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
this.output = "E" + e.Message;
}
}
}
其中的InvokeMethod方法只要提供Assembly的全名 、類的全名、待執行方法的輸入參數和其全名就可以執行該方法,該方法可以是帶參數或不帶參數,靜態的或者不是靜態的。
最後這樣 使用這兩個類:
AssemblyDynamicLoader loader = new AssemblyDynamicLoader();
String output = loader.InvokeMethod("fileName", "ymtcla", "yjoinp", "ymtpgm");
loader.Unload();