接上篇:.net源碼分析 – List<T>
Dictionary<TKey, TValue>源碼地址:https://github.com/dotnet/corefx/blob/master/src/System.Collections/src/System/Collections/Generic/Dictionary.cs
Dictionary<TKey, TValue>和List<T>的接口形式差不多,不重復說了,可以參考List<T>那篇。
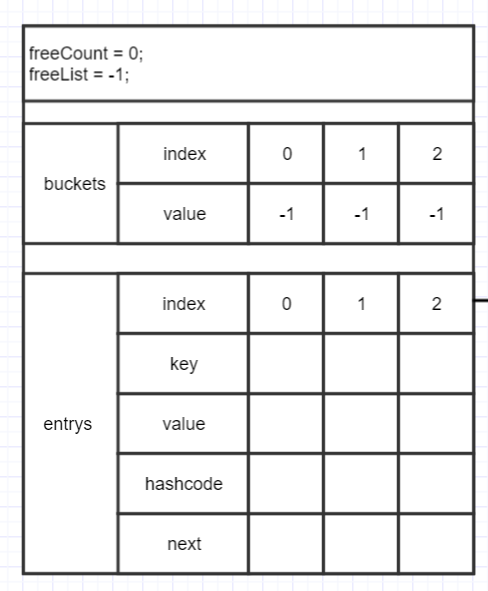
看下有哪些成員變量:
private int[] buckets; private Entry[] entries; private int count; private int version; private int freeList; private int freeCount; private IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer; private KeyCollection keys; private ValueCollection values; private Object _syncRoot;
buckets是一個int型數組,具體什麼用現在還未知,後面看,暫時可以理解成區,像硬盤我們一般會做分區歸類方便查找。
entries是Entry數組,看看Entry:
private struct Entry
{
public int hashCode; // Lower 31 bits of hash code, -1 if unused
public int next; // Index of next entry, -1 if last
public TKey key; // Key of entry
public TValue value; // Value of entry
}
是個結構,裡面有key, value, 說明我們Dictionary的key和value就是用這個結構保存的,另外還有hashcode和next,看起來像鏈表一樣,後面用到時再具體分析其用處。
count:和List <T>一樣,是指包括元素的個數(這裡其實也不是真正的個數,下面會講),並不是容量
version: List <T>篇講過,用來遍歷時禁止修改集合
freeList, freeCount這兩個看起來比較奇怪,比較難想到會有什麼用,在添加和刪除項時會用到它們,後面再講。
comparer: key的比較對象,可以用它來獲取hashcode以及進行比較key是否相同
keys, values這個我們平常也有用到,遍歷keys或values有用
_syncRoot,List<T>篇也講過,線程安全方面的,Dictionary同樣沒有用到這個對象,Dictionary也不是線程安全的,在多線程環境下使用需要自己加鎖。
Dictionary的代碼比List相對復雜些,下面不直接分析源碼,而是以下面這些常用例子來一步一步展示Dictionary是怎麼工作的:
Dictionary<string, string> dict = new Dictionary<string, string>();
dict.Add("a", "A");
dict.Add("b", "B");
dict.Add("c", "C");
dict["d"] = "D";
dict["a"] = "AA";
dict.remove("b");
dict.Add("e", "E");
var a = dict["a"];
var hasA = dict.ContainsKey("a");
這裡對hashcode做些假設,方便分析:
"a"的hashcode為3
"b"的hashcode為4
"c"的hashcode為6
"d"的hashcode為11
"e"的hashcode為10
先看第一句,new 一個Dictionary<string, string>,看源碼裡的構造函數,有6個
public Dictionary() : this(0, null) { }
public Dictionary(int capacity) : this(capacity, null) { }
public Dictionary(IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer) : this(0, comparer) { }
public Dictionary(int capacity, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer)
{
if (capacity < 0) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(capacity), capacity, "");
if (capacity > 0) Initialize(capacity);
this.comparer = comparer ?? EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default;
}
public Dictionary(IDictionary<TKey, TValue> dictionary) : this(dictionary, null) { }
public Dictionary(IDictionary<TKey, TValue> dictionary, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer) :
this(dictionary != null ? dictionary.Count : 0, comparer)
{
if (dictionary == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(dictionary));
}
if (dictionary.GetType() == typeof(Dictionary<TKey, TValue>))
{
Dictionary<TKey, TValue> d = (Dictionary<TKey, TValue>)dictionary;
int count = d.count;
Entry[] entries = d.entries;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode >= 0)
{
Add(entries[i].key, entries[i].value);
}
}
return;
}
foreach (KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> pair in dictionary)
{
Add(pair.Key, pair.Value);
}
}
大部分都是用默認值,真正用到的是public Dictionary(int capacity, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer),這個是每個構造函數都要調用的,看看它做了什麼:
if (capacity > 0) Initialize(capacity); 當capacity大於0時,也就是顯示指定了capacity時才會調用初始化函數,capacity指容量,List<T>裡也有說過,不同的是Dictionary只能在構造函數裡指定capacity,而List<T>可以隨時指定。接下來看看初始化函數做了什麼:
private void Initialize(int capacity)
{
int size = HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity);
buckets = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++) buckets[i] = -1;
entries = new Entry[size];
freeList = -1;
}
HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity)根據傳進來的capacity獲取一個質數,質數大家都知道 2,3,5,7,11,13等等除了自身和1,不能被其他數整除的就是質數,具體看看這個獲取質數的函數:
public static readonly int[] primes = {
3, 7, 11, 17, 23, 29, 37, 47, 59, 71, 89, 107, 131, 163, 197, 239, 293, 353, 431, 521, 631, 761, 919,
1103, 1327, 1597, 1931, 2333, 2801, 3371, 4049, 4861, 5839, 7013, 8419, 10103, 12143, 14591,
17519, 21023, 25229, 30293, 36353, 43627, 52361, 62851, 75431, 90523, 108631, 130363, 156437,
187751, 225307, 270371, 324449, 389357, 467237, 560689, 672827, 807403, 968897, 1162687, 1395263,
1674319, 2009191, 2411033, 2893249, 3471899, 4166287, 4999559, 5999471, 7199369, 8639249, 10367101,
