類型介紹
在幾乎所有的OOP語言中,都存在2種類型的值。
值類型 引用類型
以C#為例:其值類型為sbyte,byte,char,short,ushort,int,uint,long和ulong,float和double,當然還有decimal和bool。而引用類型則是string和object。
我想說的
我想說的就是——Ref和Out把我弄糊塗的原因是,當時沒有認真的去分析它對不同類型所做出的不同的動作。
對於值類型。
使用了Ref和Out的效果就幾乎和C中使用了指針變量一樣。它能夠讓你直接對原數進行操作,而不是對那個原數的Copy進行操作。舉個小例子:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication4
{
///
/// Class1 的摘要說明。
///
class Class1
{
///
/// 應用程序的主入口點。
///
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 5;
int b;
squareRef(ref a);
squareOut(out b);
Console.WriteLine("The a in the Main is: " + a);
Console.WriteLine("The b in the Main is: " + b);
}
static void squareRef(ref int x)
{
x = x * x;
Console.WriteLine("The x in the squareRef is: " + x);
}
static void squareOut(out int y)
{
y = 10;
y = y * y;
Console.WriteLine("The y in the squareOut is: " + y);
}
}
}
顯示的結果就是——25 100 25 100。
這樣的話,就達到了和C中的指針變量一樣的作用。
對於引用類型。
對於引用類型就比較難理解了。
先要了解到這一層——就是當一個方法接收到一個引用類型的變量的時候,它將獲得這個引用(Reference)的一個Copy。由於Ref關鍵字可以用來向方法傳遞引用。所以,如果這個功能被誤用了——比如:當一個如數組類型的引用對象用關鍵字Ref傳遞的時候,被調用的方法實際上已經控制了傳遞過來的引用本身。這樣將使得被調用方法能用不同的對象甚至NULL來代替調用者的原始引用!
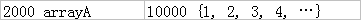
如圖。內存地址為2000的變量arrayA中其實存放著數組{1,2,3,4,……}的內存起始地址10000。如果一個方法fun()使用fun( arrayA[] )的話,它將順利的獲得數據10000,但這個10000將放在一個Copy中,不會放到內存的2000位置。而這個時候我們如果使用fun( ref arrayA[] )的話,我們得到的值就是2000啦(也就是說,被調用方法能夠修改掉arrayA中的那個引用,使之不再指向10000,甚至可以用NULL來代替10000,這樣的話,那個10000地址中的數據可能就要被垃圾回收機制清理了。)
有個例子:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
namespace RefOut
{
/// <summary>
/// Form1 的摘要說明。
/// </summary>
public class Form1 : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label label1;
/// <summary>
/// 必需的設計器變量。
/// </summary>
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
public Form1()
{
//
// Windows 窗體設計器支持所必需的
//
InitializeComponent();
//
// TODO: 在 InitializeComponent 調用後添加任何構造函數代碼
//
}
/// <summary>
/// 清理所有正在使用的資源。
/// </summary>
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
#region Windows 窗體設計器生成的代碼
/// <summary>
/// 設計器支持所需的方法 - 不要使用代碼編輯器修改
/// 此方法的內容。
/// </summary>
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.label1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// button1
//
this.button1.Dock = System.Windows.Forms.DockStyle.Top;
this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(0, 0);
this.button1.Name = "button1";
this.button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(480, 32);
this.button1.TabIndex = 0;
this.button1.Text = "顯示輸出";
this.button1.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button1_Click);
//
// label1
//
this.label1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(8, 48);
this.label1.Name = "label1";
this.label1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(456, 336);
this.label1.TabIndex = 1;
