根據“空間/IV”的評論,我寫了個動態生成用戶輸入的函數表達式的類,用以改進這個畫函數圖形的C#程序。下面是該程序的運行效果:
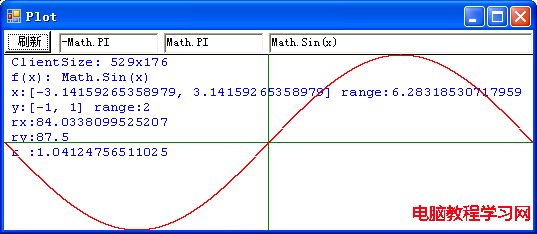
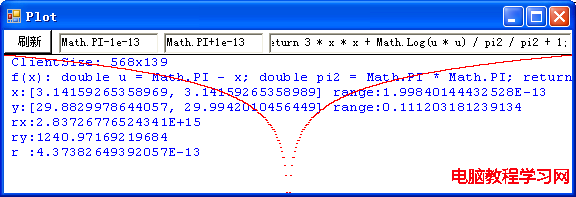
可以看到,不但要畫的函數的表達式可以由用戶動態地輸入,而且函數自變量的范圍也可以是常量表達式。 下面就是源程序:

// plot.cs: 畫函數圖形, 編譯方法: csc /t:winexe plot.cs Expression.cs

using System;

using System.Drawing;

using System.
Windows.Forms;

using Skyiv.Util;


namespace Skyiv.Ben.Plot
{

sealed class PlotForm : Form

{

const int yBase = 24; // 屏幕保留區域的高度


TextBox tbxX0, tbxX1; // 函數自變量的取值范圍

TextBox tbxExpression; // 函數的表達式


PlotForm()



{

SuspendLayout();


Button btnSubmit = new Button();

btnSubmit.Text = "刷新";

btnSubmit.Location = new Point(0, 0);

btnSubmit.Size = new Size(48, 24);

btnSubmit.Click += new EventHandler(BtnSubmit_Click);


tbxX0 = new TextBox();

tbxX0.Text = "-Math.PI";

tbxX0.Location = new Point(55, 3);

tbxX0.Size = new Size(100, 20);


tbxX1 = new TextBox();

tbxX1.Text = "Math.PI";

tbxX1.Location = new Point(160, 3);

tbxX1.Size = new Size(100, 20);


tbxExpression = new TextBox();

tbxExpression.Text = "Math.Sin(x)";

tbxExpression.Location = new Point(265, 3);

tbxExpression.Size = new Size(335, 20);

tbxExpression.Anchor = (AnchorStyles.Top | AnchorStyles.Left | AnchorStyles.Right);



Controls.AddRange(new Control[]

{btnSubmit, tbxX0, tbxX1, tbxExpression});

Text = "Plot";

BackColor = Color.White;

ClientSize = new Size(600, 600 + yBase);

// WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized;


ResumeLayout(false);
}


// 點擊“刷新”按鈕時重繪程序主窗口

void BtnSubmit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)



{

Invalidate();
}



/**//*

// 因為本程序使用 C# 的反射功能動態生成數學表達式並計算其值

// 所以重畫時有點慢,如果你的計算機的速度不是非常快的,

// 就不要在窗口改變大小時強制重繪,而是通過點擊發“刷新”按鈕重繪。

protected override void OnSizeChanged(EventArgs e)

{

Invalidate();

base.OnSizeChanged(e);

}
*/


protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)



{

Graphics gc = e.Graphics;

try



{

double x0 = new Expression(tbxX0.Text).Compute(0);

double x1 = new Expression(tbxX1.Text).Compute(0);

Size size = ClientSize;

int i0 = 0;

int i1 = size.Width - 1;

int j0 = yBase;

int j1 = size.Height - 1;

Pen pen = new Pen(Color.Black, 1);

gc.DrawLine(pen, i0, j0, i1, j0); // 畫圖區和保留區的分界線

double rx = (x1 - x0) / (i1 - i0);

double y0, y1;

Expression fx = new Expression(tbxExpression.Text);

GetFunctionValueRange(fx, x0, rx, i0, i1, out y0, out y1);

double ry = (y1 - y0) / (j1 - j0);

Out(gc, 0, "ClientSize: {0}x{1}", i1 - i0 + 1, j1 - j0 + 1);

Out(gc, 1, "f(x): " + tbxExpression.Text);

Out(gc, 2, "x:[{0}, {1}] range:{2}", x0, x1, x1 - x0);

Out(gc, 3, "y:[{0}, {1}] range:{2}", y0, y1, y1 - y0);

Out(gc, 4, "rx:{0}", 1 / rx); // 函數自變量每單位值用多少個象素表示

Out(gc, 5, "ry:{0}", 1 / ry); // 函數的值每單位值用多少個象素表示

Out(gc, 6, "r :{0}", rx / ry); // 該值如果小於1表示圖形縱向被壓扁,反之則被拉伸

pen.Color = Color.Green;

int j = j1 + (int)(y0 / ry);

if (j >= j0 && j <= j1) gc.DrawLine(pen, i0, j, i1, j); // x坐標軸

int i = i0 - (int)(x0 / rx);

if (i >= i0 && i <= i1) gc.DrawLine(pen, i, j0, i, j1); // y坐標軸

pen.Color = Color.Red;

for (i = i0; i <= i1; i++)



{

double x = x0 + (i - i0) * rx;

double y = fx.Compute(x);

if (double.IsInfinity(y) || double.IsNaN(y)) continue;

j = j1 - (int)((y - y0) / ry);

if (j > j1 || j < j0) continue;

gc.DrawLine(pen, i, j, i + 1, j); // 畫函數的圖形
}
}

catch (Exception ex)



{

Out(gc, 0, ex.Message);
}

base.OnPaint(e);
}


// 函數值的取值范圍

void GetFunctionValueRange(Expression fx, double x0, double rx, int i0, int i1, out double y0, out double y1)



{

y0 = double.MaxValue;

y1 = double.MinValue;

for (int i = i0; i <= i1; i++)



{

double x = x0 + (i - i0) * rx;

double y = fx.Compute(x);

if (double.IsInfinity(y) || double.IsNaN(y)) continue;

if (y0 > y) y0 = y;

if (y1 < y) y1 = y;
}
}


// 在指定的位置寫字符串

void Out(Graphics gc, int line, string fmt, params object [] args)



{

gc.DrawString(string.Format(fmt, args), new Font("Courier New", 10), Brushes.Blue, new PointF(5, yBase + 15 * line));
}


static void Main()



{

Application.Run(new PlotForm());
}
}
}

其中的“Expression.cs”程序請參看我的另一篇隨筆:“動態地生成用戶輸入的函數表達式(C#)”。
這裡的表達式是使用C#語法。如需要使用 VisualBasic 語法,請參閱該隨筆的評論。