12440537, 14928671, 17914409, 21497293, 25796759, 30956117, 37147349, 44576837, 53492207, 64190669,
77028803, 92434613, 110921543, 133105859, 159727031, 191672443, 230006941, 276008387, 331210079,
397452101, 476942527, 572331049, 686797261, 824156741, 988988137, 1186785773, 1424142949, 1708971541,
2050765853, MaxPrimeArrayLength };
public static int GetPrime(int min)
{
if (min < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("");
Contract.EndContractBlock();
for (int i = 0; i < primes.Length; i++)
{
int prime = primes[i];
if (prime >= min) return prime;
}
return min;
}
這裡維護了個質數數組,注意,裡面並不是完整的質數序列,而是有一些過濾掉了,因為有些挨著太緊,比方說2和3,增加一個就要擴容很沒必要。
GetPrime看if (prime >= min) return prime;這行代碼知道是要獲取第一個比傳進來的值大的質數,比方傳的是1,那3就是獲取到的初始容量。
接著看初始化部分的代碼:size現在知道是3,接下來以這個size來初始化buckets和entries,並且buckets裡的元素都設為-1,freeList同樣初始化成-1,這個後面有用。
初始化完後再調用這行代碼 : this.comparer = comparer ?? EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default; 也是初始化comparer,看EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default這個到底用的是什麼:
public static EqualityComparer<T> Default
{
get
{
if (_default == null)
{
object comparer;
if (typeof(T) == typeof(SByte))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForSByte();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Byte))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForByte();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Int16))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForInt16();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(UInt16))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForUInt16();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Int32))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForInt32();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(UInt32))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForUInt32();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Int64))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForInt64();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(UInt64))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForUInt64();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(IntPtr))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForIntPtr();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(UIntPtr))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForUIntPtr();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Single))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForSingle();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Double))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForDouble();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(Decimal))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForDecimal();
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(String))
comparer = new EqualityComparerForString();
else
comparer = new LastResortEqualityComparer<T>();
_default = (EqualityComparer<T>)comparer;
}
return _default;
}
}
為不同類型創建一個comparer,看下面代碼是我們用到的string的comparer:hashcode直接取的string的hashcode,其實這裡面的所有類型取hashcode都是一樣,equals則有個別不同。
internal sealed class EqualityComparerForString : EqualityComparer<String>
{
public override bool Equals(String x, String y)
{
return x == y;
}
public override int GetHashCode(String x)
{
if (x == null)
return 0;
return x.GetHashCode();
}
}
基本構造函數就這些,還有個構造函數可以傳一個IDictionary<TKey, TValue>進來,和List<T>一樣,也是初始化就加入這些集合,首先判斷是否是Dictionary,是的話直接遍歷它的entries,加到當前的entries裡,如果不是則用枚舉器遍歷。
為什麼不直接用枚舉器呢,因為枚舉器也是要消耗一些資源的,而且沒有直接遍歷數組來得快。
這個構造函數添加時用到了Add方法,和例子裡Add一樣,正好是接下來要講的。
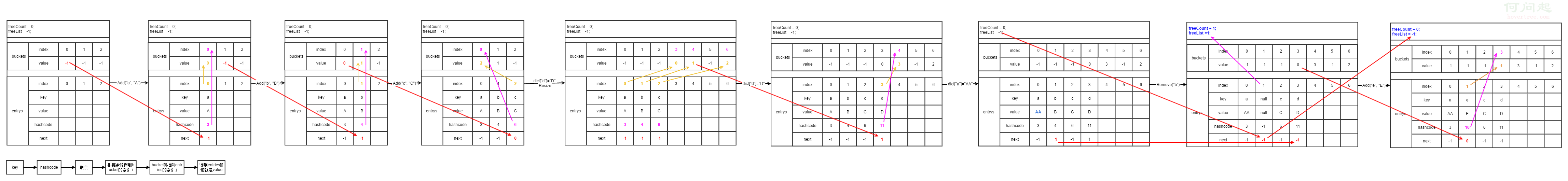
下圖就是初始變量的狀態:
Add方法直接調用Insert方法,第三個參數為true
public void Add(TKey key, TValue value)
{
Insert(key, value, true);
}
再看Insert方法,這個方法是核心方法,有點長,跟著注釋一點一點看。
private void Insert(TKey key, TValue value, bool add)
{
if (key == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(key));
}
//首先如果buckets為空則初始化,第一次調用會走到這裡,以0為capacity初始化,根據上面的分析,獲得的初始容量是3,也就是說3是Dictionary<Tkey, TValue>的默認容量。
if (buckets == null) Initialize(0);
//取hashcode後還與0x7FFFFFFF做了個與操作,0x7FFFFFFF這就是int32.MaxValue的16進制,換成二進制是?01111111111111111111111111111111?,第1位是符號位,也就是說comparer.GetHashCode(key) 為正數的情況下與0x7FFFFFFF做 & 操作結果還是它本身,如果取到的hashcode是負數,負數的二進制是取反再補碼,所以結果得到的是0x7FFFFFFF-(-hashcode)+1,結果是正數。其實簡單來說,它的目的就是高性能的取正數。??