this.label1.Text = "label1";
//
// Form1
//
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(6, 14);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(480, 405);
this.Controls.Add(this.label1);
this.Controls.Add(this.button1);
this.MaximizeBox = false;
this.MinimizeBox = false;
this.Name = "Form1";
this.Text = "Ref & Out";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// 應用程序的主入口點。
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
int[] firstArray = {1, 2, 3};
int[] firstArrayCopy = firstArray;
this.label1.Text = "Test Passing firstArray reference by value";
this.label1.Text += "\n\nContents of firstArray before calling FirstDouble:\n\t";
for(int i = 0;i < firstArray.Length; i++)
{
this.label1.Text += firstArray[i] + " ";
}
FirstDouble(firstArray);
this.label1.Text += "\n\nContents of firstArray after calling FirstDouble.\n\t";
for(int i=0;i<firstArray.Length;i++)
{
this.label1.Text += firstArray[i] + " ";
}
if(firstArray == firstArrayCopy)
this.label1.Text +="\n\nThe references refer to the same array.\n";
else
this.label1.Text +="\n\nThe reference refer to different arrays.\n";
int[] secondArray = {1, 2, 3};
int[] secondArrayCopy = secondArray;
this.label1.Text += "\nTest passing secondArray reference by reference.";
this.label1.Text += "\n\nContents of secondArray before calling SecondDouble:\n\t";
for(int i=0;i<secondArray.Length; i++)
{
this.label1.Text += secondArray[i] + " ";
}
SecondDouble(ref secondArray);
this.label1.Text +="\n\nContents of secondArray after calling SecondDouble:\n\t";
for(int i=0; i<secondArray.Length;i++)
{
this.label1.Text += secondArray[i] + " ";
}
if(secondArray== secondArrayCopy)
this.label1.Text += "\n\nThe reference refer to the same array.";
else
this.label1.Text += "\n\nThe reference refer to different arrays.";
this.label1.Text += "\n___________________heshi_________________\nsecondarray\n";
for(int i = 0;i<secondArray.Length;i++)
{
this.label1.Text += secondArray[i] + " ";
}
this.label1.Text +="\nsecondarraycopy\n";
for(int i=0;i<secondArrayCopy.Length;i++)
{
this.label1.Text += secondArrayCopy[i] + " ";
}
}
void FirstDouble(int[] array)
{
for(int i = 0;i<array.Length;i++)
array[i] *= 2;
array = new int[] {11, 12, 13};
}
void SecondDouble(ref int[] array)
{
for(int i=0;i<array.Length;i++)
{
array[i] *= 2;
}
array = new int[] {11, 12, 13};
}
}
}
運行後的結果是:
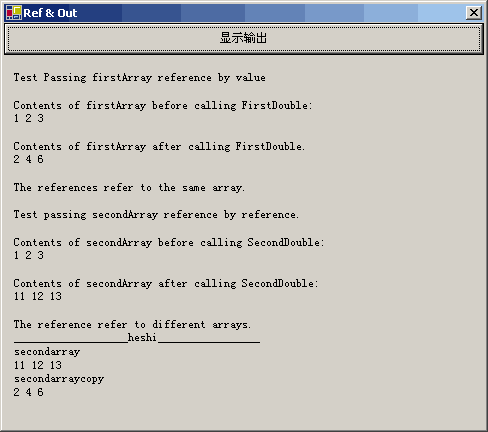
這個就說明了被調用的程序已經改變了原有的Reference。
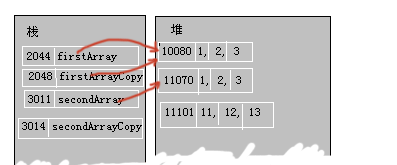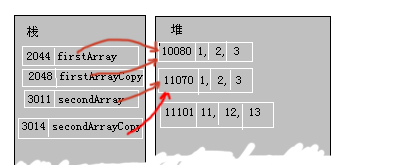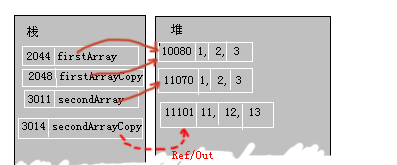
總結
總的說來,Ref和Out這兩個關鍵字都能夠提供相似的功效,其作用也很像C中的指針變量。稍有不同之處是:
使用Ref型參數時,傳入的參數必須先被初始化。而Out則不需要,對Out而言,就必須在方法中對其完成初始化。 使用Ref和Out時都必須注意,在方法的參數和執行方法時,都要加Ref或Out關鍵字。以滿足匹配。 Out更適合用在需要Return多個返回值的地方,而Ref則用在需要被調用的方法修改調用者的引用的時候。