在上一篇文章,我介紹了如何編寫模態對話框屬性編輯器,這篇文章我將介紹如何編寫下拉式屬性編 輯器。下拉式(DropDown)屬性編輯器和模態對話框屬性編輯器的不同之處就是,當你點擊屬性值修改的 時候,模態對話框編輯器是彈出一個模態對話框,而下拉式屬性編輯器卻是在緊貼著屬性值的地方顯示一 個下拉的控件。不知道大家注意到了沒有,這裡我說的是顯示一個下拉的控件,而這個控件也是需要你去 開發的,接下來我還是以Scope屬性為例,介紹一下具體的實現。
首先我們要創建一個用於編輯屬性的控件,在本系列文章的開始,我們介紹了自定義控件有三種類型 :復合控件,擴展控件,自定義控件。在本例中我們制作一個復合控件(Compsite control),復合控件 的開發比較簡單,不在本系列文章的講解范圍,我簡單做個介紹,在Solution 浏覽器裡右鍵點擊 CustomControlSample工程選擇Add->User Control…,輸入文件名ScopeEditorControl.cs。我們做的 這個復合控件上一篇文章介紹的模態對話框所包含子控件基本一樣,除了用於確認和取消的按鈕,如下圖 :
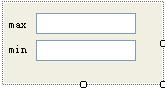
由於我們取消了用於確認和取消的按鈕,並且是一個下拉的編輯器控件,在出現下面三種情況的時候 下拉的編輯器控件會關閉:用戶敲了回車,用戶敲了ESC鍵,用戶點擊了編輯器以外的地方。當下拉編輯 器控件關閉的時候我們就需要更新屬性的值。下邊是這個控件的代碼:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CustomControlSample
{
public partial class ScopeEditorControl : UserControl
{
private Scope _oldScope;
private Scope _newScope;
private Boolean canceling;
public ScopeEditorControl(Scope scope)
{
_oldScope = scope;
_newScope = scope;
InitializeComponent();
}
public Scope Scope
{
get
{
return _newScope;
}
}
private void textBox1_Validating(object sender, CancelEventArgs e)
{
try
{
Int32.Parse(textBox1.Text);
}
catch (FormatException)
{
e.Cancel = true;
MessageBox.Show("無效的值", "驗證錯誤", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
private void textBox2_Validating(object sender, CancelEventArgs e)
{
try
{
Int32.Parse(textBox2.Text);
}
catch (FormatException)
{
e.Cancel = true;
MessageBox.Show("無效的值", "驗證錯誤", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
protected override bool ProcessDialogKey(Keys keyData)
{
if (keyData == Keys.Escape)
{
_oldScope = _newScope;
canceling = true;
}
return base.ProcessDialogKey(keyData);
}
private void ScopeEditorControl_Leave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!canceling)
{
_newScope.Max = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
_newScope.Min = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
}
}
private void ScopeEditorControl_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = _oldScope.Max.ToString();
textBox2.Text = _oldScope.Min.ToString();
}
}
}
和模態對話框編輯器一樣,開發環境並不會直接調用我們的編輯器控件,而是用過UITypeEditor類的 派生來實現編輯器的調用,所以我們必須實現一個下拉式編輯器。代碼如下:
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing.Design;
using System.Windows.Forms.Design;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CustomControlSample
{
public class ScopeDropDownEditor : UITypeEditor
{
public override UITypeEditorEditStyle GetEditStyle(ITypeDescriptorContext
context)
{
if (context != null && context.Instance != null)
{
return UITypeEditorEditStyle.DropDown;
}
return base.GetEditStyle(context);
}
public override object EditValue(ITypeDescriptorContext context,
IServiceProvider provider, object value)
{
IWindowsFormsEditorService editorService = null;
if (context != null && context.Instance != null &&
provider != null)
{
editorService = (IWindowsFormsEditorService)
provider.GetService(typeof(IWindowsFormsEditorService));
if (editorService != null)
{
MyListControl control = (MyListControl)
context.Instance;
ScopeEditorControl editorControl = new
ScopeEditorControl(control.Scope);
editorService.DropDownControl(editorControl);
value = editorControl.Scope;
return value;
}
}
return value;
}
}
}
看過上一篇文章的朋友應該對這段代碼很熟悉,是的,這兩個編輯器的代碼只有幾行不同之處,在 GetEditStyle方法中,我們返回的是UITypeEditorEditStyle.DropDown,而不是 UITypeEditorEditStyle.Modal,表明我們的編輯器是一個下拉式的編輯器。在EditValue中的不同之處是 ,我們使用DropDownControl方法來顯示編輯器。編輯器制作完畢,我們把Scope以前的編輯器替換成下拉 式編輯器,如下:
[Browsable(true)]
[Editor(typeof(ScopeDropDownEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))]
public Scope Scope
{
get
{
return _scope;
}
set
{
_scope = value;
}
}
現在build CustomControlSample工程,然後切換到測試工程查看Scope屬性。當我們點擊屬性的值, 在屬性值的後邊出現了一個按鈕:

當點擊這個按鈕的時候,下拉的屬性編輯器出現了:
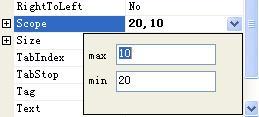
好了,屬性的編輯到這裡就講完了。