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
//用得到的新hashcode與buckets的大小取余,得到一個目標bucket索引
int targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
//做個遍歷,初始值為buckets[targetBucket],現在"a"的hashcode為3,這樣targetBucket現在是0,buckets[0]是-1,i是要>=0的,循環走不下去,跳出
for (int i = buckets[targetBucket]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (add)
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Format(SR.Argument_AddingDuplicate, key));
}
entries[i].value = value;
version++;
return;
}
}
int index;
//freeCount也是-1,走到else裡面
if (freeCount > 0)
{
index = freeList;
freeList = entries[index].next;
freeCount--;
}
else
{
//count是元素的個數0, entries經過初始化後目前length是3,所以不用resize
if (count == entries.Length)
{
Resize();
targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
}
//index = count說明index指向entries數組裡當前要寫值的索引,目前是0
index = count;
//元素個數增加一個
count++;
}
//把key的hashcode存到entries[0]裡的hashcode,免得要用時重復計算hashcode
entries[index].hashCode = hashCode;
//entries[0]的next指向buckets[0]也就是-1
entries[index].next = buckets[targetBucket];
//設置key和value
entries[index].key = key;
entries[index].value = value;
//再讓buckets[0] = 0
buckets[targetBucket] = index;
//這個不多說,不知道的可以看List<T>篇
version++;
}
看到這裡可以先猜一下用bucket的目的,dictionary是為了根據key快速得到value,用key的hashcode來對長度取余,取到的余是0到(length-1)之前一個數,最好的情況全部分散開,每個key正好對應一個bucket,也就是entries裡每一項都對應一個bucket,就可以形成下圖取value的過程:
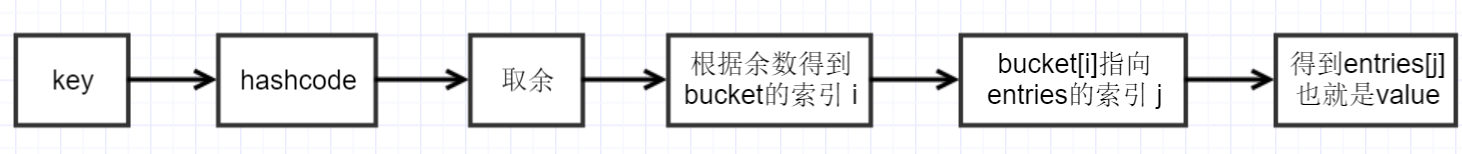
這個取值過程非常快,因為沒有任何遍歷。但實際情況是hashcode取的余不會正好都不同,總有可能會有一些重復的,那這些重復的是怎麼處理的呢,還是先繼續看Insert的代碼:
變量狀態如下圖:
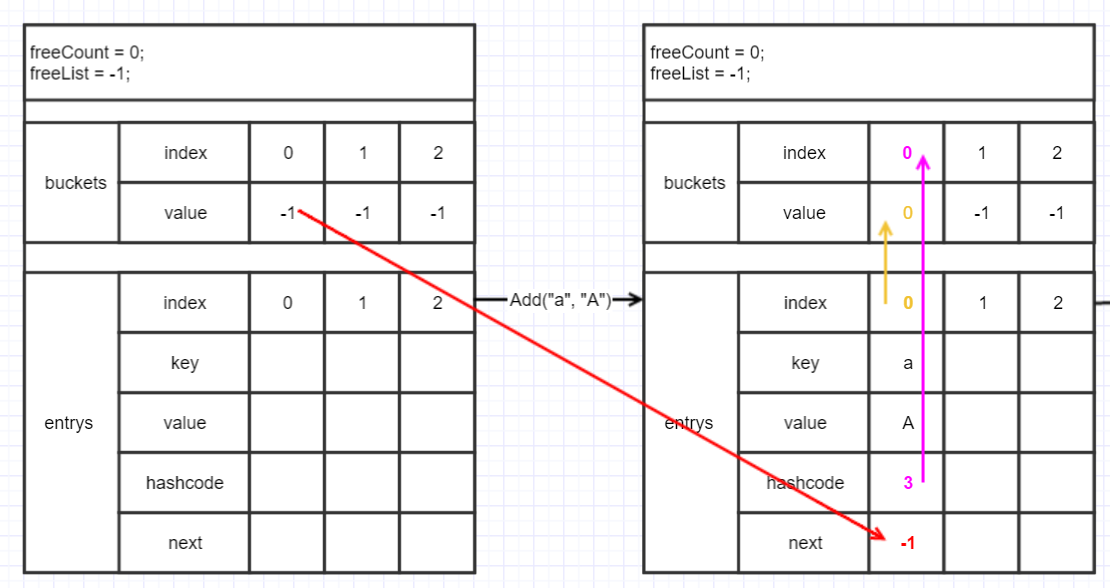
從這圖可以看出來是由hashcode得到bucket的index(紫色線),而bucket的value是指向entry的index(黃色線), entry的next又指向bucket上一次的value(紅色線),是不是有鏈表的感覺。
由於"b"的hashcode為4,取余得1,並沒有和現有的重復,所以流程和上面一樣(左邊的線不用看,屬於上面流程)
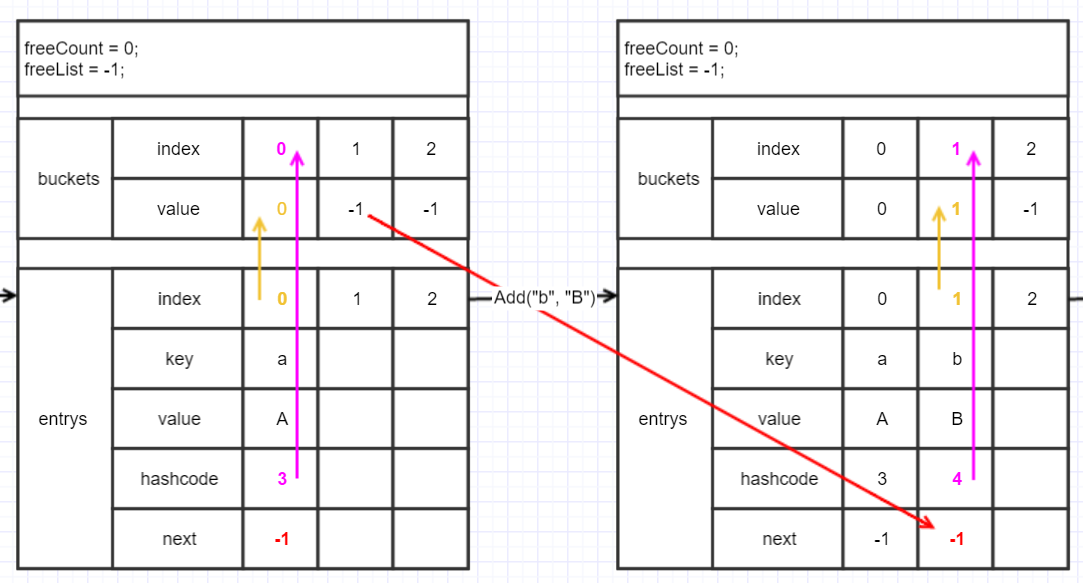
"c"的hashcode是6,取余得0,得到也是在第0個bucket,這樣就產生碰撞了,
for (int i = buckets[targetBucket]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (add)
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Format(SR.Argument_AddingDuplicate, key));
}
entries[i].value = value;
version++;
return;
}
}
這裡Insert函數裡就會走進for循環,不過"c"不是已經有的key,hashcode匹配不到所以if就不會進了。
狀態如圖:
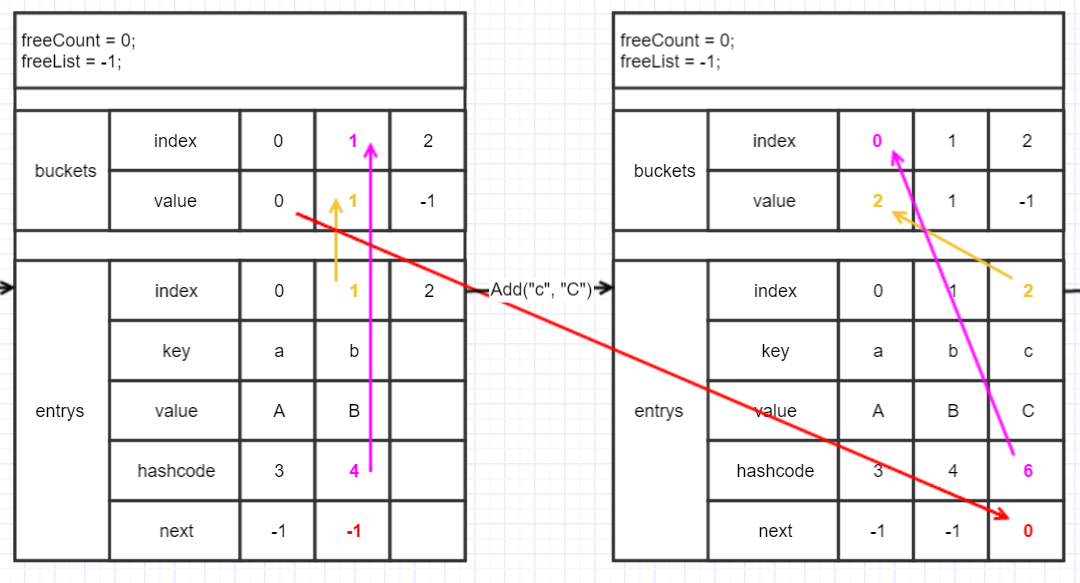
從圖上看到,新添加的entry的index給到第0個bucket的value (黃色線),而bucket上一次的value(紅色線)也就是上次添加的元素的index給到新添加entry的next,這樣通過bucket得到最新的entry,而不停的通過entry的next就可以把同一個bucket下的entry都遍歷到。
再用索引器的方式加入"d",
public TValue this[TKey key]
{
set
{
Insert(key, value, false);
}
}
也是insert,不過第三個參數是false,這樣insert裡碰到相同的key會替換掉而不是像Add那樣拋異常,這個還是不會走到if裡去,因為key不重復
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (add)
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Format(SR.Argument_AddingDuplicate, key));
}
entries[i].value = value;
version++;
return;
}
不過由於容量已經滿了,現在會走到下面這段代碼:
if (count == entries.Length)
{
Resize();
targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length;
}
觸發Resize,看看Resize代碼:
private void Resize()
{
Resize(HashHelpers.ExpandPrime(count), false);
}
先通過HashHelpers.ExpandPrime(count)取到下個容量大小。
public static int ExpandPrime(int oldSize)
{
int newSize = 2 * oldSize; //新size為兩倍當前大小
if ((uint)newSize > MaxPrimeArrayLength && MaxPrimeArrayLength > oldSize)//這裡MaxPrimeArrayLength是int32.MaxValue,size當然不能超過int32的最大值
{
Debug.Assert(MaxPrimeArrayLength == GetPrime(MaxPrimeArrayLength), "Invalid MaxPrimeArrayLength");
return MaxPrimeArrayLength;
}
return GetPrime(newSize);//這個上面講過,是取比新size大的第一個質數
}
所以resize的容量不是2倍也不是上面那個質數數組往後找,而是比2倍大的第一個質數。那現在是3,2倍是6,下一個質數是7,擴容的目標是7。
再詳細看resize實現:
private void Resize(int newSize, bool forceNewHashCodes)
{
Contract.Assert(newSize >= entries.Length);
int[] newBuckets = new int[newSize];
for (int i = 0; i < newBuckets.Length; i++) newBuckets[i] = -1; //重置buckets
Entry[] newEntries = new Entry[newSize];
Array.Copy(entries, 0, newEntries, 0, count); //建立新entries並把舊的entries復制進去
if (forceNewHashCodes) // 強制更新hashcode,dictionary不會走進去
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (newEntries[i].hashCode != -1)
{
newEntries[i].hashCode = (comparer.GetHashCode(newEntries[i].key) & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) //因為重置了buckets,所以這裡遍歷entries來重新建立bucket和entry的關系
{
if (newEntries[i].hashCode >= 0) //hashcode做了正數處理,不應該都是大於0的麼,其實不然,remove裡講hashcode為什麼會為負
{
int bucket = newEntries[i].hashCode % newSize;
newEntries[i].next = newBuckets[bucket];
newBuckets[bucket] = i; //還是insert裡的那一套,同一個bucket index, bucket指向最新的entry的index, 而新entry的next就指向老的entry的index,循環下去
}
}
buckets = newBuckets;
entries = newEntries;
}
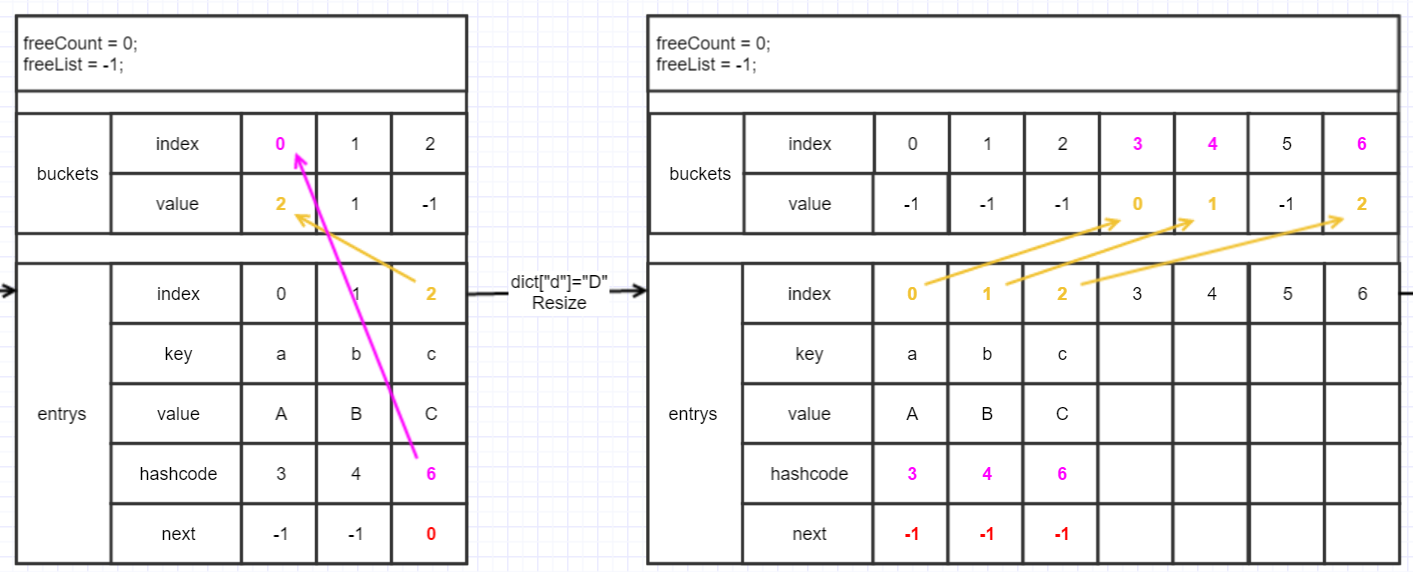
因為大小變了,取余也就不一樣,所以entry和bucket對應的位置也不同了,不過沒影響。
Resize消耗不低,比List<T>的要大,不光要copy元素,還要重建bucket。
Resize後繼續上面那一套,看狀態圖:
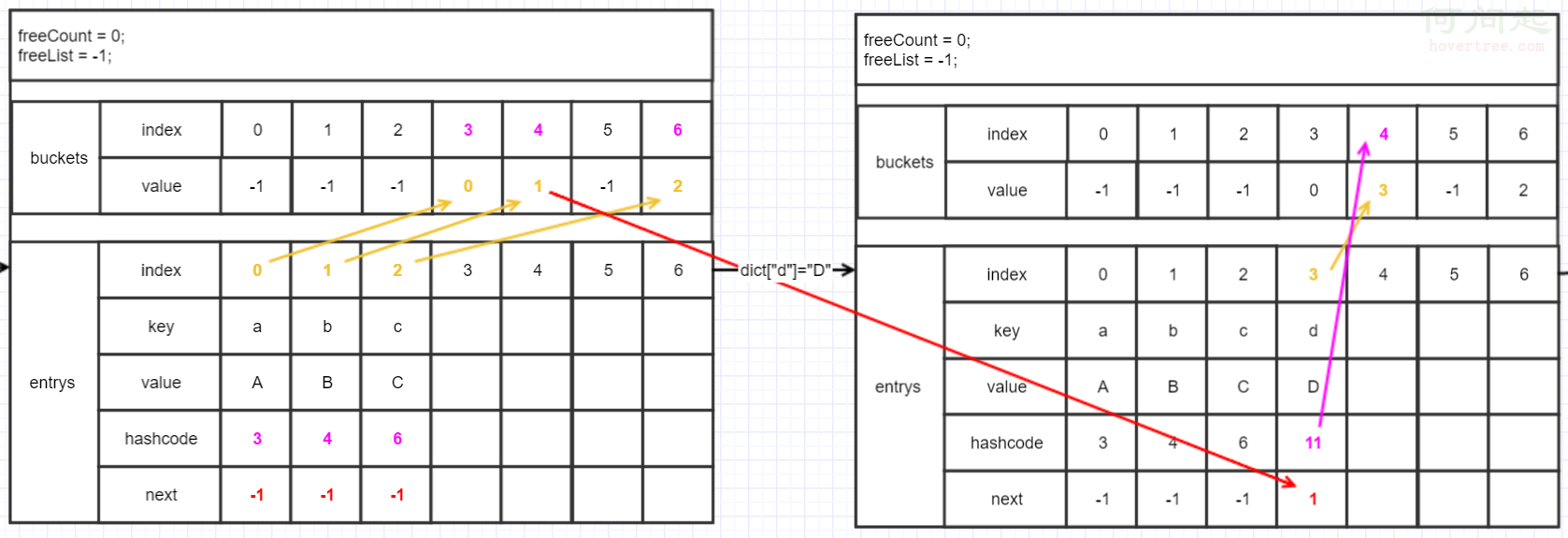
"d"的hashcode為11,余數是4(現在大小是7了哈),與"b"碰撞,所以next就指到"b"的index,而bucket則去記新添加的"d"了(典型的喜新厭舊,有沒有)。
"a"已經添加過了,再次用索引器添加"a"就走了if裡面
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key))
{
if (add) //如果用Add方法會拋異常
{
throw new ArgumentException(SR.Format(SR.Argument_AddingDuplicate, key));
}
entries[i].value = value; //替換掉目標entry的值
version++;
return; //這裡直接return了,因為只是替換值,與bucket關系並沒有改變
}
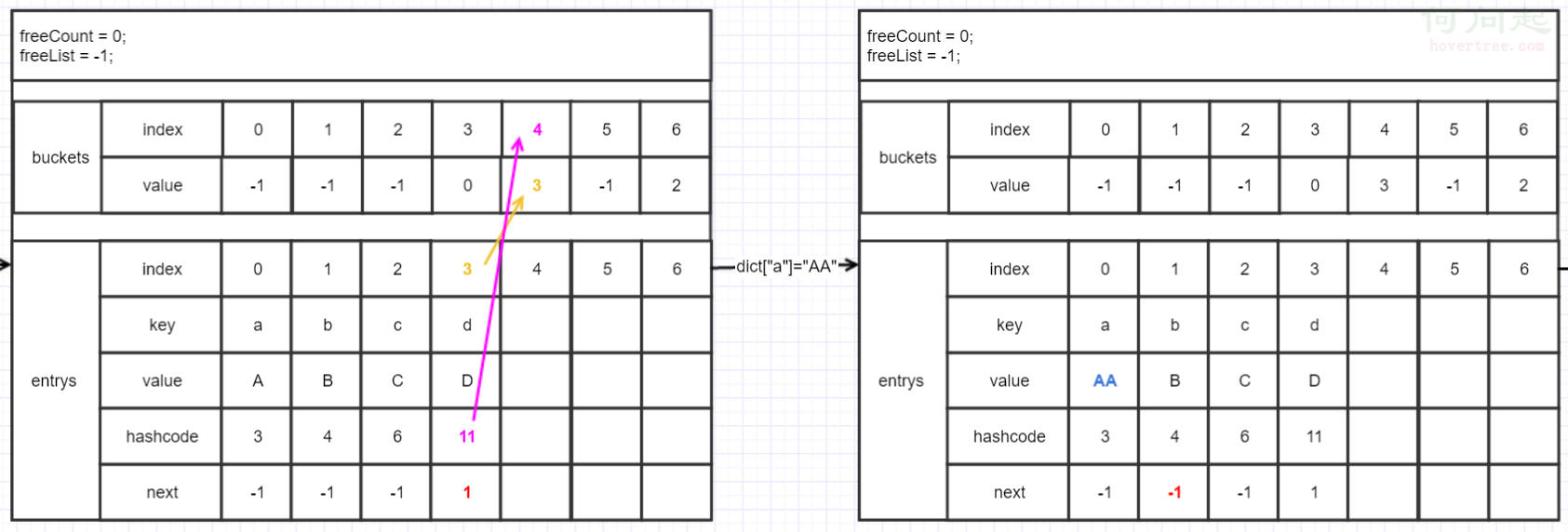
這步就非常之簡單,只是"A"替換成"AA"。
來看看Remove代碼:
public bool Remove(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(key));
}
if (buckets != null)
{
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
int bucket = hashCode % buckets.Length; //先算出hashcode
int last = -1; //last初始為-1
for (int i = buckets[bucket]; i >= 0; last = i, i = entries[i].next) //last在循環時指向上一個entry的index
{
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) //先找到相同的key
{
if (last < 0) //小於0說明是第1個,last只有初始為-1
{
buckets[bucket] = entries[i].next; //remove第一個的話就只要把bucket的值指向要remove的entry的下一個就好了,這樣鏈表就繼續存在,只是把頭去掉了。
}
else
{
entries[last].next = entries[i].next; //remove中間或最後的entry就讓上一個的next指向下一個的index,可以想像在鏈表中間去掉一個,是不是得把上下兩邊再連起來
}
entries[i].hashCode = -1; //把hashcode置為-1,上面有說hashcode有可能為負,這裡就為負數了
entries[i].next = freeList; //freeList在這裡用到了, 把刪除的entry的next指向freeList,現在為-1
entries[i].key = default(TKey); //key和value都設為默認值,這裡因為是string所以都是null
entries[i].value = default(TValue);
freeList = i; //freeList就指向這空出來的entry的index
freeCount++; //freeCount加一個,這裡可以知道freeCount是用來記entries裡空出來的個數
version++;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
這裡可以看出Dictionary並不像List那樣Remove,Dictionary為了性能並沒有在Remove做重建,而是把位置空出來,這樣節省大量時間。freeList和bucket類似(一樣喜新厭舊),總是指向最新空出來的entry的index,而entry的next又把所有空的entry連起來了。這樣insert時就可以先找到這些空填進去。
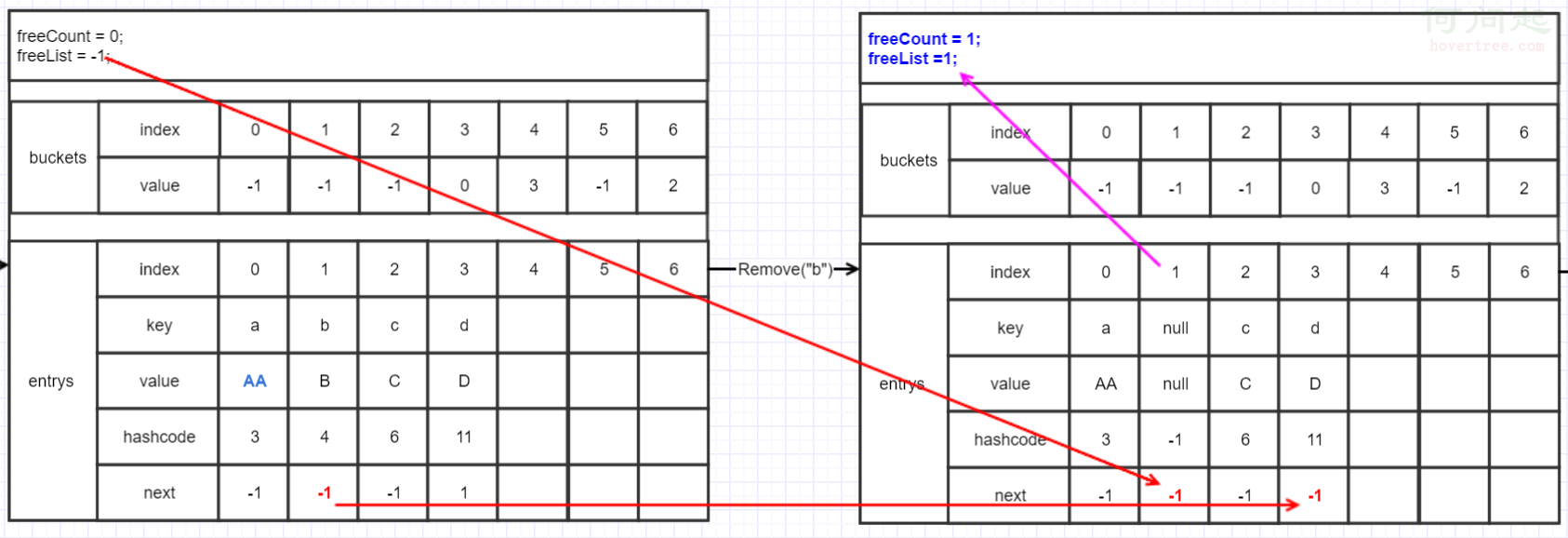
這裡"d"的next本來是指向"b"的,Remove(b)後把"b"的next給了"d"(下面那條紅線),這樣繼續保持鏈表狀態。freeList和freeCount這裡就知道了是用來記住刪除元素的index和個數。
這裡再添加一個,因為有空了,所以會優先補上空出來的。
if (freeCount > 0) //freeCount大於0,所以進來了
{
index = freeList; //當前index指向最新空出來的
freeList = entries[index].next; //把freeList再指到下一個,保持鏈表
freeCount--; //用掉一個少一個
}
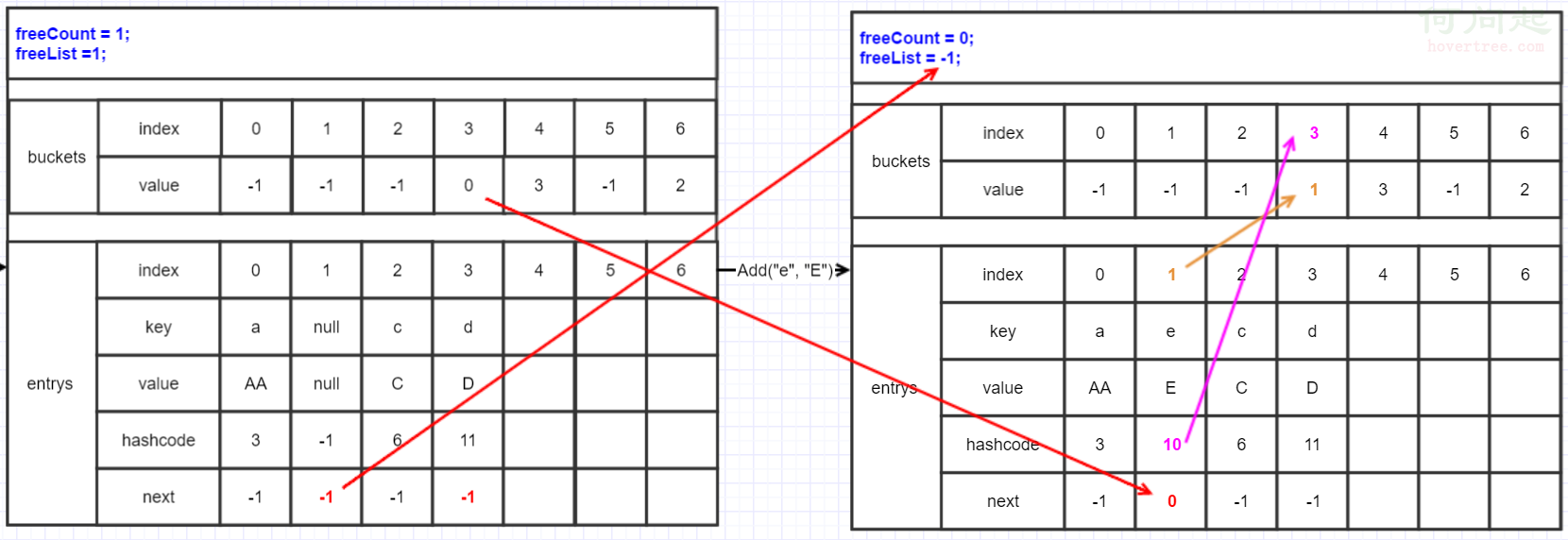
"e"的hashcode為10,所以也在index為3的bucket裡,bucket value指向剛添加的entry也就是1,而這個entry的next就指向bucket舊的那個。這樣就把空出來的又補上了。
通過上面分析,對Dictionary添加和刪除的原理已經清楚了,這樣下面的也會非常容易理解。
來看看索引器的get
public TValue this[TKey key]
{
get
{
int i = FindEntry(key);
if (i >= 0) return entries[i].value;
throw new KeyNotFoundException();
}
}
是通過FindEntry來找到entry進而得到value
private int FindEntry(TKey key)
{
if (key == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(key));
}
if (buckets != null)
{
int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF; //取hashcode
for (int i = buckets[hashCode % buckets.Length]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) //遍歷bucket鏈表
{
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) return i; //找到hashcode一致的,也就是同樣的key,返回entry索引
}
}
return -1;//沒找到key,後面就拋KeyNotFoundException了
}
看看ContainsKey代碼:
public bool ContainsKey(TKey key)
{
return FindEntry(key) >= 0;
}
和上面一樣,通過FindEntry來找索引,索引不為-1就是包含。
看看Dictionary還有哪些值得注意的:
public int Count
{
get { return count - freeCount; }
}
真正的count是entries裡個數減去裡面空著的。
public bool ContainsValue(TValue value)
{
if (value == null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode >= 0 && entries[i].value == null) return true;
}
}
else
{
EqualityComparer<TValue> c = EqualityComparer<TValue>.Default;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (entries[i].hashCode >= 0 && c.Equals(entries[i].value, value)) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
ContainsValue和ContainsKey就不一樣了,它沒有bucket可以匹配,只能遍歷entries,所以性能和List的Contains一樣,使用時需要注意。
另外還有不少代碼是為了實現Enumerator,畢竟Dictionary支持KeyValuePair, Key, Value三種方式遍歷,其實這三種遍歷都是對Entries數組的遍歷,這裡就不多做分析了。
Dictionary的默認初始容量為3,並在填滿時自動擴容,以比當前值的2倍大的第一個質數(固定質數數組裡的)作為擴容目標。
Dictionary也不是線程安全,多線程環境下需要我們自己加鎖,和List一樣也是通過version來確保遍歷時集合不被修改。
Dictionary的遍歷有三種,KeyValuePair,Key, Value,這三個本質都是遍歷entries數組。
Dictionary取值快速的原理是因為通過buckets來建立了Key與entry之前的聯系,通過Key的hashcode算出bucket的index,而bucket的value指向entry的index,這樣快速得到entry的value,當然也有不同的key指向同一個bucket,所以bucket的index總是指向最新的entry,而有沖突的entry又通過next連接,這樣即使有沖突也只要遍歷很少的entry就可以取到值,Dictionary在元素越多時性能優勢越明顯。
當然Dictionary為取值快也是付出了一點小代價,就是通過空間換取時間,多加了buckets這個數組來建立key與entry的聯系,另外還有entry結構裡的hashcode和next,不過相比速度這點代價基本可以忽略了。
下面是上面例子的整個過程圖:(右鍵在新標簽頁打開)